
As confidentially submitted to the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Section 106(a) of the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 on September 15, 2020. This draft registration statement has not been publicly filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and all information herein remains strictly confidential.
Registration Statement No. 333-
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
UNICYCIVE THERAPEUTICS,
INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 2834 | 81-3638692 | ||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
5150 El Camino Real, Suite A-32
Los Altos, CA 94022
(650) 351-4495
(Address and telephone number of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Shalabh Gupta,
M.D.
Chief Executive Officer
Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.
5150 El Camino Real, Suite A-32
Los Altos, CA 94022
(650) 351-4495
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
Jeffrey J. Fessler
Alexander T. Yarbrough
Sheppard, Mullin, Richter & Hampton LLP
30 Rockefeller Plaza
New York, NY 10112-0015
(212) 653-8700
Approximate
date of commencement of proposed sale to the public:
As soon as practicable after the effective date of this registration statement becomes effective.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933 check the following box: ☐
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ | Non-accelerated filer ☒ | Smaller reporting company ☒ | |||
| Emerging growth company ☒ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☐
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of Each Class of Securities to be Registered | Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price (1) | Amount of Registration Fee (2) | ||||||
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | $ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | Estimated solely for the purpose of computing the amount of the registration fee pursuant to Rule 457(o) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. Includes shares of common stock that the underwriters have the option to purchase to cover over-allotments, if any. |
| (2) | Calculated pursuant to Rule 457(o) based on an estimate of the proposed maximum aggregate offering price of the securities registered hereunder to be sold by the registrant. |
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. These securities may not be sold until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell nor does it seek an offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted.
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED SEPTEMBER 15, 2020
Shares

Common Stock
This is the initial public offering of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. We are offering shares of our common stock. No public market currently exists for our stock. We anticipate that the initial public offering price will be between $ and $ per share.
We intend to apply to list the shares of our common stock on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “UNCY.”
We are an “emerging growth company” as that term is used in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 and, as such, have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements.
Investing in our common stock involves risks. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 5.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
| Per Share | Total | |||||||
| Price to the public | $ | $ | ||||||
| Underwriting discounts and commissions | $ | $ | ||||||
| Proceeds to us (before expenses)1 | $ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | We refer you to “Underwriting” beginning on page 88 of this prospectus for additional information regarding underwriting compensation. |
We have granted the underwriters a -day option to purchase up to additional shares at the initial public offering price, less the underwriting discount.
The underwriters expect to deliver the shares on or about , 2020.
Prospectus dated , 2020
TABLE OF CONTENTS
We have not, and the underwriters have not, authorized anyone to provide any information or to make any representations other than those contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectus prepared by or on behalf of us or to which we have referred you. We take no responsibility for, and can provide no assurance as to the reliability of, any other information that others may give to you. The information contained in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date of this prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or any sale of our common stock.
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. No dealer, salesperson or other person is authorized to give information that is not contained in this prospectus. This prospectus is not an offer to sell nor is it seeking an offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. The information in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date of this prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or of any sale of these securities.
All trademarks, trade names and service marks appearing in this prospectus are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, the trademarks and trade names in this prospectus are referred to without the ® and TM symbols, but such references should not be construed as any indicator that their respective owners will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, their rights thereto.
i
The following summary highlights selected information contained elsewhere in this prospectus and is qualified in its entirety by the more detailed information and financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. It does not contain all the information that may be important to you and your investment decision. You should carefully read this entire prospectus, including the matters set forth under “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and our financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. In this prospectus, unless context requires otherwise, references to “we,” “us,” “our,” “Unicycive” or “Unicycive Therapeutics,” or the “Company” refer to Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.
Overview
We are a biotechnology company dedicated to developing effective treatments for unmet medical conditions. Currently, two of our programs are focused on kidney diseases that have significant unmet medical need. As we grow the Company and build our team, we intend to focus on identifying medical conditions within and outside of kidney disease. Our current development programs are focused on the development of two novel therapies: UNI 218, or Renazorb, for treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease, and UNI 494, for treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the gradual loss of kidney function that can get worse over time leading to lasting damage. As a company, our initial focus is developing drugs and getting them approved in the US, and then look to partner with the other global biopharmaceutical companies in the rest of the world. According to estimates by Center for Disease Control (CDC) in 2019, 37 million (approximately 15%) adults in the United States have CKD and, of these, approximately 2 million patients with CKD stage 3-5, and around 400 thousand patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have hyperphosphatemia. In the European Union (EU), around 20 million (approximately 8%) adults have CKD, more than 1 million CKD stage 3-5 patients, and approximately 180 thousand patients with ESRD have hyperphosphatemia. The number of patients with ESRD is increasing steadily and is projected to reach between 971,000 and 1,259,000 in 2030.
AKI is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage (within the first 90 days of injury). After 90 days, the patient is considered to have progressed into CKD. AKI affects over 2 million US patients and costs the healthcare system over $9 billion per year. AKI kills more than 300,000 patients per year in the US and is caused by multiple etiologies.
Our business model is to license technologies and drugs and pursue development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of those products in global markets. Many biotechnology companies utilize similar strategies of in-licensing and then developing and commercializing drugs. We believe, however, that our management team’s broad network, expertise in the biopharmaceutical industry, and past successful track record gives us an advantage in identifying and bringing these assets into our Company at an attractive price with limited upfront cost.
Risks Associated with Our Business
Our business is subject to a number of risks of which you should be aware of before making an investment decision. These risks are discussed more fully in the “Risk Factors” section of this prospectus immediately following this prospectus summary. Some of these risks include the following:
| ● | We have generated no revenue to date and our future profitability is uncertain. |
| ● | If we fail to obtain the capital necessary to fund our operations, we will be unable to continue or complete our product development and you will likely lose your entire investment. |
| ● | There is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. |
| ● | We have identified certain material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. If our internal controls are not effective, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud. |
1
| ● | The marketing approval process of regulatory agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), is lengthy, time consuming and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain marketing approval for our current product candidates and future product candidates we intend to develop, our business will be substantially harmed. |
| ● | There can be no assurance that the data generated from our clinical trials using modified protocols will be acceptable to the FDA or other regulatory authorities. |
| ● | Our reliance on third parties heightens the risks faced by our business. |
| ● | Our products will face significant competition, and if they are unable to compete successfully, our business will suffer. |
| ● | We may be adversely affected by the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. |
Corporate Information
We were incorporated as a Delaware corporation on August 18, 2016. Our principal executive offices are located at 5150 El Camino Real, Suite A-32, Los Altos, CA 94022 and our telephone number is (650) 351-4495. Our website address is http://www.unicycive.com. The information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this prospectus, and you should not consider any information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website as part of this prospectus or in deciding whether to purchase our common shares.
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
As a company with less than $1.07 billion in revenues during our last fiscal year, we qualify as an emerging growth company as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (“JOBS Act”) enacted in 2012. As an emerging growth company, we expect to take advantage of reduced reporting requirements that are otherwise applicable to public companies. These provisions include, but are not limited to:
| ● | being permitted to present only two years of audited financial statements, in addition to any required unaudited interim financial statements, with correspondingly reduced “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” disclosure in this prospectus; |
| ● | not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as amended (“Sarbanes-Oxley Act”); |
| ● | reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports, proxy statements and registration statements; and |
| ● | exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. |
We may use these provisions until the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the completion of this offering. However, if certain events occur prior to the end of such five-year period, including if we become a “large accelerated filer,” our annual gross revenues exceed $1.07 billion or we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt in any three-year period, we will cease to be an emerging growth company prior to the end of such five-year period.
2
THE OFFERING
| Common stock offered by us | Shares | |
| Common stock to be outstanding immediately after this offering | shares ( shares if the underwriters exercise their option in full). | |
| Option to purchase additional shares | The underwriters have an option for a period of days to purchase up to an additional shares of our common stock. | |
| Use of proceeds | We estimate that the net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $ , or approximately $ if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full, at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We intend to use the net proceeds from this offering to complete pre-clinical studies, including toxicology studies as recommended by the FDA, in connection with an NDA filing for Renazorb with the FDA. In addition, we plan to use proceeds to advance UNI-494 for pre-clinical development and the completion of all required studies for a potential IND filing in 2021. We also plan to use proceeds for general and corporate purposes, including, but not limited to, hiring additional management and conducting market research and other commercial planning. We may also use a portion of the net proceeds to in-license, acquire or invest in complementary businesses or products, however, we have no current commitments or obligations to do so. See “Use of Proceeds” for a more complete description of the intended use of proceeds from this offering. | |
| Risk factors | See “Risk Factors” on page 5 and other information included in this prospectus for a discussion of factors to consider carefully before deciding to invest in shares of our common stock. | |
| Proposed Nasdaq Capital Market symbol | “UNCY” |
The number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on 36,534,840 shares of our common stock outstanding as of September 14, 2020, and excludes as of that date:
| ● | 45,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2019 Stock Option Plan and 75,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan; |
| ● | 3,380,000 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding options with a weighted average exercise price of $0.31; |
| ● | shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of outstanding convertible notes assuming an initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). |
Except as otherwise indicated herein, all information in this prospectus assumes:
| ● | no exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase an additional shares of common stock. |
3
SUMMARY FINANCIAL DATA
The following tables set forth our summary financial data as of the dates and for the periods indicated. We have derived the summary statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary statement of operations data for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 and the summary balance sheet data as of June 30, 2020 have been derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The following summary financial data should be read with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our financial statements and related notes and other information included elsewhere in this prospectus. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in the future and the results for the six months ended June 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the full fiscal year.
Statement of Operations Data:
(in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Operating costs and expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 795 | $ | 344 | $ | 329 | $ | 231 | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 1,168 | 608 | 349 | 550 | ||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 1,963 | 952 | 678 | 781 | ||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,165 | ) | $ | (1,120 | ) | $ | (682 | ) | $ | (899 | ) | ||||
| Net loss per common share – basic and diluted(1) | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | ||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted(1) | 34,915,828 | 29,010,940 | 36,433,549 | 34,155,838 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | See Note 11 to our financial statements for an explanation of the method used to compute basic and diluted net loss per share. |
Balance Sheet Data:
(in thousands)
| June
30, 2020 (unaudited) |
||||||||||||
| Actual | Pro Forma(1) | Pro
Forma, As Adjusted(2)(3) |
||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 1 | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Working capital (deficit) | (1,284 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 28 | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 1,331 | |||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (4,340 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | (1,303 | ) | ||||||||||
| (1) | On a pro forma basis to reflect the conversion of convertible notes in the aggregate principal amount of $800,000 issued in July and August 2020 into an aggregate of shares of common stock assuming an initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). |
| (2) | On a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to our issuance and sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
| (3) | Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ equity (deficit) by approximately $ , assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Similarly, each increase (decrease) of shares in the number of shares offered by us at the assumed initial public offering price per share, the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ equity (deficit) by approximately $ . |
4
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Before making an investment decision, you should give careful consideration to the following risk factors, in addition to the other information included in this prospectus, including our financial statements and related notes, before deciding whether to invest in shares of our common stock. The occurrence of any of the adverse developments described in the following risk factors could materially and adversely harm our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects. In that case, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to our Financial Position and Need for Capital
We have generated no revenue to date and our future profitability is uncertain.
We were incorporated in August 2016 and have a limited operating history and our business is subject to all of the risks inherent in the establishment of a new business enterprise. Our likelihood of success must be considered in light of the problems, expenses, difficulties, complications and delays frequently encountered in connection with development and expansion of a new business enterprise. Since inception, we have incurred losses and expect to continue to operate at a net loss for at least the next several years as we continue our research and development efforts, conduct clinical trials and develop manufacturing, sales, marketing and distribution capabilities. Our net loss for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $0.7 million, $2.2 million and $1.1 million respectively, and our accumulated deficit as of June 30, 2020 was $4.3 million. There can be no assurance that the products currently under development or that may be under development by us in the future will be approved for sale in the U.S. or elsewhere. Furthermore, there can be no assurance that if such products are approved they will be successfully commercialized, and the extent of our future losses and the timing of our profitability are highly uncertain. If we are unable to achieve profitability, we may be unable to continue our operations.
If we fail to obtain the capital necessary to fund our operations, we will be unable to continue or complete our product development and you will likely lose your entire investment.
We will need to continue to seek capital from time to time to continue development of our product candidates. We expect the net proceeds of this offering to be sufficient to satisfy our capital requirements for a period of months from the date of this prospectus. Accordingly, we believe that we will need to raise substantial additional capital to fund our continuing operations and the development and commercialization of our current product candidates and future product candidates. Our business or operations may change in a manner that would consume available funds more rapidly than anticipated and substantial additional funding may be required to maintain operations, fund expansion, develop new or enhanced products, acquire complementary products, businesses or technologies or otherwise respond to competitive pressures and opportunities, such as a change in the regulatory environment. In addition, we may need to accelerate the growth of our sales capabilities and distribution beyond what is currently envisioned, and this would require additional capital. However, we may not be able to secure funding when we need it or on favorable terms. We may not be able to raise sufficient funds to commercialize our current and future product candidates we intend to develop.
If we cannot raise adequate funds to satisfy our capital requirements, we will have to delay, scale back or eliminate our research and development activities, clinical studies or future operations. We may also be required to obtain funds through arrangements with collaborators, which arrangements may require us to relinquish rights to certain technologies or products that we otherwise would not consider relinquishing, including rights to future product candidates or certain major geographic markets. This could result in sharing revenues which we might otherwise retain for ourselves. Any of these actions may harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The amount of capital we may need depends on many factors, including the progress, timing and scope of our product development programs; the progress, timing and scope of our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials; the time and cost necessary to obtain regulatory approvals; the time and cost necessary to further develop manufacturing processes and arrange for contract manufacturing; our ability to enter into and maintain collaborative, licensing and other commercial relationships; and our partners’ commitment of time and resources to the development and commercialization of our products.
5
We may consider strategic alternatives in order to maximize stockholder value, including financings, strategic alliances, acquisitions or the possible sale of our business. We may not be able to identify or consummate any suitable strategic alternatives.
We may consider all strategic alternatives that may be available to us to maximize stockholder value, including financings, strategic alliances, acquisitions or the possible sale of our business. We currently have no agreements or commitments to engage in any specific strategic transactions, and our exploration of various strategic alternatives may not result in any specific action or transaction. To the extent that this engagement results in a transaction, our business objectives may change depending upon the nature of the transaction. There can be no assurance that we will enter into any transaction as a result of the engagement. Furthermore, if we determine to engage in a strategic transaction, we cannot predict the impact that such strategic transaction might have on our operations or stock price. We also cannot predict the impact on our stock price if we fail to enter into a transaction.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our existing stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our product candidates on unfavorable terms to us.
We may seek additional capital through a variety of means, including through private and public equity offerings and debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, or through the issuance of shares under management or other types of contracts, or upon the exercise or conversion of outstanding derivative securities, the ownership interests of our stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of such financings may include liquidation or other preferences, anti-dilution rights, conversion and exercise price adjustments and other provisions that adversely affect the rights of our stockholders, including rights, preferences and privileges that are senior to those of our holders of common stock in the event of a liquidation. In addition, debt financing, if available, could include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take certain actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures, entering into licensing arrangements, or declaring dividends and may require us to grant security interests in our assets. If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances, or marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, product or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may need to curtail or cease our operations.
There is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, we had cash of $1 thousand and $15 thousand, respectively. In addition, we had current liabilities of approximately $1.3 million and $0.9 million as of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. We expect our existing cash as of June 30, 2020 together with proceeds from this offering will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements for at least months from the date of this prospectus. In the event that we are unable to obtain additional financing, we may be unable to continue as a going concern. There is no guarantee that we will be able to secure additional financing, including in connection with this offering. Changes in our operating plans, our existing and anticipated working capital needs, costs related to legal proceedings we might become subject to in the future, the acceleration or modification of our development activities, any near-term or future expansion plans, increased expenses, potential acquisitions or other events may further affect our ability to continue as a going concern. Similarly, the report of our independent registered public accounting firm on our financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2019 includes an explanatory paragraph indicating that there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. If we cannot continue as a viable entity, our stockholders may lose some or all of their investment in us.
6
Risks Related to Our Business
The marketing approval process of the FDA is lengthy, time consuming and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain marketing approval for our current product candidates and future product candidates we intend to develop, our business will be substantially harmed.
The product candidates we intend to develop have not gained marketing approval in the U.S., and we cannot guarantee that we will ever have marketable products. Our business is substantially dependent on our ability to complete the development of, obtain marketing approval for, and successfully commercialize our current and future product candidates in a timely manner. We cannot commercialize our product candidates in the United States without first obtaining approval from the FDA to market each product candidate. Our product candidates could fail to receive marketing approval for many reasons, including among others:
| ● | the FDA may disagree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials; |
| ● | the FDA could determine that we cannot rely on Section 505(b)(2) for our current or future product candidates; and |
| ● | the FDA may determine that we have identified the wrong reference listed drug or drugs or that approval of our Section 505(b)(2) application for any of our product candidates is blocked by patent or non-patent exclusivity of the reference listed drug or drugs. |
In addition, the process of seeking regulatory clearance or approval to market the product candidates we intend to develop is expensive and time consuming and, notwithstanding the effort and expense incurred, clearance or approval is never guaranteed. If we are not successful in obtaining timely clearance or approval of our product candidates from the FDA, we may never be able to generate significant revenue and may be forced to cease operations. The NDA process is costly, lengthy and uncertain. Any NDA application filed by us will have to be supported by extensive data, including, but not limited to, technical, pre-clinical, clinical, manufacturing and labeling data, to demonstrate to the FDA’s satisfaction the safety and efficacy of the product for its intended use.
Obtaining clearances or approvals from the FDA and from the regulatory agencies in other countries is an expensive and time-consuming process and is uncertain as to outcome. The FDA and other agencies could ask us to supplement our submissions, collect non-clinical data, conduct additional clinical trials or engage in other time-consuming actions, or it could simply deny our applications. In addition, even if we obtain an NDA approval or pre-market approvals in other countries, the approval could be revoked or other restrictions imposed if post-market data demonstrate safety issues or lack of effectiveness. We cannot predict with certainty how, or when, the FDA will act. If we are unable to obtain the necessary regulatory approvals, our financial condition and cash flow may be adversely affected, and our ability to grow domestically and internationally may be limited. Additionally, even if cleared or approved, our products may not be approved for the specific indications that are most necessary or desirable for successful commercialization or profitability.
We may encounter substantial delays in completing our clinical studies which in turn will require additional costs, or we may fail to demonstrate adequate safety and efficacy to the satisfaction of applicable regulatory authorities.
It is impossible to predict if or when our current or future product candidates, will prove safe or effective in humans or will receive regulatory approval. Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of our product candidates, we must conduct extensive clinical studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the product candidates in humans. Clinical testing is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain as to outcome. We cannot guarantee that any clinical studies will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, if at all. A failure of one or more clinical studies can occur at any stage of testing. Events that may prevent successful or timely completion of clinical development include:
| ● | delays in reaching, or failing to reach, a consensus with regulatory agencies on study design; |
| ● | delays in reaching, or failing to reach, agreement on acceptable terms with a sufficient number of prospective contract research organizations (“CROs”) and clinical study sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different CROs and trial sites; |
| ● | delays in recruiting a sufficient number of suitable patients to participate in our clinical studies; |
| ● | imposition of a clinical hold by regulatory agencies, after an inspection of our clinical study operations or study sites; |
| ● | failure by our CROs, other third parties or us to adhere to clinical study, regulatory or legal requirements; |
7
| ● | failure to perform in accordance with the FDA’s good clinical practices (“GCPs”) or applicable regulatory guidelines in other countries; |
| ● | delays in the testing, validation, manufacturing and delivery of sufficient quantities of our product candidates to the clinical sites; |
| ● | delays in having patients complete participation in a study or return for post-treatment follow-up; |
| ● | clinical study sites or patients dropping out of a study; |
| ● | delay or failure to address any patient safety concerns that arise during the course of a trial; |
| ● | unanticipated costs or increases in costs of clinical trials of our product candidates; |
| ● | occurrence of serious adverse events associated with the product candidates that are viewed to outweigh its potential benefits; or |
| ● | changes in regulatory requirements and guidance that require amending or submitting new clinical protocols. |
We could also encounter delays if a clinical trial is suspended or terminated by us, by the Institutional Review Board (“IRB”) or Ethics Commission (“EC”) of the institutions in which such trials are being conducted, by an independent Safety Review Board (“SRB”) for such trial or by the FDA or other regulatory authorities. Such authorities may suspend or terminate a clinical trial due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a drug, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial.
Any inability to successfully complete pre-clinical and clinical development could result in additional costs to us or impair our ability to generate revenues from product sales, regulatory and commercialization milestones and royalties. In addition, if we make manufacturing or formulation changes to our product candidates, we may need to conduct additional studies to bridge our modified product candidates to earlier versions.
Clinical study delays could also shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our product candidates or allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do, which could impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates. In addition, any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow down our product candidates’ development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
The outcome of pre-clinical studies and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. Further, pre-clinical and clinical data are often susceptible to various interpretations and analyses, and many companies that have believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in pre-clinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval. If the results of our clinical studies are inconclusive or if there are safety concerns or adverse events associated with our product candidates, we may:
| ● | be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our product candidates, if approved at all; |
| ● | obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired; |
| ● | obtain approval with labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or safety warnings; |
| ● | be required to change the way the product is administered; |
8
| ● | be required to perform additional clinical studies to support approval or be subject to additional post-marketing testing requirements; |
| ● | have regulatory authorities withdraw their approval of a product or impose restrictions on its distribution in the form of a modified risk evaluation and mitigation strategy; |
| ● | be sued; or |
| ● | experience damage to our reputation. |
Additionally, our product candidates could potentially cause other adverse events that have not yet been predicted. The inclusion of ill patients in our clinical studies may result in deaths or other adverse medical events due to other therapies or medications that such patients may be using. As described above, any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of our product candidates and impair our ability to commercialize our products.
If we are not able to obtain, or if there are delays in obtaining, required regulatory approvals, we will not be able to commercialize, or will be delayed in commercializing, our product candidates and our ability to generate revenue will be impaired.
Our product candidates and the activities associated with its development and commercialization, including its design, testing, manufacture, release, safety, efficacy, regulatory filings, recordkeeping, labeling, storage, approval, advertising, promotion, sale and distribution, is subject to comprehensive regulation by the FDA and other regulatory authorities in the United States and by comparable authorities in other countries. For example, in order to commence clinical trials of our product candidates in the United States, we must file an IND and obtain FDA agreement to proceed. The FDA may place our development program on clinical hold and require further pre-clinical testing prior to allowing our clinical trials to proceed.
We must obtain marketing approval in each jurisdiction in which we market our products. Failure to obtain marketing approval for a product candidate will prevent us from commercializing the product candidate. We have not submitted a marketing application or received approval to market any of our product candidates from regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction. We have only limited experience in filing and supporting the applications necessary to gain marketing approvals and expect to rely on third-party CROs to assist us in this process. Securing regulatory approval requires the submission of extensive pre-clinical and clinical data and supporting information to the various regulatory authorities for each indication to establish the product candidate’s safety and efficacy. Securing regulatory approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process, testing and release and inspection of manufacturing facilities and personnel by the relevant regulatory authority. Our product candidates may not be effective, may be only moderately effective or may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that may preclude our obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit commercial use.
The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the United States and elsewhere, is expensive, may take many years and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidate involved. We cannot assure you that we will ever obtain any marketing approvals in any jurisdiction. Changes in marketing approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment of additional statutes or regulations or changes in regulatory review for each submitted product application may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application. The FDA and comparable authorities in other countries have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept any application or may decide that our data are insufficient for approval and require additional pre-clinical or other studies, changes in the manufacturing process or facilities or clinical trials. Moreover, approval by the FDA or an equivalent foreign authority, including the HSA, does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in any other countries or jurisdictions, but a failure to obtain marketing approval in one jurisdiction may adversely impact the likelihood of approval in other jurisdictions. In addition, varying interpretations of the data obtained from pre-clinical testing, manufacturing and product testing and clinical trials could delay, limit or prevent marketing approval of a product candidate. Additionally, any marketing approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render the approved product not commercially viable.
9
Modifications to our products may require new NDA approvals.
Once a particular product receives FDA approval or clearance, expanded uses or uses in new indications of our products may require additional human clinical trials and new regulatory approvals or clearances, including additional IND and NDA submissions and premarket approvals before we can begin clinical development, and/or prior to marketing and sales. If the FDA requires new clearances or approvals for a particular use or indication, we may be required to conduct additional clinical studies, which would require additional expenditures and harm our operating results. If the products are already being used for these new indications, we may also be subject to significant enforcement actions. Conducting clinical trials and obtaining clearances and approvals can be a time-consuming process, and delays in obtaining required future clearances or approvals could adversely affect our ability to introduce new or enhanced products in a timely manner, which in turn would harm our future growth.
Additional delays to the completion of clinical studies may result from modifications being made to the protocol during the clinical trial, if such modifications are warranted and/or required by the occurrences in the given trial.
Each modification to the protocol during a clinical trial has to be submitted to the FDA. This could result in the delay or halt of a clinical trial while the modification is evaluated. In addition, depending on the quantity and nature of the changes made, the FDA could take the position that the data generated by the clinical trial are not poolable because the same protocol was not used throughout the trial. This might require the enrollment of additional subjects, which could result in the extension of the clinical trial and the FDA delaying clearance or approval of a product. Any such delay could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
There can be no assurance that the data generated from our clinical trials using modified protocols will be acceptable to the FDA or other regulatory authorities.
There can be no assurance that the data generated using modified protocols will be acceptable to the FDA or other regulatory authorities or that if future modifications during the trial are necessary, that any such modifications will be acceptable to the FDA or other regulatory authorities. If the FDA or other regulatory authorities believe that prior approval is required for a particular modification, they can delay or halt a clinical trial while they evaluate additional information regarding the change.
Serious injury or death resulting from a failure of our product candidates during current or future clinical trials could also result in the FDA or other regulatory authority delaying our clinical trials or denying or delaying clearance or approval of a product.
Even though an adverse event may not be the result of the failure of our product candidate, the FDA or other regulatory authority could delay or halt a clinical trial for an indefinite period of time while an adverse event is reviewed, and likely would do so in the event of multiple such events.
Any delay or termination of our current or future clinical trials as a result of the risks summarized above, including delays in obtaining or maintaining required approvals from the FDA or other regulatory authorities, delays in patient enrollment, the failure of patients to continue to participate in a clinical trial, and delays or termination of clinical trials as a result of protocol modifications or adverse events during the trials, may cause an increase in costs and delays in the filing of any product submissions with the FDA or other regulatory authorities, delay the approval and commercialization of our products or result in the failure of the clinical trial, which could adversely affect our business, operating results and prospects.
Conducting successful clinical studies may require the enrollment of large numbers of patients, and suitable patients may be difficult to identify and recruit.
Patient enrollment in clinical trials and completion of patient participation and follow-up depends on many factors, including the size of the patient population; the nature of the trial protocol; the attractiveness of, or the discomforts and risks associated with, the treatments received by enrolled subjects; the availability of appropriate clinical trial investigators; support staff; and the proximity of patients to clinical sites and ability to comply with the eligibility and exclusion criteria for participation in the clinical trial and patient compliance. For example, patients may be discouraged from enrolling in our clinical trials if the trial protocol requires them to undergo extensive post-treatment procedures or follow-up to assess the safety and effectiveness of our products or if they determine that the treatments received under the trial protocols are not attractive or involve unacceptable risks or discomforts. Patients may also not participate in our clinical trials if they choose to participate in contemporaneous clinical trials of competitive products.
10
The future results of our current or future clinical trials may not support our product candidates claims or may result in the discovery of unexpected adverse side effects.
Even if our clinical trials are completed as planned, we cannot be certain that their results will support our product candidates claims or that the FDA or foreign authorities will agree with our conclusions regarding them. Success in pre-clinical studies and early clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful, and we cannot be sure that the later trials will replicate the results of prior trials and pre-clinical studies. The clinical trial process may fail to demonstrate that our product candidates are safe and effective for the proposed indicated uses. If the FDA concludes that the clinical trials for any product for which we might seek clearance, has failed to demonstrate safety and effectiveness, we would not receive FDA clearance to market that product in the United States for the indications sought.
In addition, such an outcome could cause us to abandon a product candidate and might delay development of others. Any delay or termination of our clinical trials will delay the filing of any product submissions with the FDA and, ultimately, our ability to commercialize our product candidates and generate revenues. It is also possible that patients enrolled in clinical trials will experience adverse side effects that are not currently part of our product candidate’s profile.
Adverse events involving our products may lead the FDA or other regulatory authorities to delay or deny clearance for our products or result in product recalls that could harm our reputation, business and financial results.
Once a product receives FDA clearance or approval, the agency has the authority to require the recall of commercialized products in the event of adverse side effects, material deficiencies or defects in design or manufacture. The authority to require a recall must be based on an FDA finding that there is a reasonable probability that the product would cause serious injury or death. Manufacturers may, under their own initiative, recall a product if any material deficiency in a product is found. A government-mandated or voluntary recall by us or one of our distributors could occur as a result of adverse side effects, impurities or other product contamination, manufacturing errors, design or labeling defects or other deficiencies and issues. Recalls of any of our products would divert managerial and financial resources and have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. The FDA requires that certain classifications of recalls be reported to FDA within ten working days after the recall is initiated. Companies are required to maintain certain records of recalls, even if they are not reportable to the FDA. We may initiate voluntary recalls involving our products in the future. A future recall announcement could harm our reputation with customers and negatively affect our sales. In addition, the FDA and/or other regulatory agencies could take enforcement action for failing to report the recalls when they were conducted.
Even if our product candidates receive marketing approval, they may fail to achieve the degree of market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community necessary for commercial success.
If our product candidates receive marketing approval, they may nonetheless fail to gain sufficient market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community for us to achieve commercial success. If our product candidates do not achieve an adequate level of acceptance, we may not generate sufficient product revenue to become profitable. The degree of market acceptance of our product candidates, if approved for commercial sale, will depend on a number of factors, including:
| ● | the efficacy and potential advantages compared to alternative therapies; |
| ● | the size of the markets in the countries in which approvals are obtained; |
11
| ● | terms, limitations or warnings contained in any labeling approved by the FDA or other regulatory authority; |
| ● | our ability to offer any approved products for sale at competitive prices; |
| ● | convenience and ease of administration compared to alternative treatments; |
| ● | the willingness of the target patient population to try new therapies or dosing regimens; |
| ● | the willingness of physicians to prescribe these therapies; |
| ● | the strength of marketing and distribution support; |
| ● | the success of competing products and the marketing efforts of our competitors; |
| ● | sufficient third-party payor coverage and adequate reimbursement; and |
| ● | the prevalence and severity of any side effects. |
Even if we are able to commercialize our product candidates, such products may become subject to unfavorable pricing regulations, third-party reimbursement practices or healthcare reform initiatives, which would harm our business.
The regulations that govern marketing approvals, pricing, coverage and reimbursement for new drugs vary widely from country to country. In the United States, new and future legislation may significantly change the approval requirements in ways that could involve additional costs and cause delays in obtaining approvals. Some countries require approval of the sale price of a drug before it can be marketed. In many countries, the pricing review period begins after marketing or product-licensing approval is granted. In some foreign markets, prescription pharmaceutical pricing remains subject to continuing governmental control even after initial marketing approval is granted. As a result, we might obtain marketing approval for a drug in a particular country but then be subject to price regulations that delay its commercial launch, possibly for lengthy time periods, and negatively impact the revenue we are able to generate from the sale of the drug in that country. Adverse pricing limitations may hinder our ability to commercialize and generate revenue from our product candidates, even if our product candidates obtain marketing approval.
Our ability to commercialize our current and any future product candidates successfully also will depend in part on the extent to which coverage and adequate reimbursement for these products and related treatments will be available from government health programs, private health insurers, integrated delivery networks and other third-party payors. Third-party payors decide which medications they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. A significant trend in the U.S. healthcare industry and elsewhere is cost containment. Government authorities and third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of payment for particular medications. Increasingly, third-party payors are requiring that drug companies provide predetermined discounts from list prices and are challenging the prices charged for medical products. Coverage and reimbursement may not be available for any product that we commercialize and, if reimbursement is available, the level of reimbursement may not be sufficient for commercial success. Coverage and reimbursement may impact the demand for, or the price of, any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval. If coverage and reimbursement is not available or is available only to limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval.
There may be significant delays in obtaining coverage and adequate reimbursement for newly approved products, and coverage may be more limited than the purposes for which the product is approved by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside the United States. Moreover, eligibility for coverage and reimbursement does not imply that any product will be paid for in all cases or at a rate that covers our costs, including research, development, manufacture, sale and distribution. Interim reimbursement levels for new drugs, if applicable, may also not be sufficient to cover our costs and may not be made permanent. Coverage and reimbursement rates may vary according to the use of the drug and the medical circumstances under which it is used may be based on reimbursement levels already set for lower cost products or procedures or may be incorporated into existing payments for other services. Net prices for drugs may be reduced by mandatory discounts or rebates required by government healthcare programs or private payors and by any future relaxation of laws that presently restrict imports of drugs from countries where they may be sold at lower prices than in the United States. Commercial third-party payors often rely upon Medicare coverage policies and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement policies. Our inability to promptly obtain coverage and profitable payment rates from both government-funded programs and private payors for any approved products that we develop could have a material adverse effect on our operating results, our ability to raise capital needed to commercialize our approved products and our overall financial condition.
12
Any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval could be subject to marketing restrictions or withdrawal from the market and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with our products.
Any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval, along with the manufacturing processes and facilities, post-approval clinical data, labeling, advertising and promotional activities for such product, will be subject to continual requirements of and review by the FDA and other regulatory authorities. These requirements include submissions of promotional materials and safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration and listing requirements, current Good Manufacturing Practice (“cGMP”) requirements for product facilities, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents and requirements regarding the distribution of samples to physicians and related recordkeeping. Even if marketing approval of a product candidate is granted, the approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which the product may be marketed or to the conditions of approval or contain requirements for costly post-marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of the medicine. The FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs to ensure that they are marketed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling. However, companies may share truthful and not misleading information that is otherwise consistent with the product’s FDA approved labeling. The FDA imposes stringent restrictions on manufacturers’ communications regarding off-label use and if we do not comply with these restrictions, we may be subject to enforcement actions.
In addition, later discovery of previously unknown problems with our products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes and facilities or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in, among other things:
| ● | restrictions on such products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes or facilities; |
| ● | restrictions on the labeling, marketing, distribution or use of a product; |
| ● | requirements to conduct post-approval clinical trials, other studies or other post-approval commitments; |
| ● | warning or untitled letters; |
| ● | withdrawal or recall of the products from the market; |
| ● | refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications that we submit; |
| ● | fines, restitution or disgorgement of profits or revenue; |
| ● | suspension or withdrawal of marketing approvals; |
| ● | refusal to permit the import or export of our products; |
| ● | product seizure; and |
| ● | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
13
We may expend our limited resources to pursue a particular product candidate or indication and fail to capitalize on product candidates or indications that may be more profitable or for which there is a greater likelihood of success.
We have limited financial resources. As a result, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with future product candidates or for other indications that later prove to have greater commercial potential than opportunities we pursue. Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable commercial products or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and product candidates for specific indications may not yield any commercially viable products. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target markets for a particular product candidate or opportunity, we may relinquish valuable rights to that product candidate or opportunity through collaboration, licensing or other royalty arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such product candidate or opportunity.
We may be adversely affected by the ongoing coronavirus pandemic.
The outbreak of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has evolved into a global pandemic. The coronavirus has spread to many regions of the world. The extent to which the coronavirus impacts our business and operating results will depend on future developments that are highly uncertain and cannot be accurately predicted, including new information that may emerge concerning the coronavirus and the actions to contain the coronavirus or treat its impact, among others.
As a result of the continuing spread of the coronavirus, our business operations could be delayed or interrupted. For instance, our clinical trials may be affected by the pandemic. Site initiation, participant recruitment and enrollment, participant dosing, distribution of clinical trial materials, study monitoring and data analysis may be paused or delayed due to changes in hospital or university policies, federal, state or local regulations, prioritization of hospital resources toward pandemic efforts, or other reasons related to the pandemic. If the coronavirus continues to spread, some participants and clinical investigators may not be able to comply with clinical trial protocols. For example, quarantines or other travel limitations (whether voluntary or required) may impede participant movement, affect sponsor access to study sites, or interrupt healthcare services, and we may be unable to conduct our clinical trials. Further, if the spread of the coronavirus pandemic continues and our operations are adversely impacted, we risk a delay, default and/or nonperformance under existing agreements which may increase our costs. These cost increases may not be fully recoverable or adequately covered by insurance.
Infections and deaths related to the pandemic may disrupt the United States’ healthcare and healthcare regulatory systems. Such disruptions could divert healthcare resources away from, or materially delay FDA review or review by other regulatory agencies and/or approval with respect to, our clinical trials. It is unknown how long these disruptions could continue, were they to occur. Any elongation or de-prioritization of our clinical trials or delay in regulatory review resulting from such disruptions could materially affect the development and study of our product candidates.
As a result of the shelter-in-place order and other mandated local travel restrictions, our employees conducting research and development or manufacturing activities may not be able to access their laboratory or manufacturing space which may result in our core activities being significantly limited or curtailed, possibly for an extended period of time.
The spread of the coronavirus, which has caused a broad impact globally, including restrictions on travel and quarantine policies put into place by businesses and governments, may have a material economic effect on our business. While the potential economic impact brought by and the duration of the pandemic may be difficult to assess or predict, it has already caused, and is likely to result in further, significant disruption of global financial markets, which may reduce our ability to access capital either at all or on favorable terms. In addition, a recession, depression or other sustained adverse market event resulting from the spread of the coronavirus could materially and adversely affect our business and the value of our common stock.
The ultimate impact of the current pandemic, or any other health epidemic, is highly uncertain and subject to change. We do not yet know the full extent of potential delays or impacts on our business, our clinical trials, our research programs, healthcare systems or the global economy as a whole. However, these effects could have a material impact on our operations, and we will continue to monitor the situation closely.
14
Our reliance on third parties heightens the risks faced by our business.
We rely on suppliers, vendors and partners for certain key aspects of our business, including support for information technology systems and certain human resource functions. We do not control these partners, but we depend on them in ways that may be significant to us. If these parties fail to meet our expectations or fulfill their obligations to us, we may fail to receive the expected benefits. In addition, if any of these third parties fails to comply with applicable laws and regulations in the course of its performance of services for us, there is a risk that we may be held responsible for such violations as well. This risk is particularly serious in emerging markets, where corruption is often prevalent and where many of the third parties on which we rely do not have internal compliance resources comparable to our own. Any such failures by third parties, in emerging markets or elsewhere, could adversely affect our business, reputation, financial condition or results of operations.
We intend to rely on third parties to conduct our clinical trials and to conduct some aspects of our research and pre-clinical testing and those third parties may not perform satisfactorily, including failing to meet deadlines for the completion of such trials, research or testing.
We expect to rely on third parties, such as CROs, contract manufacturers of clinical supplies, clinical data management organizations, medical institutions and clinical investigators, to conduct our clinical trials and to conduct some aspects of our research and pre-clinical testing. These third parties may terminate their engagements with us at any time. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their duties, meet expected deadlines or conduct our studies in accordance with regulatory requirements or our stated protocols, we will not be able to obtain, or may be delayed in obtaining, marketing approvals for our product candidates and will not be able to, or may be delayed in our efforts to, successfully commercialize our product candidates. Furthermore, these third parties may also have relationships with other entities, some of which may be our competitors. If we are required to enter into alternative arrangements, it could delay our product development activities.
Our reliance on third parties for research and development activities will reduce our control over these activities but will not relieve us of our responsibilities. For example, we will remain responsible for ensuring that each of our clinical trials is conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols for the trial. Moreover, the FDA and other international regulatory authorities require us to comply with GCP standards for conducting, recording and reporting the results of clinical trials to assure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of trial participants are protected. We also are required to register ongoing clinical trials and post the results of completed clinical trials on a government-sponsored database, available at www.clinicaltrials.gov, within certain timeframes. Failure to do so can result in fines, adverse publicity and civil and criminal sanctions.
Upon commercialization of our products, we may be dependent on third parties to market, distribute and sell our products.
Our ability to receive revenues may be dependent upon the sales and marketing efforts of any future co-marketing partners and third-party distributors. At this time, we have not entered into an agreement with any commercialization partner and only plan to do so prior to commercialization. If we fail to reach an agreement with any commercialization partner, or upon reaching such an agreement that partner fails to sell a large volume of our products, it may have a negative impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have no experience manufacturing product candidates on a clinical or commercial scale and will be dependent on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates. If we experience problems with any of these third parties, they could delay clinical development or marketing approval of our product candidates or our ability to sell any approved products.
We do not have any manufacturing facilities. We expect to rely on third-party manufacturers for the manufacture of our product candidates for clinical trials and for commercial supply of any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval.
15
We may be unable to establish agreements with third-party manufacturers for clinical or commercial supply on terms favorable to us, or at all. Even if we are able to establish agreements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails additional risks, including:
| ● | reliance on the third party for regulatory compliance and quality assurance; |
| ● | the possible breach of the manufacturing agreement by the third party, including the inability to supply sufficient quantities or to meet quality standards or timelines; and |
| ● | the possible termination or nonrenewal of the agreement by the third party at a time that is costly or inconvenient for us. |
Third-party manufacturers may not be able to comply with U.S. cGMPs or similar regulatory requirements outside the United States. Our failure, or the failure of our third-party manufacturers, to comply with cGMPs or other applicable regulations, even if such failures do not relate specifically to our product candidates or approved products, could result in sanctions being imposed on us or the manufacturers, including fines, injunctions, civil penalties, delays, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, seizures or recalls of product candidates, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could adversely affect supplies of our product candidates and harm our business and results of operations.
Any product that we develop may compete with other product candidates and products for access to these manufacturing facilities. There are a limited number of manufacturers that operate under cGMPs and that might be capable of manufacturing for us.
Any performance failure on the part of our manufacturers, including a failure that may not relate specifically to our product candidates or approved products, could delay clinical development or marketing approval or adversely impact our ability to generate commercial sales. If our contract manufacturers cannot perform as agreed, we may be required to replace that manufacturer.
Our anticipated future dependence upon others for the manufacture of our current and future product candidates or products may adversely affect our future profit margins and our ability to commercialize any product candidates that receive marketing approval on a timely and competitive basis.
Furthermore, we expect to rely on third parties to release, label, store and distribute drug supplies for our clinical trials. Any performance failure on the part of these third parties, including a failure that may not relate specifically to our product candidates, could delay or otherwise adversely impact clinical development or marketing approval of our product candidates or commercialization of our drug, producing losses and depriving us of potential revenue.
Moreover, our manufacturers and suppliers may experience difficulties related to their overall businesses and financial stability, which could result in delays or interruptions of supply of our product candidates.
We may have conflicts with our partners that could delay or prevent the development or commercialization of our current and future product candidates.
We may have conflicts with our partners, such as conflicts concerning the interpretation of pre-clinical or clinical data, the achievement of milestones, the interpretation of contractual obligations, payments for services, development obligations or the ownership of intellectual property developed during our collaboration. If any conflicts arise with any of our partners, such partner may act in a manner that is adverse to our best interests. Any such disagreement could result in one or more of the following, each of which could delay or prevent the development or commercialization of our current and future product candidates, and in turn prevent us from generating revenues:
| ● | unwillingness on the part of a partner to pay us milestone payments or royalties we believe are due to us under a collaboration; |
| ● | uncertainty regarding ownership of intellectual property rights arising from our collaborative activities, which could prevent us from entering into additional collaborations; |
| ● | unwillingness by the partner to cooperate in the development or manufacture of the product, including providing us with product data or materials; |
16
| ● | unwillingness on the part of a partner to keep us informed regarding the progress of its development and commercialization activities or to permit public disclosure of the results of those activities; |
| ● | initiating of litigation or alternative dispute resolution options by either party to resolve the dispute; or |
| ● | attempts by either party to terminate the agreement. |
Our products will face significant competition, and if they are unable to compete successfully, our business will suffer.
Our current product candidates and future candidates face, and will continue to face, intense competition from large pharmaceutical companies, as well as academic and research institutions. We compete in an industry that is characterized by: (i) rapid technological change, (ii) evolving industry standards, (iii) emerging competition and (iv) new product introductions. Our competitors have existing products and technologies that will compete with our products and technologies and may develop and commercialize additional products and technologies that will compete with our products and technologies. Because several competing companies and institutions have greater financial resources than us, they may be able to: (i) provide broader services and product lines, (ii) make greater investments in research and development and (iii) carry on larger research and development initiatives. Our competitors also have greater development capabilities than we do and have substantially greater experience in undertaking pre-clinical and clinical testing of products, obtaining regulatory approvals, and manufacturing and marketing pharmaceutical products. They also have greater name recognition and better access to customers than us.
Product liability lawsuits against us could cause us to incur substantial liabilities and to limit commercialization of any products that we may develop.
We face an inherent risk of product liability exposure related to the testing of our current product candidates or future product candidates in human clinical trials and will face an even greater risk if we commercially sell any products that we may develop. Product liability claims may be brought against us by subjects enrolled in our clinical trials, patients, healthcare providers or others using, administering or selling our product. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against claims that our product candidates or product caused injuries, we could incur substantial liabilities. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
| ● | decreased demand for any product candidates or products that we may develop; |
| ● | termination of clinical trial sites or entire clinical trial programs; |
| ● | injury to our reputation and significant negative media attention; |
| ● | withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
| ● | significant costs to defend the related litigation; |
| ● | substantial monetary awards to trial subjects or patients; |
| ● | loss of revenue; |
| ● | diversion of management and scientific resources from our business operations; and |
| ● | the inability to commercialize any products that we may develop. |
Prior to engaging in future clinical trials, we intend to obtain product liability insurance coverage at a level that we believe is customary for similarly situated companies and adequate to provide us with insurance coverage for foreseeable risks; however, we may be unable to obtain such coverage at a reasonable cost, if at all. If we are able to obtain product liability insurance, we may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise and such insurance may not be adequate to cover all liabilities that we may incur. Furthermore, we intend to expand our insurance coverage for products to include the sale of commercial products if we obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates in development, but we may be unable to obtain commercially reasonable product liability insurance for any products that receive regulatory approval. Large judgments have been awarded in class action lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us, particularly if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, could decrease our cash and adversely affect our business.
17
We may engage in acquisitions that could disrupt our business, cause dilution to our stockholders or reduce our financial resources.
In the future, we may enter into transactions to acquire other businesses, products or technologies. If we do identify suitable candidates, we may not be able to make such acquisitions on favorable terms, or at all. Any acquisitions we make may fail to strengthen our competitive position and these transactions may be viewed negatively by customers or investors. We may decide to incur debt in connection with an acquisition or issue our common stock or other equity securities to the stockholders of the acquired company, which would reduce the percentage ownership of our existing stockholders. We could incur losses resulting from undiscovered liabilities of the acquired business that are not covered by the indemnification we may obtain from the seller. In addition, we may not be able to successfully integrate the acquired personnel, technologies and operations into our existing business in an effective, timely and non-disruptive manner. Acquisitions may also divert management attention from day-to-day responsibilities, increase our expenses and reduce our cash available for operations and other uses. We cannot predict the number, timing or size of future acquisitions or the effect that any such transactions might have on our operating results.
Security threats to our information technology infrastructure and/or our physical buildings could expose us to liability and damage our reputation and business.
It is essential to our business strategy that our technology and network infrastructure and our physical buildings remain secure and are perceived by our customers and corporate partners to be secure. Despite security measures, however, any network infrastructure may be vulnerable to cyber-attacks by hackers and other security threats. We may face cyber-attacks that attempt to penetrate our network security, sabotage or otherwise disable our research, products and services, misappropriate our or our customers’ and partners’ proprietary information, which may include personally identifiable information, or cause interruptions of our internal systems and services. Despite security measures, we also cannot guarantee security of our physical buildings. Physical building penetration or any cyber-attacks could negatively affect our reputation, damage our network infrastructure and our ability to deploy our products and services, harm our relationship with customers and partners that are affected, and expose us to financial liability.
Additionally, there are a number of state, federal and international laws protecting the privacy and security of health information and personal data. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”) imposes limitations on the use and disclosure of an individual’s healthcare information by healthcare providers, healthcare clearinghouses, and health insurance plans, or, collectively, covered entities, and also grants individuals rights with respect to their health information. HIPAA also imposes compliance obligations and corresponding penalties for non-compliance on individuals and entities that provide services to healthcare providers and other covered entities. As part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (“ARRA”) the privacy and security provisions of HIPAA were amended. ARRA also made significant increases in the penalties for improper use or disclosure of an individual’s health information under HIPAA and extended enforcement authority to state attorneys general. As amended by ARRA and subsequently by the final omnibus rule adopted in 2013, HIPAA also imposes notification requirements on covered entities in the event that certain health information has been inappropriately accessed or disclosed, notification requirements to individuals, federal regulators, and in some cases, notification to local and national media. Notification is not required under HIPAA if the health information that is improperly used or disclosed is deemed secured in accordance with encryption or other standards developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Most states have laws requiring notification of affected individuals and/or state regulators in the event of a breach of personal information, which is a broader class of information than the health information protected by HIPAA. Many state laws impose significant data security requirements, such as encryption or mandatory contractual terms, to ensure ongoing protection of personal information. Activities outside of the U.S. implicate local and national data protection standards, impose additional compliance requirements and generate additional risks of enforcement for non-compliance. We may be required to expend significant capital and other resources to ensure ongoing compliance with applicable privacy and data security laws, to protect against security breaches and hackers or to alleviate problems caused by such breaches.
18
We will need to grow the size of our organization in the future, and we may experience difficulties in managing this growth.
As of September 14, 2020, we had 1 full-time employee. We will need to grow the size of our organization in order to support our continued development and potential commercialization of our product candidates. As our development and commercialization plans and strategies continue to develop, our need for additional managerial, operational, manufacturing, sales, marketing, financial and other resources may increase. Our management, personnel and systems currently in place may not be adequate to support this future growth. Future growth would impose significant added responsibilities on members of management, including:
| ● | managing our clinical trials effectively; |
| ● | identifying, recruiting, maintaining, motivating and integrating additional employees; |
| ● | managing our internal development efforts effectively while complying with our contractual obligations to licensors, licensees, contractors and other third parties; |
| ● | improving our managerial, development, operational, information technology, and finance systems; and |
| ● | expanding our facilities. |
If our operations expand, we will also need to manage additional relationships with various strategic partners, suppliers and other third parties. Our future financial performance and our ability to commercialize our product candidates and to compete effectively will depend, in part, on our ability to manage any future growth effectively, as well as our ability to develop a sales and marketing force when appropriate. To that end, we must be able to manage our development efforts and pre-clinical studies and clinical trials effectively and hire, train and integrate additional management, research and development, manufacturing, administrative and sales and marketing personnel. The failure to accomplish any of these tasks could prevent us from successfully growing our company.
Our future success depends on our ability to retain our executive officers and to attract, retain and motivate qualified personnel.
We are highly dependent upon our personnel, including Shalabh Gupta, our Chief Executive Officer and members of our board of directors. The loss of Dr. Gupta’s services could impede the achievement of our research, development and commercialization objectives. We have not obtained, do not own, nor are we the beneficiary of, key-person life insurance. Our future growth and success depend on our ability to recruit, retain, manage and motivate our employees. The loss of any member of our senior management team or the inability to hire or retain experienced management personnel could compromise our ability to execute our business plan and harm our operating results. Because of the specialized scientific and managerial nature of our business, we rely heavily on our ability to attract and retain qualified scientific, technical and managerial personnel. The competition for qualified personnel in the pharmaceutical field is intense and as a result, we may be unable to continue to attract and retain qualified personnel necessary for the development of our business.
Our Chief Executive Officer, Shalabh Gupta, is also the Chief Executive Officer of Globavir Biosciences, Inc. (“Globavir”) and may allocate his time to such other business thereby causing conflicts of interest in his determination as to how much time to devote to our affairs. Furthermore, certain members of our Board of Directors are members of the board of directors of Globavir and may allocate their time to, among other ventures, the business of Globavir which may cause conflicts of interest with respect to their determination as to how much time to devote to our affairs. This could have a negative impact on our ability to implement our plan of operation.
Our Chief Executive Officer, Shalabh Gupta, is also the Chief Executive Officer of Globavir and may not commit his full time to our affairs, which may result in a conflict of interest in allocating his time between our business and the other business. Similarly, certain members of our Board of Directors are members of the board of directors of Globavir and may not commit their full time to our affairs, which may result in a conflict of interest in allocating their time between our business and the other business. Furthermore, neither our Chief Executive Officer, our executive team, nor our directors are obligated to contribute any specific number of his hours per week to our affairs. If other business affairs require our Chief Executive Officer and/or directors to devote more amounts of time to other affairs, including the business of Globavir, it could limit their ability to devote time to our affairs and could have a negative impact on our ability to implement our plan of operation.
19
Inadequate funding for the FDA, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and other government agencies could hinder their ability to hire and retain key leadership and other personnel, prevent new products and services from being developed or commercialized in a timely manner or otherwise prevent those agencies from performing normal business functions on which the operation of our business may rely, which could negatively impact our business.
The ability of the FDA to review and approve new products can be affected by a variety of factors, including government budget and funding levels, ability to hire and retain key personnel and accept the payment of user fees, and statutory, regulatory, and policy changes. Average review times at the agency have fluctuated in recent years as a result. In addition, government funding of the SEC and other government agencies on which our operations may rely, including those that fund research and development activities is subject to the political process, which is inherently fluid and unpredictable.
Disruptions at the FDA and other agencies may also slow the time necessary for new drugs to be reviewed and/or approved by necessary government agencies, which would adversely affect our business. For example, over the last several years, including beginning on December 22, 2018, the U.S. government has shut down several times and certain regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and the SEC, have had to furlough critical FDA, SEC and other government employees and stop critical activities. If a prolonged government shutdown occurs, it could significantly impact the ability of the FDA to timely review and process our regulatory submissions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. Further, upon completion of this offering and in our operations as a public company, future government shutdowns could impact our ability to access the public markets and obtain necessary capital in order to properly capitalize and continue our operations.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
It is difficult and costly to protect our proprietary rights, and we may not be able to ensure their protection. If our patent position does not adequately protect our product candidates, others could compete against us more directly, which would harm our business, possibly materially.
Our commercial success will depend in part on obtaining and maintaining patent protection and trade secret protection of our current product candidates and future product candidates, the processes used to manufacture them and the methods for using them, as well as successfully defending these patents against third-party challenges. Our ability to stop third parties from making, using, selling, offering to sell or importing our product candidates is dependent upon the extent to which we have rights under valid and enforceable patents or trade secrets that cover these activities.
The patent positions of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions for which important legal principles remain unresolved. No consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims allowed in pharmaceutical patents has emerged to date in the U.S. or in foreign jurisdictions outside of the U.S. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretations of patent laws in the U.S. and other countries may diminish the value of our intellectual property. Accordingly, we cannot predict the breadth of claims that may be enforced in the patents that may be issued from the applications we currently license or may in the future own or license from third parties. Further, if any patents we obtain or license are deemed invalid and unenforceable, our ability to commercialize or license our product candidates or technology could be adversely affected.
Others may file patent applications covering products and technologies that are similar, identical or competitive to ours or important to our business. We cannot be certain that any patent application owned by a third party will not have priority over patent applications filed or in-licensed by us, or that we or our licensors will not be involved in interference, opposition, reexamination, review, reissue, post grant review or invalidity proceedings before U.S. or non-U.S. patent offices.
20
The degree of future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain because legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage. For example:
| ● | others may be able to make compounds that are similar to our product candidates, but that are not covered by the claims of our licensed patents; |
| ● | any patents that we obtain from licensing or otherwise may not provide us with any competitive advantages; |
| ● | any granted patents that we rely upon may be held invalid or unenforceable as a result of legal challenges by third parties; and |
| ● | the patents of others may have an adverse effect on our business. |
If we fail to comply with our obligations in the agreements under which we may license intellectual property rights from third parties or otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our licensors, we could lose rights that are important to our business.
We may be required to enter into intellectual property license agreements that are important to our business. These license agreements may impose various diligence, milestone payment, royalty and other obligations on us. For example, we may enter into exclusive license agreements with various universities and research institutions, we may be required to use commercially reasonable efforts to engage in various development and commercialization activities with respect to licensed products, and may need to satisfy specified milestone and royalty payment obligations. If we fail to comply with any obligations under our agreements with any of these licensors, we may be subject to termination of the license agreement in whole or in part; increased financial obligations to our licensors or loss of exclusivity in a particular field or territory, in which case our ability to develop or commercialize products covered by the license agreement will be impaired.
In addition, disputes may arise regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
| ● | the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; |
| ● | the extent to which our technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; |
| ● | our diligence obligations under the license agreement and what activities satisfy those obligations; |
| ● | if a third-party expresses interest in an area under a license that we are not pursuing, under the terms of certain of our license agreements, we may be required to sublicense rights in that area to a third party, and that sublicense could harm our business; and |
| ● | the ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensors and us. |
If disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize our product candidates.
We may need to obtain licenses from third parties to advance our research or allow commercialization of our product candidates. We may fail to obtain any of these licenses at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, if at all. In that event, we would be unable to further develop and commercialize our product candidates, which could harm our business significantly.
21
We may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which may prevent or delay our product development efforts and stop us from commercializing or increase the costs of commercializing our product candidates.
Our success will depend in part on our ability to operate without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. We cannot guarantee that our product candidates, or manufacture or use of our product candidates, will not infringe third-party patents. Furthermore, a third party may claim that we are using inventions covered by the third party’s patent rights and may go to court to stop us from engaging in our normal operations and activities, including making or selling our product candidates. These lawsuits are costly and could affect our results of operations and divert the attention of managerial and scientific personnel. Some of these third parties may be better capitalized and have more resources than us. There is a risk that a court would decide that we are infringing the third party’s patents and would order us to stop the activities covered by the patents. In that event, we may not have a viable way around the patent and may need to halt commercialization of our product candidates. In addition, there is a risk that a court will order us to pay the other party damages for having violated the other party’s patents. In addition, we may be obligated to indemnify our licensors and collaborators against certain intellectual property infringement claims brought by third parties, which could require us to expend additional resources. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have produced a proliferation of patents, and it is not always clear to industry participants, including us, which patents cover various types of products or methods of use. The coverage of patents is subject to interpretation by the courts, and the interpretation is not always uniform.
If we are sued for patent infringement, we would need to demonstrate that our product candidates or methods either do not infringe the patent claims of the relevant patent or that the patent claims are invalid, and we may not be able to do this. Proving invalidity is difficult. For example, in the U.S., proving invalidity requires a showing of clear and convincing evidence to overcome the presumption of validity enjoyed by issued patents. Even if we are successful in these proceedings, we may incur substantial costs and diversion of management’s time and attention in pursuing these proceedings, which could have a material adverse effect on us. If we are unable to avoid infringing the patent rights of others, we may be required to seek a license, which may not be available, defend an infringement action or challenge the validity of the patents in court. Patent litigation is costly and time consuming. We may not have sufficient resources to bring these actions to a successful conclusion. In addition, if we do not obtain a license, develop or obtain non-infringing technology, fail to defend an infringement action successfully or have infringed patents declared invalid, we may incur substantial monetary damages, encounter significant delays in bringing our product candidates to market and be precluded from manufacturing or selling our product candidates.
Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than us or the third parties from whom we license intellectual property because they have substantially greater resources. In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our operations.
If we are not able to adequately prevent disclosure of trade secrets and other proprietary information, the value of our technology and product could be significantly diminished.
We also rely on trade secrets to protect our proprietary technologies, especially where we do not believe patent protection is appropriate or obtainable. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. We rely in part on confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers and other advisors to protect our trade secrets and other proprietary information. These agreements may not effectively prevent disclosure of confidential information and may not provide an adequate remedy in the event of unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. In addition, others may independently discover our trade secrets and proprietary information. For example, the FDA, as part of its transparency initiative, is currently considering whether to make additional information publicly available on a routine basis, including information that we may consider to be trade secrets or other proprietary information, and it is not clear at the present time how the FDA’s disclosure policies may change in the future, if at all. Costly and time-consuming litigation could be necessary to enforce and determine the scope of our proprietary rights, and failure to obtain or maintain trade secret protection could adversely affect our competitive business position.
22
We may be subject to claims that our employees, consultants or independent contractors have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets.
As is common in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, we employ individuals who were previously employed at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Although we try to ensure that our employees, consultants and independent contractors do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or our employees, consultants or independent contractors have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed trade secrets or other proprietary information of their former employers. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we could lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel, which could adversely impact our business. Even if we are successful in defending against these claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management.
Our intellectual property may not be sufficient to protect our product candidates from competition, which may negatively affect our business as well as limit our partnership or acquisition appeal.
We may be subject to competition despite the existence of intellectual property we license or may in the future own. We can give no assurances that our intellectual property claims will be sufficient to prevent third parties from designing around patents we own or license and developing and commercializing competitive products. The existence of competitive products that avoid our intellectual property could materially adversely affect our operating results and financial condition. Furthermore, limitations, or perceived limitations, in our intellectual property may limit the interest of third parties to partner, collaborate or otherwise transact with us, if third parties perceive a higher than acceptable risk to commercialization of our product candidates or future product candidates.
We may elect to sue a third party, or otherwise make a claim, alleging infringement or other violation of patents, trademarks, trade dress, copyrights, trade secrets, domain names or other intellectual property rights that we either own or license from a third party. If we do not prevail in enforcing our intellectual property rights in this type of litigation, we may be subject to:
| ● | paying monetary damages related to the legal expenses of the third party; |
| ● | facing additional competition that may have a significant adverse effect on our product pricing, market share, business operations, financial condition, and the commercial viability of our product; and |
| ● | restructuring our company or delaying or terminating select business opportunities, including, but not limited to, research and development, clinical trial, and commercialization activities, due to a potential deterioration of our financial condition or market competitiveness. |
A third party may also challenge the validity, enforceability or scope of the intellectual property rights that we license or own and the result of these challenges may narrow the scope or claims of or invalidate patents that are integral to our product candidates in the future. There can be no assurance that we will be able to successfully defend patents we own or license in an action against third parties due to the unpredictability of litigation and the high costs associated with intellectual property litigation, amongst other factors.
Intellectual property rights and enforcement may be less extensive in jurisdictions outside of the U.S. Therefore, we may not be able to protect our intellectual property and third parties may be able to market competitive products that may use some or all of our intellectual property.
Changes to patent law, including the Leahy-Smith America Invests Act of 2011 and the Patent Reform Act of 2009 and other future article of legislation, may substantially change the regulations and procedures surrounding patent applications, issuance of patents and prosecution of patents. We can give no assurances that the patents of our licensor can be defended or will protect us against future intellectual property challenges, particularly as they pertain to changes in patent law and future patent law interpretations.
23
Risks Related to Healthcare Compliance and Other Regulations
If we fail to comply with healthcare regulations, we could face substantial enforcement actions, including civil and criminal penalties and our business, operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
We could be subject to healthcare fraud and abuse laws and patient privacy laws of both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. The laws include:
| ● | the federal healthcare program anti-kickback law, which prohibits, among other things, persons from soliciting, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, to induce either the referral of an individual, for an item or service or the purchasing or ordering of a good or service, for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
| ● | federal false claims laws which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment from Medicare, Medicaid, or other third-party payers that are false or fraudulent, and which may apply to entities like us which provide coding and billing information to customers; |
| ● | HIPAA which prohibits executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters and which also imposes certain requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
| ● | the FDCA which among other things, strictly regulates drug manufacturing and product marketing, prohibits manufacturers from marketing drug products for off-label use and regulates the distribution of drug samples; and |
| ● | state law equivalents of each of the above federal laws, such as anti-kickback and false claims laws which may apply to items or services reimbursed by any third-party payer, including commercial insurers, and state laws governing the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by federal laws, thus complicating compliance efforts. |
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. Any penalties, damages, fines, curtailment or restructuring of our operations could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results. Although compliance programs can mitigate the risk of investigation and prosecution for violations of these laws, the risks cannot be entirely eliminated. Any action against us for violation of these laws, even if we successfully defend against it, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert management’s attention from the operation of our business. Moreover, achieving and sustaining compliance with applicable federal and state privacy, security and fraud laws may prove costly.
Healthcare Reform in the United States.
In the United States, there have been, and continue to be, a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes to the healthcare system that could affect the future results of pharmaceutical manufactures’ operations. In particular, there have been and continue to be a number of initiatives at the federal and state levels that seek to reduce healthcare costs. Most recently, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (“PPACA”) was enacted in March 2010, which includes measures to significantly change the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers. Among the provisions of the PPACA of greatest importance to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry are the following:
| ● | an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain branded prescription drugs and biologic agents, apportioned among these entities according to their market share in certain government healthcare programs; |
| ● | implementation of the federal physician payment transparency requirements, sometimes referred to as the “Physician Payments Sunshine Act”; |
| ● | a licensure framework for follow-on biologic products; |
| ● | a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research; |
24
| ● | establishment of a Center for Medicare Innovation at the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to test innovative payment and service delivery models to lower Medicare and Medicaid spending, potentially including prescription drug spending; |
| ● | an increase in the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, to 23.1% and 13% of the average manufacturer price for most branded and generic drugs, respectively and capped the total rebate amount for innovator drugs at 100% of the Average Manufacturer Price; |
| ● | a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for certain drugs and biologics, including our product candidates, that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected; |
| ● | extension of manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability to covered drugs dispensed to individuals who are enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations; |
| ● | expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals and by adding new mandatory eligibility categories for individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level, thereby potentially increasing manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability; |
| ● | a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; and |
| ● | expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health program. |
Some of the provisions of the PPACA have yet to be implemented, and there have been legal and political challenges to certain aspects of the PPACA. Since January 2017, President Trump has signed executive orders and other directives designed to delay, circumvent, or loosen certain requirements mandated by the PPACA. Concurrently, Congress has considered legislation that would repeal or repeal and replace all or part of the PPACA. While Congress has not passed repeal legislation, the Tax Act includes a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the PPACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” Congress may consider other legislation to repeal or replace elements of the PPACA.
Many of the details regarding the implementation of the PPACA are yet to be determined, and at this time, the full effect that the PPACA would have on a pharmaceutical manufacturer remains unclear. In particular, there is uncertainty surrounding the applicability of the biosimilars provisions under the PPACA. The FDA has issued several guidance documents, but no implementing regulations, on biosimilars. A number of biosimilar applications have been approved over the past few years. The regulations that are ultimately promulgated and their implementation are likely to have considerable impact on the way pharmaceutical manufacturers conduct their business and may require changes to current strategies. A biosimilar is a biological product that is highly similar to an approved drug notwithstanding minor differences in clinically inactive components, and for which there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biological product and the approved drug in terms of the safety, purity, and potency of the product.
Individual states have become increasingly aggressive in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical and biological product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access, and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. Legally mandated price controls on payment amounts by third-party payors or other restrictions could harm a pharmaceutical manufacturer’s business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. In addition, regional healthcare authorities and individual hospitals are increasingly using bidding procedures to determine what pharmaceutical products and which suppliers will be included in their prescription drug and other healthcare programs. This could reduce ultimate demand for certain products or put pressure product pricing, which could negatively affect a pharmaceutical manufacturer’s business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
25
In addition, given recent federal and state government initiatives directed at lowering the total cost of healthcare, Congress and state legislatures will likely continue to focus on healthcare reform, the cost of prescription drugs and biologics and the reform of the Medicare and Medicaid programs. While no one cannot predict the full outcome of any such legislation, it may result in decreased reimbursement for drugs and biologics, which may further exacerbate industry-wide pressure to reduce prescription drug prices. This could harm a pharmaceutical manufacturer’s ability to generate revenue. Increases in importation or re-importation of pharmaceutical products from foreign countries into the United States could put competitive pressure on a pharmaceutical manufacturer’s ability to profitably price products, which, in turn, could adversely affect business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. A pharmaceutical manufacturer might elect not to seek approval for or market products in foreign jurisdictions in order to minimize the risk of re-importation, which could also reduce the revenue generated from product sales. It is also possible that other legislative proposals having similar effects will be adopted.
Furthermore, regulatory authorities’ assessment of the data and results required to demonstrate safety and efficacy can change over time and can be affected by many factors, such as the emergence of new information, including on other products, changing policies and agency funding, staffing and leadership. We cannot be sure whether future changes to the regulatory environment will be favorable or unfavorable to our business prospects. For example, average review times at the FDA for marketing approval applications can be affected by a variety of factors, including budget and funding levels and statutory, regulatory and policy changes.
Our employees may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements, which could cause significant liability for us and harm our reputation.
We are exposed to the risk of employee fraud or other misconduct, including intentional failures to comply with FDA regulations or similar regulations of comparable foreign regulatory authorities, provide accurate information to the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, comply with manufacturing standards we have established, comply with federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations and similar laws and regulations established and enforced by comparable foreign regulatory authorities, report financial information or data accurately or disclose unauthorized activities to us. Employee misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. It is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business and results of operations, including the imposition of significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment, exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and integrity oversight and reporting obligations.
We are subject to U.S. and certain foreign export and import controls, sanctions, embargoes, anti-corruption laws and anti-money laundering laws and regulations. Compliance with these legal standards could impair our ability to compete in domestic and international markets. We can face criminal liability and other serious consequences for violations, which can harm our business.
We are subject to export control and import laws and regulations, including the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, U.S. Customs regulations, various economic and trade sanctions regulations administered by the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Controls, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended, the U.S. domestic bribery statute contained in 18 U.S.C. § 201, the U.S. Travel Act, the USA PATRIOT Act and other state and national anti-bribery and anti-money laundering laws in the countries in which we conduct activities. Anti-corruption laws are interpreted broadly and prohibit companies and their employees, agents, contractors, and other collaborators from authorizing, promising, offering or providing, directly or indirectly, improper payments or anything else of value to recipients in the public or private sector. We may engage third parties for clinical trials outside of the United States, to sell our products abroad once we enter a commercialization phase and/or to obtain necessary permits, licenses, patent registrations, and other regulatory approvals. We have direct or indirect interactions with officials and employees of government agencies or government-affiliated hospitals, universities and other organizations. We can be held liable for the corrupt or other illegal activities of our employees, agents, contractors and other collaborators, even if we do not explicitly authorize or have actual knowledge of such activities. Any violations of the laws and regulations described above may result in substantial civil and criminal fines and penalties, imprisonment, the loss of export or import privileges, debarment, tax reassessments, breach of contract and fraud litigation, reputational harm and other consequences.
26
Risks Related to Owning our Common Stock and this Offering
An active trading market for our common stock may not develop, and you may not be able to sell your common stock at or above the initial public offering price.
Prior to the consummation of this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. An active trading market for shares of our common stock may never develop or be sustained following this offering. If an active trading market does not develop, you may have difficulty selling your shares of common stock at an attractive price, or at all. The price for our common stock in this offering will be determined by negotiations between us and the underwriters, and it may not be indicative of prices that will prevail in the open market following this offering. Consequently, you may not be able to sell your common stock at or above the initial public offering price or at any other price or at the time that you would like to sell. An inactive market may also impair our ability to raise capital by selling our common stock, and it may impair our ability to attract and motivate our employees through equity incentive awards and our ability to acquire other companies, products or technologies by using our common stock as consideration.
The price of our common stock may fluctuate substantially.
You should consider an investment in our common stock to be risky, and you should invest in our common stock only if you can withstand a significant loss and wide fluctuations in the market value of your investment. Some factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to fluctuate, in addition to the other risks mentioned in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this prospectus, are:
| ● | sale of our common stock by our stockholders, executives, and directors; |
| ● | volatility and limitations in trading volumes of our shares of common stock; |
| ● | our ability to obtain financings to conduct and complete research and development activities including, but not limited to, our clinical trials, and other business activities; |
| ● | possible delays in the expected recognition of revenue due to lengthy and sometimes unpredictable sales timelines; |
| ● | the timing and success of introductions of new products by us or our competitors or any other change in the competitive dynamics of our industry, including consolidation among competitors, customers or strategic partners; |
| ● | network outages or security breaches; |
| ● | our ability to attract new customers; |
| ● | our ability to secure resources and the necessary personnel to conduct clinical trials on our desired schedule; |
| ● | commencement, enrollment or results of our clinical trials for our product candidates or any future clinical trials we may conduct; |
| ● | changes in the development status of our product candidates; |
| ● | any delays or adverse developments or perceived adverse developments with respect to the FDA’s review of our planned pre-clinical and clinical trials; |
27
| ● | any delay in our submission for studies or product approvals or adverse regulatory decisions, including failure to receive regulatory approval for our product candidates; |
| ● | unanticipated safety concerns related to the use of our product candidates; |
| ● | failures to meet external expectations or management guidance; |
| ● | changes in our capital structure or dividend policy, future issuances of securities, sales of large blocks of common stock by our stockholders; |
| ● | our cash position; |
| ● | announcements and events surrounding financing efforts, including debt and equity securities; |
| ● | our inability to enter into new markets or develop new products; |
| ● | reputational issues; |
| ● | competition from existing technologies and products or new technologies and products that may emerge; |
| ● | announcements of acquisitions, partnerships, collaborations, joint ventures, new products, capital commitments, or other events by us or our competitors; |
| ● | changes in general economic, political and market conditions in or any of the regions in which we conduct our business; |
| ● | changes in industry conditions or perceptions; |
| ● | changes in valuations of similar companies or groups of companies; |
| ● | analyst research reports, recommendation and changes in recommendations, price targets, and withdrawals of coverage; |
| ● | departures and additions of key personnel; |
| ● | disputes and litigations related to intellectual property, proprietary rights, and contractual obligations; |
| ● | changes in applicable laws, rules, regulations, or accounting practices and other dynamics; and |
| ● | other events or factors, many of which may be out of our control. |
In addition, if the market for stocks in our industry or industries related to our industry, or the stock market in general, experiences a loss of investor confidence, the trading price of our common stock could decline for reasons unrelated to our business, financial condition and results of operations. If any of the foregoing occurs, it could cause our stock price to fall and may expose us to lawsuits that, even if unsuccessful, could be costly to defend and a distraction to management.
We have broad discretion in the use of the net proceeds from this offering and may not use them effectively.
Our management will have broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds from this initial public offering, including for any of the currently intended purposes described in the section entitled “Use of Proceeds.” Because of the number and variability of factors that will determine our use of the net proceeds from this offering, their ultimate use may vary substantially from their currently intended use. Our management may not apply our cash from this offering in ways that ultimately increase the value of any investment in our securities or enhance stockholder value. The failure by our management to apply these funds effectively could harm our business. Pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from this offering in short-term, investment-grade, interest-bearing securities. These investments may not yield a favorable return to our stockholders. If we do not invest or apply our cash in ways that enhance stockholder value, we may fail to achieve expected financial results, which may result in a decline in the price of our shares of common stock, and, therefore, may negatively impact our ability to raise capital, invest in or expand our business, acquire additional products or licenses, commercialize our product, or continue our operations.
28
Market and economic conditions may negatively impact our business, financial condition and share price.
Concerns over medical epidemics, energy costs, geopolitical issues, the U.S. mortgage market and a deteriorating real estate market, unstable global credit markets and financial conditions, and volatile oil prices have led to periods of significant economic instability, diminished liquidity and credit availability, declines in consumer confidence and discretionary spending, diminished expectations for the global economy and expectations of slower global economic growth, increased unemployment rates, and increased credit defaults in recent years. Our general business strategy may be adversely affected by any such economic downturns (including the current downturn related to the current COVID-19 pandemic), volatile business environments and continued unstable or unpredictable economic and market conditions. If these conditions continue to deteriorate or do not improve, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult to complete, more costly, and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance, and share price and could require us to delay or abandon development or commercialization plans.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports, or publish unfavorable research or reports about our business, our stock price and trading volume may decline.
The trading market for our common stock will rely in part on the research and reports that industry or financial analysts publish about us, our business, our markets and our competitors. We do not control these analysts. If securities analysts do not cover our common stock after the closing of this offering, the lack of research coverage may adversely affect the market price of our common stock. Furthermore, if one or more of the analysts who do cover us downgrade our stock or if those analysts issue other unfavorable commentary about us or our business, our stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease coverage of us or fails to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the market and interest in our stock could decrease, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline and may also impair our ability to expand our business with existing customers and attract new customers.
Because certain of our stockholders control a significant number of shares of our common stock, they may have effective control over actions requiring stockholder approval.
Following this offering, our directors, executive officers and principal stockholders, and their respective affiliates, will beneficially own approximately % of our outstanding shares of common stock. As a result, these stockholders, acting together, would have the ability to control the outcome of matters submitted to our stockholders for approval, including the election of directors and any merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. In addition, these stockholders, acting together, would have the ability to control the management and affairs of our company. Accordingly, this concentration of ownership might harm the market price of our common stock by:
| ● | delaying, deferring or preventing a change in corporate control; |
| ● | impeding a merger, consolidation, takeover or other business combination involving us; or |
| ● | discouraging a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us. |
You will incur immediate dilution as a result of this offering.
If you purchase common stock in this offering, you will pay more for your shares than the net tangible book value of your shares. As a result, you will incur immediate dilution of $ per share, representing the difference between the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range on the cover of this prospectus) and our estimated pro forma net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2020 of $ . Accordingly, should we be liquidated at our book value, you would not receive the full amount of your investment.
29
Future sales and issuances of our common stock could result in additional dilution of the percentage ownership of our stockholders and could cause our share price to fall.
We expect that significant additional capital will be needed in the future to continue our planned operations, including increased marketing, hiring new personnel, commercializing our product, and continuing activities as an operating public company. To the extent we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience substantial dilution. We may sell common stock, convertible securities or other equity securities in one or more transactions at prices and in a manner we determine from time to time. If we sell common stock, convertible securities or other equity securities in more than one transaction, investors may be materially diluted by subsequent sales. Such sales may also result in material dilution to our existing stockholders, and new investors could gain rights superior to our existing stockholders.
We do not intend to pay cash dividends on our shares of common stock so any returns will be limited to the value of our shares.
We currently anticipate that we will retain future earnings for the development, operation and expansion of our business and do not anticipate declaring or paying any cash dividends for the foreseeable future. Any return to stockholders will therefore be limited to the increase, if any, of our share price.
We are an “emerging growth company” and will be able to avail ourselves of reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies, which could make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act and we intend to take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies” including not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. In addition, pursuant to Section 107 of the JOBS Act, as an “emerging growth company” we intend to take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an “emerging growth company” can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile. We may take advantage of these reporting exemptions until we are no longer an “emerging growth company.” We will remain an “emerging growth company” until the earliest of (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1.07 billion or more; (ii) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of this offering; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the SEC.
We may be at risk of securities class action litigation.
We may be at risk of securities class action litigation. In the past, biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies have experienced significant stock price volatility, particularly when associated with binary events such as clinical trials and product approvals. If we face such litigation, it could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which could harm our business and results in a decline in the market price of our common stock.
There is no guarantee that our common stock will be listed on Nasdaq.
We have applied to have our shares of common stock listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market. Upon completion of this offering, we believe that we will satisfy the listing requirements and expect that our common stock will be listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market. Such listing, however, is not guaranteed. If the application is not approved, we may seek to have our common stock quoted on the OTCQB operated by the OTC Markets Group, Inc. Even if such listing is approved, there can be no assurance any broker will be interested in trading our common stock. Therefore, it may be difficult to sell any shares you purchase in this offering if you desire or need to sell them.
30
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation (“Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation”) and our amended and restated bylaws (the “Amended and Restated Bylaws”), to be effective upon completion of this offering, and Delaware law may have anti-takeover effects that could discourage, delay or prevent a change in control, which may cause our stock price to decline.
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and our Amended and Restated Bylaws, to be effective upon completion of this offering, and Delaware law could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us, even if closing such a transaction would be beneficial to our stockholders. We are authorized to issue up to 10 million shares of preferred stock. This preferred stock may be issued in one or more series, the terms of which may be determined at the time of issuance by our board of directors without further action by stockholders. The terms of any series of preferred stock may include voting rights (including the right to vote as a series on particular matters), preferences as to dividend, liquidation, conversion and redemption rights and sinking fund provisions. The issuance of any preferred stock could materially adversely affect the rights of the holders of our common stock, and therefore, reduce the value of our common stock. In particular, specific rights granted to future holders of preferred stock could be used to restrict our ability to merge with, or sell our assets to, a third party and thereby preserve control by the present management.
Provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, our Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law also could have the effect of discouraging potential acquisition proposals or making a tender offer or delaying or preventing a change in control, including changes a stockholder might consider favorable. Such provisions may also prevent or frustrate attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our management. In particular, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, our Amended and Restated Bylaws and Delaware law, as applicable, among other things:
| ● | provide the board of directors with the ability to alter the bylaws without stockholder approval; |
| ● | place limitations on the removal of directors; |
| ● | establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon at stockholder meetings; and |
| ● | provide that vacancies on the board of directors may be filled by a majority of directors in office, although less than a quorum. |
Financial reporting obligations of being a public company in the U.S. are expensive and time-consuming, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to compliance matters.
As a publicly traded company we will incur significant additional legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a privately held company. The obligations of being a public company in the U.S. require significant expenditures and will place significant demands on our management and other personnel, including costs resulting from public company reporting obligations under the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations regarding corporate governance practices, including those under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, and the listing requirements of the stock exchange on which our securities are listed. These rules require the establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and procedures, internal control over financial reporting and changes in corporate governance practices, among many other complex rules that are often difficult to implement, monitor and maintain compliance with. Moreover, despite recent reforms made possible by the JOBS Act, the reporting requirements, rules, and regulations will make some activities more time-consuming and costly, particularly after we are no longer an “emerging growth company.” In addition, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to ensure that we comply with all of these requirements and to keep pace with new regulations, otherwise we may fall out of compliance and risk becoming subject to litigation or being delisted, among other potential problems.
31
Our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering provides that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for substantially all disputes between the Company and its stockholders, which could limit stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with the Company or its directors, officers or employees.
Our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering provides that unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the State of Delaware is the sole and exclusive forum for: (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of us, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director, officer or other employee of our Company to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law (the “DGCL”) or our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering, or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers, employees or agents governed by the internal affairs doctrine, except for, as to each of (i) through (iv) above, any claim as to which the Court of Chancery determines that there is an indispensable party not subject to the jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery (and the indispensable party does not consent to the personal jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery within ten days following such determination), which is vested in the exclusive jurisdiction of a court or forum other than the Court of Chancery, or for which the Court of Chancery does not have subject matter jurisdiction. This exclusive forum provision would not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Securities Act or the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal courts have exclusive jurisdiction. To the extent that any such claims may be based upon federal law claims, Section 27 of the Exchange Act creates exclusive federal jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Exchange Act or the rules and regulations thereunder.
Section 22 of the Securities Act creates concurrent jurisdiction for federal and state courts over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Securities Act or the rules and regulations thereunder. However, our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering contain a federal forum provision which provides that unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock are deemed to have notice of and consented to this provision.
These choice of forum provisions may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and other employees. Alternatively, if a court were to find our choice of forum provisions contained in our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such action in other jurisdictions, which could harm our business, results of operations, and financial condition.
Failure to maintain effective internal controls could cause our investors to lose confidence in us and adversely affect the market price of our common stock. If our internal controls are not effective, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud.
Effective internal control over financial reporting is necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports in a timely manner. In connection with the preparation of our financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and the six months ended June 30, 2020, we concluded that there were material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. A material weakness is a significant deficiency, or a combination of significant deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that it is reasonably possible that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. While we are taking steps to remediate the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, we may not be successful in remediating such weaknesses which may undermine our ability to provide accurate, timely and reliable reports on our financial and operating results. Furthermore, if we remediate our current material weaknesses but identify new material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting investors may lose confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports and the market price of our common stock may be negatively affected. As a result of such failures, we could also become subject to investigations by the stock exchange on which our securities are listed, the SEC, or other regulatory authorities, and become subject to litigation from investors and stockholders, which could harm our reputation, financial condition or divert financial and management resources from our core business.
32
INFORMATION REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this prospectus are forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements in this prospectus are only predictions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In some cases, you can identify these forward-looking statements by terms such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “continue,” “could,” “depends,” “estimate,” “expects,” “intend,” “may,” “ongoing,” “plan,” “potential,” “predict,” “project,” “should,” “will,” “would” or the negative of those terms or other similar expressions, although not all forward-looking statements contain those words. We have based these forward-looking statements on our current expectations and projections about future events and trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, strategy, short- and long-term business operations and objectives, and financial needs. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements concerning the following:
| ● | our projected financial position and estimated cash burn rate; |
| ● | our estimates regarding expenses, future revenues and capital requirements; |
| ● | our ability to continue as a going concern; |
| ● | our need to raise substantial additional capital to fund our operation; |
| ● | the success, cost and timing of our clinical trials; |
| ● | our dependence on third parties in the conduct of our clinical trials; |
| ● | our ability to obtain the necessary regulatory approvals to market and commercialize our product candidates; |
| ● | the ultimate impact of the current COVID-19 pandemic, or any other health epidemic, on our business, our clinical trials, our research programs, healthcare systems or the global economy as a whole; |
| ● | the potential that results of pre-clinical and clinical trials indicate our current product candidates or any future product candidates we may seek to develop are unsafe or ineffective; |
| ● | the results of market research conducted by us or others; |
| ● | our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our current product candidates; |
| ● | our ability to protect our intellectual property rights and the potential for us to incur substantial costs from lawsuits to enforce or protect our intellectual property rights; |
| ● | the possibility that a third party may claim we or our third-party licensors have infringed, misappropriated or otherwise violated their intellectual property rights and that we may incur substantial costs and be required to devote substantial time defending against claims against us; |
| ● | our reliance on third-party suppliers and manufacturers; |
| ● | the success of competing therapies and products that are or become available; |
| ● | our ability to expand our organization to accommodate potential growth and our ability to retain and attract key personnel; |
| ● | the potential for us to incur substantial costs resulting from product liability lawsuits against us and the potential for these product liability lawsuits to cause us to limit our commercialization of our product candidates; |
33
| ● | market acceptance of our product candidates, the size and growth of the potential markets for our current product candidates and any future product candidates we may seek to develop, and our ability to serve those markets; and |
| ● | the successful development of our commercialization capabilities, including sales and marketing capabilities. |
These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including those described in “Risk Factors.” Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment. New risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances discussed in this prospectus may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements.
You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. Moreover, except as required by law, neither we nor any other person assumes responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason after the date of this prospectus to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations.
You should read this prospectus and the documents that we reference in this prospectus and have filed with the SEC as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part with the understanding that our actual future results, levels of activity, performance and events and circumstances may be materially different from what we expect.
This prospectus contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. We obtained the industry and market data in this prospectus from our own research as well as from industry and general publications, surveys and studies conducted by third parties. These data involve a number of assumptions and limitations and contains projections and estimates of the future performance of the industries in which we operate that are subject to a high degree of uncertainty, including those discussed in “Risk Factors.” We caution you not to give undue weight to such projections, assumptions and estimates. Further, industry and general publications, studies and surveys generally state that they have been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, although they do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of such information. While we believe that these publications, studies and surveys are reliable, we have not independently verified the data contained in them. In addition, while we believe that the results and estimates from our internal research are reliable, such results and estimates have not been verified by any independent source.
34
We estimate that the net proceeds from our issuance and sale of shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $ million, based on an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, we estimate that the net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $ million.
We intend to use the net proceeds from this offering to complete pre-clinical studies, including toxicology studies as recommended by the FDA, in connection with an NDA filing for Renazorb with the FDA. In addition, we plan to use proceeds to advance UNI-494 for pre-clinical development and the completion of all required studies for a potential IND filing in 2021. We also plan to use proceeds for general and corporate purposes, including, but not limited to, hiring additional management and conducting market research and other commercial planning.
We may also use a portion of the net proceeds to in-license, acquire or invest in complementary businesses or products, however, we have no current commitments or obligations to do so.
A $1.00 increase or decrease in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share would increase or decrease the net proceeds from this offering by approximately $ million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions.
This expected use of the net proceeds from this offering and our existing cash represents our intentions based upon our current plans, financial condition and business conditions. Predicting the cost necessary to develop product candidates can be difficult and the amounts and timing of our actual expenditures may vary significantly depending on numerous factors, including the progress of our development and commercialization efforts, the status of and results from clinical trials, any collaborations that we may enter into with third parties for our product candidates and any unforeseen cash needs. As a result, our management will retain broad discretion over the allocation of the net proceeds from this offering and our existing cash.
In the ordinary course of our business, we expect to from time to time evaluate the acquisition of, investment in or in-license of complementary products, technologies or businesses, and we could use a portion of the net proceeds from this offering for such activities. We currently do not have any agreements, arrangements or commitments with respect to any potential acquisition, investment or license.
Pending our use of the net proceeds from this offering, we intend to invest the net proceeds in a variety of capital preservation investments, including short-term, investment-grade, interest-bearing instruments and government securities.
We have never paid or declared any cash dividends on our common stock, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings to fund the development and expansion of our business. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon a number of factors, including our results of operations, financial condition, future prospects, contractual restrictions, restrictions imposed by applicable law and other factors our board of directors deems relevant.
35
The following table sets forth our cash and capitalization as of June 30, 2020:
| ● | on an actual basis; |
| ● | on a pro forma basis to give effect to the issuance in July 2020 and August 2020 of an aggregate principal amount of $800,000 of convertible promissory notes; and |
| ● | on a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to (i) our issuance and sale of shares of our common stock included in the shares of common stock being sold in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and our estimated offering expenses and (ii) the conversion of $800,000 of principal amount and accrued interest of outstanding notes into an aggregate of shares of common stock upon the closing of this offering based upon an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus. |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | Actual (unaudited) |
Pro
Forma (unaudited) (1) |
Pro
Forma, As Adjusted (2)(3) (unaudited) |
|||||||||
| Cash | $ | 1 | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Loan from stockholder | 762 | |||||||||||
| Stockholders’ deficit: | ||||||||||||
| Preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share; 10,000,000 shares authorized, no issued and outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued and outstanding | - | |||||||||||
| Common stock, par value $0.001 per share; 200,000,000 shares authorized, 36,534,840 shares issued and outstanding, actual; shares authorized, shares issued and outstanding, pro forma; shares authorized, shares issued and outstanding, pro forma as adjusted | 36 | |||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 3,001 | |||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (4,340 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit | (1,303 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total capitalization | $ | (541 | ) | $ | $ | |||||||
| (1) | On a pro forma basis to reflect the conversion of convertible notes in the aggregate principal amount of $800,000 issued in July and August 2020 into an aggregate of shares of common stock assuming an initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). |
| (2) | On a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to our issuance and sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
| (3) | A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by $ million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions. An increase (decrease) of shares in the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by $ million, assuming no change in the assumed initial public offering price per share and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions. |
The number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on 36,534,840 shares of our common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020, assumes no exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option and excludes:
| ● | 205,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2019 Stock Option Plan; |
| ● | 75,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan; and |
| ● | 3,220,000 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding options with a weighted average exercise price of $0.31. |
36
If you invest in our common stock, your ownership interest will be diluted to the extent of the difference between initial public offering price per share of our common stock and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock immediately after this offering.
As of June 30, 2020 we had a historical net tangible book (deficit) of $(1.3 million), or ($0.04) per share of common stock, based on 36,534,840 shares of common stock outstanding at June 30, 2020. Our historical net tangible book value per share is the amount of our total tangible assets less our total liabilities at June 30, 2020, divided by the number of shares of common stock outstanding at June 30, 2020.
After giving effect to the issuance in July 2020 and August 2020 of an aggregate principal amount of $800,000 of convertible notes, our pro forma net tangible book value (deficit) as of June 30, 2020 was $ , or $ per share of common stock.
After giving further effect to (i) the sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the estimated offering price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value at June 30, 2020 would have been $ million, or $ per share of common stock. This represents an immediate increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $ per share to existing stockholders and immediate dilution of $ per share to new investors purchasing shares of common stock in this offering and (ii) the conversion of $ of principal amount and accrued interest of outstanding notes into an aggregate of shares of common stock upon the closing of this offering based upon an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range listed on the cover page of this prospectus.
The following table illustrates this dilution on a per share basis:
| Assumed initial public offering price per share | $ | |||||||
| Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2020 | $ | |||||||
| Increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share attributable to new investors in this offering | ||||||||
| Pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share immediately after this offering | ||||||||
| Dilution per share to new investors in this offering | $ |
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value after this offering by $ per share and the dilution to new investors purchasing common stock in this offering by $ per share, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discount and commissions. An increase of shares in the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value after this offering by $ per share and decrease the dilution to new investors purchasing common stock in this offering by $ per share, assuming no change in the assumed initial public offering price per share and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions. A decrease of shares in the number of shares offered by us would decrease the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value after this offering by $ per share and increase the dilution to new investors purchasing common stock in this offering by $ per share, assuming no change in the assumed initial public offering price per share and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions.
If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after giving effect to the offering would be $ per share. This represents an increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $ per share to existing stockholders and dilution in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $ per share to new investors.
37
The number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on 36,534,840 shares of our common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020, assumes no exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option and excludes:
| ● | 205,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2019 Stock Option Plan; |
| ● | 75,000 shares of common stock available for future grants under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan; and |
| ● | 3,220,000 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding options with a weighted average exercise price of $0.31. |
The following table summarizes, on the pro forma as adjusted basis described above, the total number of shares of common stock purchased from us, the total consideration paid or to be paid, and the average price per share paid or to be paid by existing stockholders and by new investors in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, before deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us:
| Shares Purchased | Total Consideration | Average Price | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Percentage | Amount | Percentage | Per Share | ||||||||||||||||
| Existing stockholders | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
| New investors | $ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | |||||||||||||||||||
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the total consideration paid by new investors by $ million and, in the case of an increase, would increase the percentage of total consideration paid by new investors by percentage points and, in the case of a decrease, would decrease the percentage of total consideration paid by new investors by percentage points, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same. An increase (decrease) of shares in the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the total consideration paid by new investors by $ million and, in the case of an increase, would increase the percentage of total consideration paid by new investors by percentage points and, in the case of a decrease of shares, would decrease the percentage of total consideration paid by new investors by percentage points, assuming no change in the assumed initial public offering price.
The table above assumes no exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option in this offering. If the underwriters’ over-allotment option is exercised in full, the number of common shares held by new investors purchasing common stock in this offering would be increased to % of the total number of shares of common stock outstanding after this offering, and the number of shares held by existing stockholders would be reduced to % of the total number of shares of common stock outstanding after this offering.
To the extent that stock options or warrants are exercised or convertible debt is converted, we issue new stock options under our equity incentive plan, or we issue additional common stock in the future, there will be further dilution to investors participating in this offering. In addition, if we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of these securities could result in further dilution to our stockholders.
38
The following table sets forth our selected financial data as of the dates and for the periods indicated. We have derived the statements of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The statement of operations data for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 and the balance sheet data as of June 30, 2020 have been derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The following summary financial data should be read with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our financial statements and related notes and other information included elsewhere in this prospectus. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in the future.
Statement of Operations Data:
(in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Operating costs and expenses | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 795 | $ | 344 | $ | 329 | $ | 231 | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 1,168 | 608 | 349 | 550 | ||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 1,963 | 952 | 678 | 781 | ||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (2,165 | ) | $ | (1,120 | ) | $ | (682 | ) | $ | (899 | ) | ||||
| Net loss per common share – basic and diluted(1) | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | ||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted(1) | 34,915,828 | 29,010,940 | 36,433,549 | 34,155,838 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | See Note 11 to our financial statements for an explanation of the method used to compute basic and diluted net loss per share. |
Balance Sheet Data:
(in thousands)
| December 31, | June 30, 2020 | |||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | (unaudited) | ||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 15 | $ | 25 | $ | 1 | ||||||
| Working capital deficit | (884 | ) | (1,206 | ) | (1,284 | ) | ||||||
| Total assets | 19 | 29 | 28 | |||||||||
| Total liabilities | (903 | ) | (1,235 | ) | (1,331 | ) | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (3,658 | ) | (1,493 | ) | (4,340 | ) | ||||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit | (884 | ) | (1,206 | ) | (1,303 | ) | ||||||
39
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the related notes to those statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. In addition to historical financial information, the following discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results and timing of selected events may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of many factors, including those discussed under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. See “Information Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.” All amounts in this report are in U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted.
Overview
We are a biotechnology company dedicated to developing effective treatments for kidney diseases that have significant unmet medical need. Our development programs are focused on the development of two novel therapies: UNI 218, or Renazorb, for treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease, and UNI 494, for treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the gradual loss of kidney function that can get worse over time leading to lasting damage. As a company, our initial focus is developing drugs and getting them approved in the US, and then look to partner with the other global biopharmaceutical companies in the rest of the world. According to estimates by Center for Disease Control (CDC) in 2019, 37 million (approximately 15%) adults in the United States have CKD and, of these, approximately 2 million patients with CKD stage 3-5, and around 400 thousand patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have hyperphosphatemia. In the European Union (EU), around 20 million (approximately 8%) adults have CKD, more than 1 million CKD stage 3-5 patients, and approximately 180 thousand patients with ESRD have hyperphosphatemia. The number of patients with ESRD is increasing steadily and is projected to reach between 971,000 and 1,259,000 in 2030.
AKI is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage (within the first 90 days of injury). After 90 days, the patient is considered to have progressed into CKD. AKI affects over 2 million US patients and costs the healthcare system over $9 billion per year. AKI kills more than 300,000 patients per year in the US and is caused by multiple etiologies.
Our business model is to license technologies and drugs and pursue development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of those products in global markets. Many biotechnology companies utilize similar strategies of in-licensing and then developing and commercializing drugs. We believe, however, that our management team’s broad network, expertise in the biopharmaceutical industry, and past successful track record gives us an advantage in identifying and bringing these assets into the Company at an attractive price with limited upfront cost.
Since our formation we have devoted substantially all of our resources to developing our product candidates. We have incurred significant operating losses to date. Our net losses were $2.2 million and $1.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and $0.7 million and $0.9 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively. As of June 30, 2020, we had an accumulated deficit of $4.3 million. We expect that our operating expenses will increase significantly as we advance our product candidates through pre-clinical and clinical development, seek regulatory approval, and prepare for and, if approved, proceed to commercialization; acquire, discover, validate and develop additional product candidates; obtain, maintain, protect and enforce our intellectual property portfolio; and hire additional personnel. In addition, upon the completion of this offering, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company.
We have funded our operations primarily from the sale and issuance of common stock, convertible notes and from a loan, including cash and deferred salary from our Chief Executive Officer and majority stockholder. We believe that our current available cash will not be sufficient to fund our planned expenditures and meet our obligations by the end of the third quarter of 2020 and for at least the one-year period following the date upon which our financial statements were issued.
Our ability to generate product revenue will depend on the successful development, regulatory approval and eventual commercialization of our current product candidates and future product candidates. Until such time as we can generate significant revenue from product sales, if ever, we expect to finance our operations through private or public equity or debt financings, collaborative or other arrangements with corporate sources, or through other sources of financing. Adequate funding may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we fail to raise capital or enter into agreements to raise capital as and when needed, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development and commercialization of our current product candidates and future product candidates.
40
We plan to continue to use third-party service providers, including contract manufacturing organization, to carry out our pre-clinical and clinical development and to manufacture and supply the materials to be used during the development and commercialization of our product candidates.
Recent Developments
In July and August 2020, we issued a series of convertible promissory notes in the aggregate principal amount of $800,000. These notes bear interest at a rate of 12% per annum and mature on the one year anniversary of their respective date of issuance. These notes automatically convert into common stock upon consummation of this offering.
Renazorb Purchase Agreement
On September 20, 2018, we entered into an Assignment and Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Renazorb Purchase Agreement”) with Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Spectrum”), pursuant to which we purchased certain assets from Spectrum, including Spectrum’s right, title, interest in and intellectual property related to Renazorb RZB 012, also known as RENALAN™ (“Renalan”) and RZB 014, also known as SPI 014 (“SPI” and together with Renalan, the “Compounds”). Pursuant to the Renazorb Purchase Agreement, in consideration for the Compounds, we issued 1,348,750 shares of common stock to Spectrum.
Additionally, the Renazorb Purchase Agreement provides that until the earlier of (i) 36 months from the first date on which our stock trades on a public market, or (ii) the date upon which we attain a public market capitalization of $50,000,000 or greater, we are required to issue additional shares of our common stock as may be needed to ensure Spectrum maintains a 4% ownership of our issued and outstanding common stock on a fully-diluted basis. Fully-diluted shares of common stock for purposes of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement assumes conversion of any security convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for common stock or any combination thereof, including any common stock reserved for issuance under a stock option plan, restricted stock plan, or other equity incentive plan approved by the Board of Directors of the Company immediately following the issuance of additional shares of our common stock (but prior to the issuance of any additional shares of common stock to Spectrum). We are also required to pay Spectrum 40% of all of our sublicense income for any sublicense granted to certain sublicensees during the first 12 months after the Closing Date (as that term is defined in the Renazorb Purchase Agreement) and 20% of all other sublicense income. Our payment obligations to Spectrum will expire on the twentieth (20th) anniversary of the Closing Date of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement.
Components of Results of Operations
Operating Expenses
Research and Development Expenses
Substantially all of our research and development expenses consist of expenses incurred in connection with the development of our product candidates. These expenses include fees paid to third parties to conduct certain research and development activities on our behalf, consulting costs, costs for laboratory supplies, product acquisition and license costs, certain payroll and personnel-related expenses, including salaries and bonuses, employee benefit costs and stock-based compensation expenses for our research and product development employees and allocated overheads, including information technology costs and utilities and expenses for issuance of shares pursuant to the anti-dilution clause in the purchase of in process research and development technology (“IPR&D”). We expense both internal and external research and development expenses as they are incurred.
We do not allocate our costs by product candidate, as a significant amount of research and development expenses include internal costs, such as payroll and other personnel expenses, laboratory supplies and allocated overhead, and external costs, such as fees paid to third parties to conduct research and development activities on our behalf, are not tracked by product candidate.
We expect our research and development expenses to increase substantially for at least the next few years, as we seek to initiate additional clinical trials for our product candidates, complete our clinical programs, pursue regulatory approval of our product candidates and prepare for the possible commercialization of such product candidates. Predicting the timing or cost to complete our clinical programs or validation of our commercial manufacturing and supply processes is difficult and delays may occur because of many factors, including factors outside of our control. For example, if the FDA or other regulatory authorities were to require us to conduct clinical trials beyond those that we currently anticipate, we could be required to expend significant additional financial resources and time on the completion of clinical development. Furthermore, we are unable to predict when or if our product candidates will receive regulatory approval with any certainty.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist principally of payroll and personnel expenses, including salaries and bonuses, benefits and stock-based compensation expenses, professional fees for legal, consulting, accounting and tax services, including information technology costs and utilities, and other general operating expenses not otherwise classified as research and development expenses, as well as services incurred by a services agreement with Globavir Biosciences Inc., a related party.
We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase as a result of increased personnel costs, expanded infrastructure and higher consulting, legal and accounting services costs associated with complying with the applicable stock exchange and the SEC requirements, investor relations costs and director and officer insurance premiums associated with being a public company.
41
Interest Expense
Interest expense consists primarily of interest expense related to convertible notes.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Six Months Ended June 30, 2019 and 2020
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the periods indicated:
| Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) (unaudited) | (in thousands) (unaudited) | (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 231 | $ | 329 | $ | 98 | 42 | % | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 550 | 349 | (201 | ) | (37 | %) | ||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 781 | 678 | (103 | ) | (13 | %) | ||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (781 | ) | (678 | ) | 103 | 13 | % | |||||||||
| Other income (expenses): | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (118 | ) | (4 | ) | 114 | (97 | %) | |||||||||
| Total other income (expenses) | (118 | ) | (4 | ) | 114 | (97 | %) | |||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (899 | ) | $ | (682 | ) | $ | 217 | (24 | %) | ||||||
42
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $98,000, or 42%, from the six months ended June 30, 2019 to the six months ended June 30, 2020 primarily due our direct spending in payroll and the expense for issuance of shares pursuant to the anti-dilution clause in the purchase of IPR&D technology, partially offset by the increase in our consulting expenses.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses decreased by $201,000, or 37%, from the six months ended June 30, 2019 to the six months ended June 30, 2020. The decrease in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to the decrease in our service agreement fees with Globavir of $240,000, offset by increases in salaries, bonuses and stock-based compensation for a total of $127,000.
Other income (expenses)
Other expenses decreased by $114,000, or 97%, from the six months ended June 30, 2019 to the six months ended June 30, 2020. The decrease in other expenses was primarily due to a decrease in interest expense driven by the conversion of the convertible notes, which occurred in July 2019.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2018 and 2019
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the periods indicated:
| Years Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | (in thousands) | (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 344 | $ | 795 | $ | 451 | 131 | % | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 608 | 1,168 | 560 | 92 | % | |||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 952 | 1,963 | 1,011 | 106 | % | |||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (952 | ) | (1,963 | ) | (1,011 | ) | (106 | %) | ||||||||
| Other income (expenses): | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (168 | ) | (139 | ) | 29 | (17 | %) | |||||||||
| Other Expenses - Loss on debt conversion | - | (63 | ) | (63 | ) | 100 | % | |||||||||
| Total other income (expenses) | (168 | ) | (202 | ) | (34 | ) | 20 | % | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,120 | ) | $ | (2,165 | ) | $ | (1,045 | ) | 93 | % | |||||
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $451,000, or 131%, from the year ended December 31, 2018 to the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase in research and development expenses was primarily due to increase in our consultant expenses, equal to $383,000 and $187,000 for expenses for issuance of shares as part of the anti-dilution clause in the agreement to purchase IPR&D technology.
43
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $560,000, or 92%, from the year ended December 31, 2018 to the year ended December 31, 2019 primarily due to increase in salaries for $121,000, legal and accounting consulting for $148,000 and increase in travel for $77,000.
Other income (expenses)
Other income (expenses) increased by $34,000, or 20% from the year ended December 31, 2018 to the year ended December 31, 2019. The movement in other expenses was due to the loss on conversion of the convertible notes, which occurred in July 2019 and the reduced interest expenses on the convertible notes.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources of Liquidity
Since our formation through June 30, 2020, we have funded our operations with the sale of common stock, convertible notes and from a loan from our Chief Executive Officer and principal stockholder. In the first six months of 2020 we raised additional funds through private placements by issuing common stock for $142,000. As of June 30, 2020, we had cash of less than $1,000. In July and August 2020 we raised $800,000 by issuing convertible notes to investors. After the utilization of these funds, cash as of August 2020 was equal to $70,000.
Future Funding Requirements
We have incurred net losses since our inception. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had net losses of $2.2 million and $1.1 million, respectively, and we expect to incur substantial additional losses in future periods. As of June 30, 2020, we had an accumulated deficit of $4.3 million.
We expect to continue incurring losses for the foreseeable future and are required to raise additional capital to complete our clinical trials, pursue product development initiatives and penetrate markets for the sale of our products. We believe that we will continue to have access to capital resources through possible private equity offerings, debt financings, corporate collaborations or other means. There can be no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional financing on terms acceptable to us, on a timely basis or at all. If we are unable to secure additional capital, we may be required to curtail any clinical trials and development of new or existing products and take additional measures to reduce expenses in order to conserve our cash in amounts sufficient to sustain operations and meet our obligations. We believe that we will need funding by the end of the third quarter 2020 to continue operations, satisfy its obligations and fund the future expenditures that will be required to conduct the clinical and regulatory work to develop our product candidates. There is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern for one year after the date that these financial statements are available to be issued, which is not alleviated by our plans. The financial statements do not reflect any adjustments relating to the recoverability and reclassification of assets and liabilities that might be necessary from the outcome of this uncertainty.
We anticipate that we will need to raise substantial additional capital, the requirements for which will depend on many factors, including:
| ● | the scope, timing, rate of progress and costs of our drug discovery efforts, pre-clinical development activities, laboratory testing and clinical trials for our current product candidates and future product candidates; |
| ● | the number and scope of clinical programs we decide to pursue; |
| ● | the cost, timing and outcome of preparing for and undergoing regulatory review of our current product candidates and future product candidates; |
| ● | the scope and costs of development and commercial manufacturing activities; |
| ● | the cost and timing associated with commercializing our current product candidates and future product candidates, if they receive marketing approval; |
| ● | the extent to which we acquire or in-license other product candidates and technologies; |
| ● | the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending intellectual property-related claims; |
44
| ● | our ability to establish and maintain collaborations on favorable terms, if at all; |
| ● | our efforts to enhance operational systems and our ability to attract, hire and retain qualified personnel, including personnel to support the development of our current product candidates and future product candidates and, ultimately, the sale of our products, following FDA approval; |
| ● | our implementation of operational, financial and management systems; and |
| ● | the costs associated with being a public company. |
A change in the outcome of any of these or other variables with respect to the development of any of our current product candidates or future product candidates could significantly change the costs and timing associated with the development of that product candidate. Furthermore, our operating plans may change in the future, and we will continue to require additional capital to meet operational needs and capital requirements associated with such operating plans. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience dilution. Any future debt financing into which we enter may impose upon us additional covenants that restrict our operations, including limitations on our ability to incur liens or additional debt, pay dividends, repurchase our common stock, make certain investments or engage in certain merger, consolidation or asset sale transactions. Any debt financing or additional equity that we raise may contain terms that are not favorable to us or our stockholders.
Adequate funding may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and our ability to pursue our business strategies. If we are unable to raise additional funds when needed, we may be required to delay, reduce, or terminate some or all of our development programs and clinical trials or we may also be required to sell or license to others rights to our product candidates in certain territories or indications that we would prefer to develop and commercialize ourselves. If we are required to enter into collaborations and other arrangements to supplement our funds, we may have to give up certain rights that limit our ability to develop and commercialize our product candidates or may have other terms that are not favorable to us or our stockholders, which could materially affect our business and financial condition.
Related Party Payable
We entered into a Service Agreement on July 1, 2017, as amended on April 6, 2020 (“Service Agreement”), with Globavir Biosciences, Inc. (“Globavir”). Our Chief Executive Officer is also the Chief Executive Officer of Globavir. Pursuant to the Service Agreement, we receive administrative, consulting services, shared office space and other services in connection with Unicycive’s drug development program. Pursuant to the Service Agreement, we paid Globavir $50,000 per month through December 31, 2019 and $10,000 per month commencing on January 1, 2020. As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and 2018, $103,000, $108,000 and $111,000, respectively, is payable to Globavir in service fees. Service fee expenses were $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 and $0.1 million and $0.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and were recorded as expense in general and administrative expenses in the statements of operations.
Convertible Notes
In 2018, we raised $550,000 from the issuance of twelve convertible promissory notes (Notes). These Notes bear interest at 10% per annum which was payable at maturity. The Notes principal and interest were due and payable on written demand by the majority of the Note holders on the two-year anniversary of the first Note issued. The first note was issued on October 5, 2017 and, accordingly, all Notes would have matured on October 5, 2019.
In the event we consummated an equity financing with an aggregate sales price of not less than $500,000, then the aggregate outstanding principal and unpaid interest would automatically convert into shares of our common stock. The per share price of the conversion would be equal to 75% of the price per share paid by the cash purchasers of the capital stock sold in the financing.
45
We have accounted for the Notes as stock-settled debt and accreted the carrying amount of the Notes to the settlement amount through maturity.
On July 31, 2019, all Notes were extinguished and converted into 1,159,065 shares of common stock upon the consummation of a 2019 equity financing in excess of $500,000, and recognized a loss on conversion equal to $63,000.
Interest expense was $139,000 and $168,000 for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and $4,000 and $118,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and June 30, 2019, respectively. Accrued interest of $0, $43,000 and $56,000 was included with the principal amount on the balance sheets within Convertible notes as of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Summary of Cash Flows
The following table sets forth the primary sources and uses of cash for each of the periods presented below:
| Years Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by: | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating activities | $ | (775 | ) | $ | (1,176 | ) | $ | (625 | ) | $ | (215 | ) | ||||
| Financing activities | 800 | 1,166 | 601 | 201 | ||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash | $ | 25 | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (24 | ) | $ | (14 | ) | |||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $1.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Cash used in operating activities resulted from a net loss of $2.2 million primarily driven by the use of funds in our operations to develop our product candidates as well as the deferral of the chief executive officer compensation of $0.3 million and an increase in accounts payable of $0.3 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. Cash used in operating activities was primarily due to the use of funds in our operations to develop our product candidates, resulting from a net loss of $1.1 million as well as the deferral of the chief executive officer compensation of $0.2 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $0.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020. Cash used in operating activities was primarily due to a net loss of $0.6 million, primarily driven by the deferral of the chief executive officer compensation of $0.2 million and by increase in accounts payable of $0.1 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $0.6 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019. Cash used in operating activities was primarily due to a net loss of $0.9 million, primarily driven by the deferral of the chief executive officer compensation of $0.2 million.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $1.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from the issuance of common stock to investors.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 which consisted of $0.5 million from issuance of convertible notes, as well as $0.2 million from the issuance of common stock to investors.
46
Net cash provided by financing activities was $0.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 mainly related to the issuance of common stock to investors for $0.1 million.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $0.6 million for the year ended June 30, 2019 primarily driven by the issuance of common stock to investors for $0.6 million.
Critical Accounting Policies, Significant Judgments and Use of Estimates
Our financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported expenses incurred during the reporting periods. Our estimates are based on our historical experience and on various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. We consider our critical accounting policies and estimates to be related to research and development, stock-based compensation and common stock valuations. There have been no material changes to our critical accounting policies and estimates during the six months ended June 30, 2020 from those used for the year ended December 31, 2019. The below policies are listed to provide a list of our policies for the most significant critical policies.
Research and Development
We expense costs when incurred related to the research and development associated with the design, development and testing of product candidates, as well as acquisition of product candidates or compounds. Research and development expenses include fees paid to third parties to conduct certain research and development activities on our behalf, consulting costs, costs for laboratory supplies, product acquisition and license costs, certain payroll and personnel-related expenses, including salaries and bonuses, employee benefit costs and stock-based compensation expenses for our research and product development employees and allocated overheads, including information technology costs and utilities and expenses for issuance of shares pursuant to anti-dilution clause in the purchase of IPR&D technology. We expense both internal and external research and development expenses as they are incurred.
Stock-Based Compensation
We account for stock-based compensation for all share-based payments made to employees and non-employees by estimating the fair value on the date of grant and recognizing compensation expense over the requisite service period on a straight-line basis. We recognize forfeitures related to stock-based compensation as they occur. We estimate the fair value of stock options using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The Black-Scholes model requires the input of subjective assumptions, including expected common stock volatility, expected dividend yield, expected term, risk-free interest rate, and the estimated fair value of the underlying common stock on the date of grant.
Common Stock Valuations
We are required to periodically estimate the fair value of common stock when issuing stock options and computing their estimated stock-based compensation expense. The fair value of common stock was determined on a periodic basis, with the assistance of an independent third-party valuation expert. The assumptions underlying these valuations represented management’s best estimates, which involved inherent uncertainties and the application of significant levels of management judgment.
In order to determine the fair value, we considered, among other things, contemporaneous transactions involving the sale of our common stock to unrelated third parties; the lack of marketability of our common stock and the market performance of comparable publicly traded companies.
Internal Controls and Procedures
In connection with the preparation of our financial statements, we concluded that there were material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. A material weakness is a significant deficiency, or a combination of significant deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that it is reasonably possible that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The material weaknesses that we identified related to our finance department not having adequate staff to process, in a timely manner, complex, non-routine transactions, as well as not having adequate resources to perform such activities with duties properly segregated between processing and review. Furthermore, our policies, particularly related to approving related party transactions, have not been documented.
47
The lack of adequate staffing levels resulted in insufficient time spent on review and approval of certain information used to prepare our financial statements and the maintenance of effective controls to adequately monitor and review significant transactions for financial statement completeness and accuracy. These control deficiencies, although varying in severity, contributed to the material weaknesses in the control environment. If one or more material weaknesses persist or if we fail to establish and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting, our ability to accurately report our financial results could be adversely affected.
Management is taking steps to remediate the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, including the identification of gaps in our skill set and expertise of the staff required to meet the financial reporting requirements of a public company. To address the issues, we have hired financial consultants and plan to hire additional senior accounting personnel upon completion of this offering.
We will be required, pursuant to Section 404(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, to furnish a report by management on, among other things, the effectiveness of our internal control once we become a public company. This assessment will need to include disclosure of any material weaknesses identified by management over our internal control over financial reporting. However, our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act until we are no longer an emerging growth company and a smaller reporting company.
We are in the very early stages of the costly and challenging process of compiling the system and processing documentation necessary to perform the evaluation needed to comply with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We may not be able to complete our evaluation, testing or any required remediation in a timely fashion. During the evaluation and testing process, if we identify one or more material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, we will be unable to conclude that our internal controls are designed and operating effectively.
JOBS Act Accounting Election
On April 5, 2012, the JOBS Act was enacted. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an “emerging growth company” can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies.
We have chosen to take advantage of the extended transition periods available to emerging growth companies under the JOBS Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies provided under the JOBS Act. As a result, our financial statements may not be comparable to those of companies that comply with public company effective dates for complying with new or revised accounting standards.
Subject to certain conditions set forth in the JOBS Act, as an “emerging growth company,” we intend to rely on certain of exemptions, including, without limitation, (i) providing an auditor’s attestation report on our system of internal controls over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and (ii) complying with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements, known as the auditor discussion and analysis. We will remain an “emerging growth company” until the earliest of (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1.07 billion or more; (ii) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of this offering; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the SEC.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See the section titled “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Recent Accounting Pronouncements” in Note 2 to our financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for additional information.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined under SEC rules.
48
Overview
We are a biotechnology company dedicated to developing effective treatments for unmet medical conditions. Currently, two of our programs are focused on kidney diseases that have significant unmet medical need. As we grow our Company and build our team, we intend to be focused on identifying medical conditions within and outside kidney disease. Our current development programs are focused on the development of two novel therapies: UNI 218, or Renazorb, for treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease, and UNI 494, for treatment of acute kidney injury (AKI).
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the gradual loss of kidney function that can get worse over time leading to lasting damage. As a company, our initial focus is developing drugs and getting them approved in the US, and then look to partner with the other global biopharmaceutical companies in the rest of the world. According to estimates by Center for Disease Control (CDC) in 2019, 37 million (approximately 15%) adults in the United States have CKD and, of these, approximately 2 million patients with CKD stage 3-5, and around 400 thousand patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have hyperphosphatemia. In the European Union (EU), around 20 million (approximately 8%) adults have CKD, more than 1 million CKD stage 3-5 patients, and approximately 180 thousand patients with ESRD have hyperphosphatemia. The number of patients with ESRD is increasing steadily and is projected to reach between 971,000 and 1,259,000 in 2030.
AKI is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage (within the first 90 days of injury). After 90 days, the patient is considered to have progressed into CKD. AKI affects over 2 million US patients, and costs the healthcare system over $9 billion per year. AKI kills more than 300,000 patients per year in the US and is caused by multiple etiologies.
Our Strategy
Our business model is to license technologies and drugs and pursue development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of those products in global markets. Many biotechnology companies utilize similar strategies of in-licensing and then developing and commercializing drugs. We believe, however, that our management team’s broad network, expertise in the biopharmaceutical industry, and past successful track record gives us an advantage in identifying and bringing these assets into the Company at an attractive price with limited upfront cost.
Key elements of our strategy are to:
| ● | Develop and commercialize Renazorb; |
| ● | Develop UNI 494 and other licensed products and advance them at least to the stage of clinical proof-of-concept; and |
| ● | Build a core, in-house team of experts that can create long-term value for our investors and for patients. |
Product Candidates
Our proprietary pipeline is comprised of our two product candidates – UNI 218 (Renazorb) and UNI 494 – which are described below.
UNI 218 (Renazorb)
Disease overview: hyperphosphatemia
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the gradual loss of kidney function that can get worse over time leading to lasting damage. The stages of chronic kidney disease are shown below in table 1.
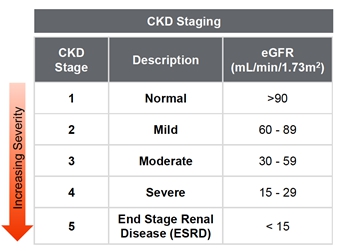
Table 1: adapted from The Renal Association (https://renal.org/information-resources/the-uk-eckd-guide/ckd-stages/)
eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate (a measure of kidney function)
49
Complications of CKD include electrolyte imbalances, fluid build-up, anemia, bone disease, and heart disease. Hyperphosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which untreated elevated phosphate levels in the blood lead to cardiovascular complications and vascular calcification. According to Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcome (KDIGO) guidelines, hyperphosphatemia is defined as an abnormally high serum phosphate concentration >1.46 mmol/L. In healthy people, phosphate levels are maintained as phosphate is absorbed from food and excreted in the urine and feces. In people with CKD, not enough phosphate is excreted, leading to elevated levels of phosphate in the blood. In CKD, hyperphosphatemia is caused by a chronic dysregulation of phosphates as a result of progressive kidney damage. According to a 2009 paper authored by Covic A. hyperphosphatemia is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, metabolic bone disease, and all-cause mortality. According to a study completed by Palmer in 2011, it is estimated that all-cause mortality is increased by 18% for every 1 mg/dL increase in serum phosphate concentration. Hyperphosphatemia is a major cause of morbidity in CKD patients, increasing the economic and clinical burden on patients and the health system.
According to Lederer in 2018, hyperphosphatemia occurs in at least 70% of patients with advanced (stage 5) CKD, which equates to approximately 500,000 patients. According to the 2019 National Chronic Kidney Disease Fact Sheet (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019), it is estimated that 15% of US adults (i.e. approximately 37 million people) in the US are estimated to have CKD. Furthermore, in a paper published by McCullough in 2019, the number of patients in the US with ESRD is increasing steadily and is projected to reach between 971,000 and 1,259,000 in 2030.
Current treatment of hyperphosphatemia
The treatment goal for patients with hyperphosphatemia is focused on controlling the level of phosphate in the body. Current Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes, or KDIGO, guidelines recommend three main strategies for managing hyperphosphatemia: diet restrictions, phosphate binders, and dialysis, as shown in figure 1 below.
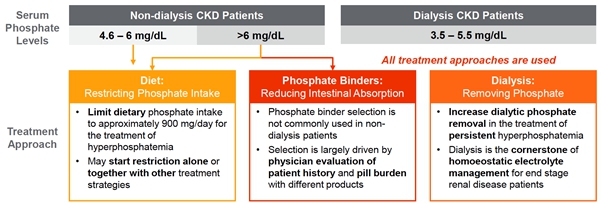
Figure 1: KDIGO guidelines recommend 3 main strategies
50
While KDIGO guidelines support the treatment of hyperphosphatemia with phosphate binders in patients with CKD, they do not recommend one agent over another. Examples of different types of phosphate binders are shown in figure 2 below.

Figure 2: Phosphate Binders
This means that physicians prescribe their medication of choice, usually based on clinical and patient factors. In non-dialysis CKD patients, hyperphosphatemia is most commonly treated with non-calcium phosphate binders.
The Unmet Medical Need for Treatment of Hyperphosphatemia
The mechanism of action and what we believe to be the advantages and disadvantages of various phosphate binders is shown below.
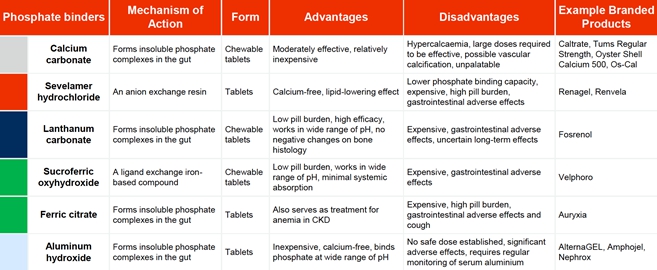
Table 2: Adapted from Covic and Rastogi, 2013.
In 2005, Unruh, ML published a paper that showed poor adherence to treatment is common in patients with ESRD and has been associated with an increased risk of mortality. In addition, poor adherence to phosphate binder therapy has been associated with failure to adequately control serum phosphorus concentrations as shown in a publication by Arenas, MD and others in 2010. Results from a study of 233 patients on maintenance dialysis from three different units in the US showed that patients took a mean of 11 ± 4 medications with a median daily pill intake of 19 as shown by Chiu, YW in 2009. Phosphate binders accounted for 49 ± 19% of the total pill burden, with a median pill count of 9. Only 38% of patients in this study were adherent to their prescribed phosphate binder therapy and adherence decreased significantly with increased pill count also shown by Chiu, YW in 2009 publication.
51
Potential strategies to improve adherence to phosphate binders in patients with ESRD include: (i) a reduction in pill size and burden, (ii) improvement of palatability (taste), and (iii) a reduction in associated adverse effects as published in a study by Covic and Rastogi in 2013.
Therefore, we believe there is a high, unmet need for better phosphate binders that have low solubility, high and rapid phosphate binding, alongside a reduced pill burden for better medication compliance.
Background on Renazorb
We believe Renazorb (lanthanum dioxycarbonate) is a potent and selective second-generation phosphate binding agent utilizing proprietary nanoparticle technology. The drug is being developed for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with ESRD or in those with early stages of CKD. We have completed a clinical trial studying Renazorb in 32 healthy volunteers. In this study it was concluded that Renazorb was efficacious, demonstrating that dietary phosphorus is bound by lanthanum dioxycarbonate and excreted in the feces, reducing the burden of phosphorus to the kidneys. Renazorb was minimally absorbed to the systemic circulation and was safe and well-tolerated at doses up to 6000 mg/day.
Renazorb Purchase Agreement
On September 20, 2018, we entered into an Assignment and Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Renazorb Purchase Agreement”) with Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Spectrum”), pursuant to which we purchased certain assets from Spectrum, including Spectrum’s right, title, interest in and intellectual property related to Renazorb RZB 012, also known as RENALAN™ (“Renalan”) and RZB 014, also known as SPI 014 (“SPI” and together with Renalan, the “Compounds”). Pursuant to the Renazorb Purchase Agreement, in consideration for the Compounds, we issued 1,348,750 shares of common stock to Spectrum.
Additionally, the Renazorb Purchase Agreement provides that until the earlier of (i) 36 months from the first date on which our stock trades on a public market, or (ii) the date upon which we attain a public market capitalization of $50,000,000 or greater, we are required to issue additional shares of our common stock as may be needed to ensure Spectrum maintains a 4% ownership of our issued and outstanding common stock on a fully-diluted basis. Fully-diluted shares of common stock for purposes of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement assumes conversion of any security convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for common stock or any combination thereof, including any common stock reserved for issuance under a stock option plan, restricted stock plan, or other equity incentive plan approved by the Board of Directors of the Company immediately following the issuance of additional shares of our common stock (but prior to the issuance of any additional shares of common stock to Spectrum ). We are also required to pay Spectrum 40% of all of our sublicense income for any sublicense granted to certain sublicensees during the first 12 months after the Closing Date (as that term is defined in the Renazorb Purchase Agreement) and 20% of all other sublicense income. Our payment obligations to Spectrum will expire on the twentieth (20th) anniversary of the Closing Date of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement.
Mechanism of Action
Renazorb binds to phosphates and forms an insoluble lanthanum phosphate complex which is then excreted via the feces. This results in reduction of serum phosphate levels.
52
In an in vitro test, Renazorb exhibited faster phosphate binding kinetics than lanthanum carbonates (such as Fosrenol) (see figure below). In addition, it has a lower water solubility at various pH values than the corresponding lanthanum carbonates and also produces less carbon dioxide than Fosrenol when binding with phosphate.

Source: Company Data
Blue line = Renazorb (phosphate binding capacity 338 mg/g)
Pink line = Fosrenol (phosphate binding capacity 217 mg/g)
Animal studies to evaluate the potential efficacy of Renazorb versus lanthanum carbonate (Fosrenol) and sevelamer hydrochloride in rats and dogs demonstrated significant lowering of phosphate levels in both urine and serum. Low levels of lanthanum were observed in serum which were comparable for Renazorb and Fosrenol.
The chemical design of Renazorb allows for smaller tablet size and pill burden versus currently available alternatives of phosphate binders. In addition, it has the potential to be effective with a dosing regimen of only one tablet per meal. The tablet is designed to disintegrate in the stomach after swallowing and disperse the product in a short period of time at a pH ≥3.0.
Clinical Trial Experience
Renazorb was studied in a clinical trial in 32 healthy volunteers. The trial investigated the tolerability and phosphate binding capacity of Renazorb compared with placebo. In this study, it was concluded that Renazorb was efficacious, demonstrating that dietary phosphorus is bound by lanthanum dioxycarbonate and excreted in the feces, reducing the burden of phosphorus to the kidneys. Renazorb was minimally absorbed to the systemic circulation and was safe and well-tolerated at doses up to 6000 mg/day. The doses resulted in no serious adverse events (SAEs) and all patients completed the study.
Potential advantages of Renazorb
Renazorb represents a potential effective phosphate binder for hyperphosphatemia in ESRD and is intended to be administered as a tablet that will be swallowed whole at mealtimes. CKD patients typically have co-morbilities, which often requires them to be on strict pill schedules. Current phosphate binder products such as Fosrenol, Renagel/Renvela and Phoslo involve patients needing to take multiple and/or larger pills (on average, 9 pills/day), in addition to other, non-phosphate binder pills they sometimes need to take, resulting in poor adherence to the prescribed drug therapy (Figure 4 below). In this regard, we believe that the combined effect of smaller pill size, lower pill burden and lack of unpleasant taste with Renazorb versus currently available phosphate binders is likely to lead to improved patient compliance and more effective disease management.
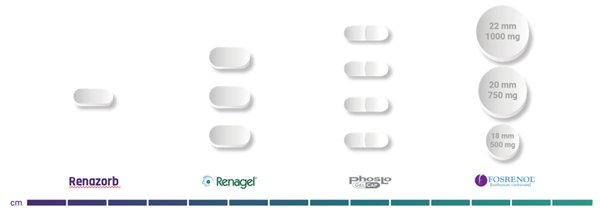
Figure 4: Size comparisons of different phosphate binders
53
Market Potential
According to a study conducted by Syneos Health for the Company, based on the market data the total hyperphosphatemia market is estimated to be approximately $1.05 billion in 2018. According to Shire Pharmaceuticals, global revenues for Fosrenol which holds approximately 24% of market share exceeded $400 million in 2012 based on reports by Shire (see figure 5 below).
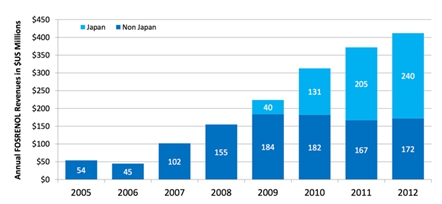
Figure 5: Annual Fosrenol revenue forecast 2005-2012
Based on the available data on overall efficacy, safety and compliance, we believe that Renazorb is well-positioned to become a product of choice in the multi-billion phosphate binder market.
Regulatory Strategy for Renazorb
We are pursuing a 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for the potential US approval of Renazorb. With this strategy, we believe we would be able to leverage existing preclinical and clinical data for an existing lanthanum-based product (Fosrenol) to reduce the overall scope of the required clinical development program. We have met with and discussed this strategy with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, and we believe that pursuit of such a strategy will require the following studies for Renazorb:
| ● | in vitro comparability of phosphate binding versus lanthanum carbonate |
| ● | 6-month oral toxicity study in one animal species |
| ● | Standard information on manufacturability and commercial supply of product |
We have plans in place to fulfill each of these requirements and we believe that we can complete these studies by mid-2021. It is our intention to hold additional discussions with FDA in early 2021, including a Pre-NDA meeting, to confirm their concurrence with our dataset and NDA submission strategy.
During our previous interaction the FDA indicated that some amount of clinical experience will be needed to assess safety and tolerability of Renazorb, a request which we believe is satisfied by our existing Phase 1 clinical safety and tolerability study. We believe that those data along with the planned phosphate binding comparability study will enable a 505(b)(2) NDA filing approach for Renazorb. Following our next FDA interaction in early 2021, in the event that FDA requests additional clinical data, we would intend to fulfill this request with a single open-label 8-week safety, tolerability, and efficacy dose-ranging study of Renazorb in hyperphosphatemic patients on hemodialysis, which we believe could be completed by the second half of 2022.
54
UNI 494
Disease overview: acute kidney injury (AKI)
Acute kidney injury (AKI) — a loose collection of syndromes characterized by a sudden decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) — is estimated to affect 2–3 people per 1,000 individuals in the USA as showin in a study published in Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) by Kellum, JA in 2012. AKI is a serious condition characterized by a sudden decline in kidney function that can lead to kidney failure. AKI, Acute Kidney Disease (AKD) and CKD can form a continuum (see figure below) whereby initial kidney injury can lead to persistent renal injury, eventually leading to CKD as shown in a 2017 study published by Chawla, LS in Nature Reviews Nephrology.
AKI is defined as an abrupt decrease in kidney function occurring over 7 days or less, whereas CKD is defined by the persistence of kidney disease for a period of >90 days. AKD describes acute or subacute damage and/or loss of kidney function for a duration of between 7 and 90 days after exposure to an AKI initiating event (Figure 6).
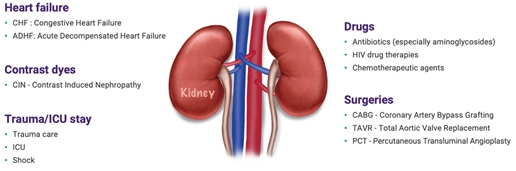
Figure 6: Adapted from Nature Review-Nephrology; Chawla LS et al. 2017
In the United States, approximately 1% of patients admitted to hospitals have AKI at the time of admission. The estimated incidence rate of AKI during hospitalization is 2-5%. AKI develops within 30 days postoperatively in approximately 1% of general surgery cases as shown in a paper by Kheterpal S in Journal Anaesthesiology and arises in up to 67% of intensive care unit (ICU) patients as published in a paper by Goldberg R, 2008 in Advances in Chronic Kidney Diseases. In recipients of solitary kidney transplants, 21% developed AKI within the first 6 months after transplantation as shown in a paper published by Panek R in 2016 in Clinical Transplantation.
In a prospective national cohort study that used an electronic AKI alert, the incidence of AKI was 577 per 100,000 population. Community-acquired AKI accounted for 49.3% of all incidence episodes, and 42% occurred in the context of preexisting chronic kidney disease. The 90-day mortality rate was 25.6%, and 23.7% of episodes progressed to a higher AKI stage as published by Holmes J et al. in Clinical Journal of American Society of Nephrology in 2016.
The KDIGO criteria for AKI are shown below in table 3. According to a study by Susantitaphong et al in 2013, using the KDIGO definition, an estimated 1 in 5 adults and 1 in 3 children worldwide experience AKI during a hospital episode of care.
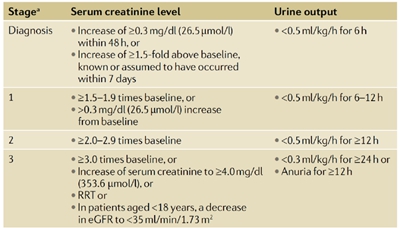
Table 3: KDIGO criteria for AKI
The incidence of AKI varies among different patient populations and is shown below. A 2018 study by Pavkov reported that the total number of hospitalizations with AKI increased from 953,926 in 2000 to 1,823,054 in 2006 and 3,959,560 in 2014. Among persons with diabetes AKI hospitalizations increased by 139%, from 23.1 to 55.3 per 1,000 persons and by 230% among persons without diabetes, from 3.5 to 11.7 per 1,000 persons (both p<0.001).
55
Hospital-acquired AKI is linked to 3 main areas: sepsis, procedures, and drug toxicity as shown below in Table 4.
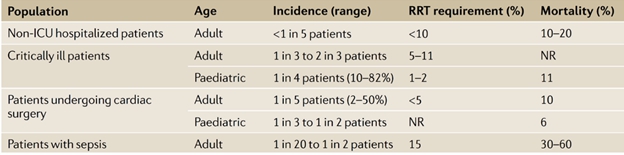
Table 4: Adapted from Hoste et al. 2018
Current treatment of acute kidney injury
Treatment options for AKI include renal replacement therapy, renal transplant and radical surgery and dialysis. In majority of the cases the damage to the kidney is irreversible, and the patient needs to have a renal transplant or be on dialysis for life. There are no approved medicines to treat AKI; there is therefore a high unmet medical need. If approved and developed, UNI 494 (a patented prodrug of nicorandil) has the potential to be a first-in-class drug for the treatment of AKI.
Background on nicorandil
Nicorandil, marketed as such products as Ikorel and Dancor, is indicated for the treatment of chronic stable angina pectoris. It is not currently approved in the United States but has been approved for use in Australia, the United Kingdom and most of Europe, and in India, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. Nicorandil is a dual-action potassium channel opener that relaxes vascular smooth muscle through membrane hyperpolarization via increased transmembrane potassium conductance and increased intracellular concentration of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP). It is shown to dilate normal and stenotic coronary arteries and reduces both ventricular preload and afterload.
Nicorandil in acute kidney injury
The kidney has one of the highest mitochondrial densities in the body. Both acute and chronic kidney disease is associated with mitochondrial loss and impaired replacement, which subsequently results in increased oxidative damage and cellular injury. The diagram below in figure 7 (Che R, 2014) shows how mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to kidney disease.
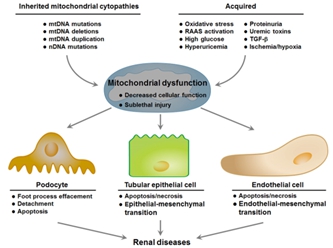
Figure 7: Che R, 2014: Mitochondria Dysfunction
Since mitochondrial dysfunction is an important factor in the pathogenesis of AKI, the mitochondria has emerged as a therapeutic target for treatment as published in a study by Ishimoto Y in 2016 in Journal Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. In preclinical studies, nicorandil has been shown to improve mitochondrial function by blocking the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores and stabilizing mitochondria against oxidative stress as published by Afzal, M in 2016 in Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.
56
Figure 8 below shows the potential mechanisms of how nicorandil can improve mitochondrial function in renal disease
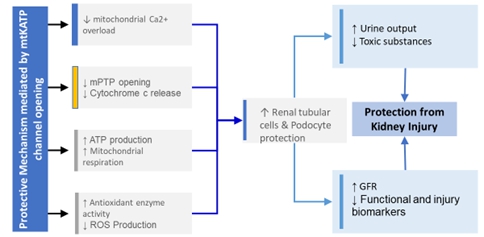
Since mitochondrial dysfunction is an important factor in the pathogenesis of AKI, the mitochondria has emerged as a therapeutic target for treatment (Ishimoto 2016). In preclinical studies, nicorandil has been shown to improve mitochondrial function by blocking the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores and stabilizing mitochondria against oxidative stress (Afzal 2016). Nicorandil has been reported to have a potential protective effect in the kidneys in nonclinical (Shiraishi 2014, Tamura 2012, Tanabe 2012) and human studies (Zhan 2018, Ma 2018). Further, no significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters of nicorandil have been observed in patients with normal renal function as compared to those with impaired renal function (Molinaro 1992).
In animal studies, nicorandil has demonstrated efficacy in multiple standard models of kidney disease in table 5 below. Notably, these effects occur in a blood pressure-independent manner, indicating that these beneficial effects are not simply a result of decreasing pressure-mediated kidney damage, but a direct beneficial effect on the kidney:
Table 5: Efficacy of nicorandil in standard models of kidney disease
57
Limitations of Nicorandil
Despite these promising results, development of nicorandil for use in acute kidney injury has not been successfully pursued to date. Nicorandil possesses at least two features that may limit its use in this clinical setting. First, nicorandil has a short half-life in humans of approximately 1 hour, which results in the need to dose nicorandil multiple times per day to achieve sustained blood levels.
Second, nicorandil is well tolerated by most patients, with less than 10 % of patients reporting side-effects after 30 days of treatment, and roughly 70 % remaining on nicorandil at one year. Similar to nitrates, headache is the most common side effect to nicorandil, occurring in roughly one third of patients. Other relatively common side effects are: dizziness, flushing, malaise and gastro-intestinal upset. However, nicorandil has been associated with rare but serious ulcerations in the gastrointestinal tract. The chance of this rare but potentially severe side effect increases with higher doses and long term use of this drug, and heals after drug withdrawal. A recent population-based study of this drug’s association with GI ulceration or perforation has been reported. This study, based on more than 600,000 randomly selected patients, found a 43% increase in the risk of GI ulceration and a 60% increase in the risk of GI perforation. This effect appears dose-dependent, and limits the maximum labeled dose of nicorandil in Europe.
UNI 494: a Pro-drug of Nicorandil
UNI 494 is a patented pro-drug that was designed to be absorbed into the systemic circulation, and once absorbed, to release nicorandil into the bloodstream. By avoiding direct exposure to the gastrointestinal tract of nicorandil, it is believed that UNI 494 may be able to minimize or avoid the gastrointestinal side effects of nicorandil. Also, based on the rate of conversion of UNI 494 to nicorandil in the systemic circulation, UNI 494 may offer greater and/or more prolonged exposure to nicorandil for the treatment of patients with acute kidney injury. Our technology for UNI 494 is a licensed technology from Sphaera Pharmaceutical Private Limited, a Singapore-based company (“Sphaera”), with offices in India and the US. We have the global, exclusive license to UNI 494.
Preliminary data available from Sphaera indicate that in rats and dogs, oral dosing with UNI 494 produces greater systemic exposure to nicorandil compared with oral dosing of nicorandil itself. We are currently conducting a preclinical program designed to directly measure conversion of UNI 494 to nicorandil across multiple preclinical species and humans, and to select the optimal preclinical species for additional pharmacokinetic and toxicology studies of UNI 494.
Sphaera License Agreement
On October 1, 2017, we entered into an exclusive license agreement (the “Sphaera License Agreement”) with Sphaera Pharma Pte. Ltd., a Singaporean pharmaceutical corporation (“Sphaera”). Pursuant to the Sphaera License Agreement, we acquired an exclusive royalty-bearing worldwide license to develop, make, have made, use, practice, research, distribute, lease, sell, offer for sale, license, import or otherwise dispose of certain rights owned or controlled by Sphaera and/or any of its affiliates, related to UNI494 (the “UNI494 Rights”). We also acquired a non-exclusive license to certain know-how and technology related to the UNI494 Rights. Under the terms of the Sphaera License Agreement, we are obligated to pay to Sphaera, on a quarterly basis, a running royalty of 2% of our net sales (including our affiliates) in connection with the sales of UNI 494; provided, however, that if we are required to make royalty payments to one or more third parties whose patent rights would be infringed by the exercise of the UNI494 Rights, we may reduce such running royalty due to Sphaera by the amount of such third party royalty rate.
58
We are also required to also pay to Sphaera certain milestone payments, including, upon our initiation of a second clinical trial; $50,000 at the time the first patient in such trial is dosed; an additional $50,000 within 30 days of completion of such trial; and at the time the FDA accepts a New Drug Application for UNI494, $1.65 million. In addition, we are responsible for the prosecution of patent rights, and any related costs and expenses for patent prosecution and maintenance.
We also have the right, but not the obligation, to defend the UNI 494 rights during the term of the Sphaera License Agreement; provided, however, that if we determine not to prosecute or maintain such rights in any country, we must provide ninety (90) days written notice to Sphaera. We may terminate the Sphaera License Agreement at any time by providing thirty (30) days’ written notice to Sphaera. Additionally, in the event that either we or Sphaera breach any of our respective material obligations, the non-breaching party may, in its sole discretion, have the right to terminate the Sphaera License Agreement, provided that it give the breaching party written notice specifying the nature of the breach and amounts of running royalty payments due, if any. In such an occurrence, the termination notice is effective ninety (90) days from receipt of the notice if the breaching party has failed to cure the breach.
Clinical trials for UNI 494 in AKI
It is challenging to conduct clinical trials in AKI trials due to the multiple etiologies of AKI. We believe that UNI 494 should be evaluated in clinical trials focusing on a few select etiologies in which UNI 494 has a very strong mechanistic rationale based on nicorandil clinical experience in terms of protection of kidney function and secondary benefits.
Based on our understanding of the drug and discussions with key opinion leaders (KOLs), we believe that the AKI subsets where UNI 494 can be most effective is in patients who have either prior cardiac dysfunction or patients with liver dysfunction. We have also identified patient populations where we would not likely evaluate UNI 494 in clinical trials, including patients with prior history of gastrointestinal ulcerations and patients who have been in intensive care units. These will become exclusion criteria in future clinical trials for UNI 494.
Regulatory Strategy for UNI 494
Nicorandil is already approved in Europe and Asia for the treatment of heart disease; therefore its safety and toxicology is well established and documented. We believe there is a possibility these historical nicorandil data, along with preclinical and clinical data with UNI 494 itself, can be utilized for streamlined US FDA review of UNI 494, potentially using a 505(b)(2) pathway. However, there is no guarantee that the FDA will approve a request to use a 505(b)(2) pathway and if not, we plan to pursue a standard clinical development and regulatory approval pathway for UNI 494.
Market Potential
According to a 2017 article by Silver and Chertow, the current cost of care for AKI in the U.S. is estimated to be between $5.4 to $24 billion per year. In England, inpatient costs related to AKI are estimated to make up 1% of the total National Health Service budget. With no effective treatment for AKI, it is not possible to definitely state a market figure. However, with the high cost and burden of AKI, we believe a conservative market estimate is approximately $3 billion in the US alone. The lack of effective therapeutic interventions for AKI means that UNI 494 has the potential to be the first drug approved for the treatment of AKI.
Competition
We operate in a highly competitive and regulated industry that is subject to rapid and frequent changes. We face significant competition from organizations that are pursuing products that would compete with the product candidates we are developing and the same or similar products that target the same conditions we intend to treat. Due to our limited resources, we may not be able to compete successfully against these organizations, which include many large, well- financed and experienced pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, as well as academic and research institutions and government agencies.
59
Manufacturing
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of clinical or commercial quantities of our product candidates. We currently have no plans to build our own clinical or commercial scale manufacturing capabilities. If and when any of our product candidates are approved, we plan to obtain manufacturing capacity through contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) to meet projected needs for commercial sale quantities and serve patient needs.
Intellectual Property
Our commercial success depends in part on our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our product candidates, as well as novel discoveries, product development technologies, and know-how.
Our commercial success also depends in part on our ability to operate without infringing on the proprietary rights of others and to prevent others from infringing our proprietary rights. Our policy is to develop and maintain protection of our proprietary position by, among other methods, filing or in-licensing U.S. and foreign patents and applications related to our technology, inventions, and improvements that are important to the development and implementation of our business.
We also rely on trademarks, trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovation, confidentiality agreements, and invention assignment agreements to develop and maintain our proprietary position. The confidentiality agreements are designed to protect our proprietary information and the invention assignment agreements are designed to grant us ownership of technologies that are developed for us by our employees, consultants, or other third parties. We seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in our agreements and security measures, either may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or independently discovered by competitors.
With respect to both licensed and company-owned intellectual property, we cannot be sure that patents will be granted with respect to any of our pending patent applications or with respect to any patent applications filed by us in the future, nor can we be sure that any of our existing patents or any patents that may be granted to us in the future will be commercially useful in protecting our commercial products and methods of using and manufacturing the same.
Renazorb Patent Portfolio
Our Renazorb patent portfolio includes one family of granted United States patents, with related applications pending, and an additional family of granted foreign patents, with related applications also pending. Granted and pending claims offer various forms of protection for Renazorb including claims to compositions of matter, pharmaceutical compositions, specific forms (such as polymorphs of lanthanum dioxycarbonate), methods of making the composition of matter, and methods for treating elevated levels of phosphate in the blood using Renazorb. These United States patents and applications, and their foreign equivalents, are described in more detail below.
Both the U.S. patent family and the foreign patent family containing claims to Renazorb and related compounds were filed in 2011. Exclusive of patent term extension, the U.S. patents from this family containing claims covering Renazorb has a statutory expiration date in 2031. Corresponding patents granted in Canada, Europe (validated in multiple European Patent Convention member states), Japan, China, Australia, and other countries have statutory expiration dates in 2031.
In some cases, granted United States patents claiming Renazorb have a longer statutory term than the corresponding foreign patents. This results from the USPTO’s practice of granting patent term adjustments for prosecution delays originating at the USPTO. Such adjustments are generally not available under foreign patent laws. If Renazorb is approved for marketing in the United States, under the Hatch-Waxman Act we may be eligible for up to five years patent term extension for a granted United States patent containing claims covering Renazorb. Similar term extensions may be available in Europe, Japan, Australia, and certain other foreign jurisdictions. The amount of any such term extension, and the identity of the patent to which it would apply, are dependent upon several factors including the duration of the development program and the date of marketing approval.
60
The most relevant granted United States patents with claims covering Renazob are listed below, along with their projected expiration dates exclusive of any patent term extension.
| Patent Number | Title | Projected Expiration | ||||
| 8,961,917 | Lanthanum carbonate hydroxide, lanthanum oxycarbonate and methods of their manufacture and use | May 12, 2031 | ||||
| 10,350,240 | Lanthanum carbonate hydroxide, lanthanum oxycarbonate and methods of their manufacture and use | May 12, 2031 | ||||
UNI 494
We believe that we have a strong global intellectual property position and substantial know how and trade secrets relating to UNI 494. As of September 14, 2020, we have one granted U.S. patent and pending patent applications in China, Japan, and Europe that are exclusively licensed to us from Sphaera. In addition, we have one provisional U.S. application that we own. The granted U.S. patent is directed to methods of making UNI 494, and it is expected to expire in 2033. The provisional U.S. application is directed to methods of using UNI 494. Should the US and other patents issue from this provisional U.S. application, they are expected to expire in 2041.
Government Regulation and Approval Process
Government authorities in the United States at the federal, state and local level, including the FDA, the FTC and the DEA, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacturing, quality control, approval, labeling, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, promotion, advertising, distribution, marketing and export and import of products such as those we plan to develop and market. For both the products under development and to be marketed, failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can, among other things, result in suspension of regulatory approval and possible civil and criminal sanctions. Regulations, enforcement positions, statutes and legal interpretations applicable to the pharmaceutical industry are constantly evolving and are not always clear. Significant changes in regulations, enforcement positions, statutes and legal interpretations could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of our operations.
Additionally, future healthcare legislation or other legislative proposals at the federal and state levels could bring about major changes in the affected health care systems, including statutory restrictions on the means that can be employed by brand and generic pharmaceutical companies to settle Paragraph IV patent litigations. We cannot predict the outcome of such initiatives, but such initiatives, if passed, could result in significant costs to us in terms of costs of compliance and penalties associated with failure to comply.
Pharmaceutical Regulation in the United States
In the United States, the FDA regulates drugs under the FDCA and its implementing regulations. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. Failure to comply with the applicable U.S. requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process or after approval may subject an applicant to administrative or judicial sanctions. These sanctions could include the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, a clinical hold, Warning Letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution of product(s), injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement or civil or criminal penalties. Any agency or judicial enforcement action could have a material adverse effect on us.
FDA approval is required before any new unapproved drug or dosage form, including a new use of a previously approved drug or a generic version of a previously approved drug, can be marketed in the United States.
The process required by the FDA before a new drug may be marketed in the United States generally involves:
| ● | Completion of preclinical laboratory and animal testing and formulation studies in compliance with the FDA’s current GLP regulations; |
61
| ● | Submission to the FDA of an IND for human clinical testing, which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin in the United States; |
| ● | Approval by an IRB at each clinical site before each trial may be initiated; |
| ● | Performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials in accordance with the FDA to establish the safety and efficacy of the proposed drug product for each intended use; |
| ● | Satisfactory completion of a pre-approval inspection by FDA of the facility or facilities at which the product is manufactured to assess compliance with the FDA’s cGMP regulations and to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to preserve the drug’s identity, strength, quality and purity; |
| ● | Submission to the FDA of an NDA; |
| ● | Satisfactory completion of a potential review by an FDA advisory committee, if applicable; and |
| ● | FDA review and approval of the NDA. |
Preclinical Studies
When developing a branded product and bringing it to market, the first step in proceeding to clinical studies is preclinical testing. Preclinical tests are intended to provide a laboratory or animal study evaluation of the product to determine its chemistry, formulation and stability. Toxicology studies are also performed to assess the potential safety of the product. The conduct of the preclinical tests must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including GLPs. The results of these studies are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND application along with other information, including product chemistry, manufacturing and controls and a proposed clinical trial protocol. Long-term preclinical tests, such as animal tests of reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity, may continue concurrently with the IND application.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational new drug to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCP requirements, which include the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing for their participation in any clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. In addition, an IRB at each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it is initiated at that institution. Information about certain clinical trials must be submitted within specific timeframes to the NIH for public dissemination on their www.clinicaltrials.gov website.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, which may be distinct, or overlap or be combined:
| ● | Phase 1: The drug is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or patients with the target disease or condition, and tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution, excretion and, if possible, to gain an early indication of its effectiveness. |
| ● | Phase 2: The drug is administered to a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the product for specific targeted diseases and to determine dosage tolerance. |
| ● | Phase 3: The drug is administered to an expanded patient population, generally at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites, in well-controlled clinical trials to generate enough data to statistically evaluate the efficacy and safety of the product for approval, to establish the overall risk-benefit profile of the product, and to provide adequate information for the labeling of the product. |
62
Progress reports detailing the results of the clinical trials must be submitted at least annually to the FDA and more frequently if serious adverse events occur. Phase 1, Phase 2, and Phase 3 trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, or at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution if it is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
Marketing Approval
After completion of the required clinical testing, an NDA is prepared and submitted to the FDA. FDA approval of the NDA is required before marketing of the product may begin in the United States. The NDA must include, among other things, the results of all preclinical, clinical and other testing and a compilation of data relating to the product’s pharmacology, chemistry, manufacture and controls. Under federal law, the submission of most NDAs is subject to a substantial application user fee, and the manufacturer or sponsor of an approved NDA is also subject to annual program fees. The FDA has 60 days from its receipt of an NDA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on the agency’s threshold determination that it is sufficiently complete to permit its substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an NDA for filing. In some events, the NDA may be required to be resubmitted with the additional information and it may be subject to payment of additional user fees. The resubmitted application is also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review. Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act, as amended, the FDA has agreed to certain performance goals for itself for the review of NDAs through a two-tiered classification system, Standard Review and Priority Review. Priority Review designation is given to drugs that are intended to treat a serious condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness over existing therapies. The FDA endeavors to review most applications subject to Standard Review within ten to twelve months whereas its goal is to complete most Priority Review applications within six to eight months, depending on whether the drug is a new molecular entity.
The FDA may refer applications for certain drug products which present difficult questions related to its safety or efficacy to an advisory committee for review, evaluation and recommendation, and to seek advice as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. Before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP requirements. Additionally, the FDA will inspect the facility or the facilities at which the drug is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the NDA unless it determines that the manufacturing process and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and are adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications, and the NDA contains data that provide substantial evidence that the drug is safe and effective for the labeled indication.
After the FDA evaluates the NDA and the manufacturing facilities, it issues either an approval letter or a complete response letter to indicate that the review cycle for an application is complete and that the application is not ready for approval. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing, or information, in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA may ultimately decide that an application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval. If, or when, the deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug with specific prescribing information for specific indications.
As a condition of NDA approval, the FDA may require a REMS to help ensure that the benefits of the drug outweigh the potential risks. If the FDA determines a REMS is necessary during review of the application, the drug sponsor must agree to the REMS plan at the time of approval. A REMS may be required to include various elements, such as a medication guide or patient package insert, a communication plan to educate healthcare providers of the drug’s risks, limitations on who may prescribe or dispense the drug, or other elements to assure safe use, such as special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring and the use of patient registries. In addition, the REMS must include a timetable to periodically assess the strategy. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of a drug.
63
Sometimes, product approval may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance to monitor the drug’s safety or efficacy, and the FDA has the authority to prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of these post-marketing programs. Once granted, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or certain problems are identified following initial marketing. Drugs may be marketed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling, and, even if the FDA approves a product, it may limit the approved indications for use for the product or impose other conditions, including labeling or distribution restrictions or other risk-management mechanisms.
Further changes to some of the conditions established in an approved application, including changes in indications, labeling, or manufacturing processes or facilities, require submission and FDA approval of a new NDA or NDA supplement before the change can be implemented, which may require us to develop additional data or conduct additional preclinical studies and clinical trials. An NDA supplement for a new indication typically requires clinical data similar to that in the original application, and the FDA uses the similar procedures in reviewing NDA supplements as it does in reviewing the original NDAs.
Disclosure of Clinical Trial Information
Sponsors of certain clinical trials of FDA-regulated products, including drugs, are required to register and disclose certain clinical trial information on www.ClinicalTrials.gov. Information related to the product, subject population, phase of investigation, study sites and investigators, and other aspects of the clinical trial is then made public as part of the registration. Sponsors are also obligated to discuss certain results of their clinical trials after its completion. Disclosure of the results of these trials can be delayed until the new product or new indication being studied has been approved. Competitors may use this publicly available information to gain knowledge regarding the progress of development programs.
Post-Approval Requirements
Once an NDA is approved, a product will be subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to drug listing and registration, recordkeeping, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, adverse event reporting, and advertising, marketing and promotion, including standards and regulations for direct-to-consumer advertising, off-label promotion, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities and promotional activities involving the Internet. Drugs may be marketed only for the approved indications and in a manner consistent with the provisions of the approved labeling. While physicians may choose to prescribe a drug for off-label uses, manufacturers may only promote it for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant liability. There also are extensive DEA regulations applicable to controlled substances.
Adverse event reporting and submission of periodic reports is also required following FDA approval of an NDA. Additionally, the FDA may require post-marketing testing, known as Phase 4 testing, REMS, and/or surveillance to monitor the effects of an approved product. Alternatively, the FDA may place conditions on an approval that could restrict the distribution or use of the product. In addition, quality-control, drug manufacture, packaging and labeling procedures must continue to comply with cGMPs after its approval. Drug manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments and list their marketed products with the FDA and certain state agencies. Registration with the FDA subjects entities to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA, during which the agency inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMPs. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the areas of production and quality-control to maintain compliance with cGMPs. Regulatory authorities may withdraw product approvals or request product recalls if a company fails to comply with regulatory standards, if it encounters problems following initial marketing or if previously unrecognized problems are subsequently discovered. The FDA may also impose a REMS requirement on a drug already on the market if the FDA determines, based on new safety information, that a REMS is necessary to ensure that the drug’s benefits outweigh its risks. In addition, regulatory authorities may take other enforcement action, including, among other things, Warning Letters, the seizure of products, injunctions, consent decrees placing significant restrictions on or suspending manufacturing operations, refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications, civil penalties and criminal prosecution.
64
The Hatch-Waxman Amendments
505(b)(2) NDAs
The FDA is also authorized to approve an alternative type of NDA under Section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA. Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference from the data owner. The applicant may rely upon the FDA’s findings of safety and efficacy for an approved product that acts as the “listed drug.” The FDA may also require 505(b)(2) applicants to perform additional studies or measurements to support the change from the listed drug. The FDA may then approve the new product candidate for all, or some, of the conditions of use for which the branded reference drug has been approved, or for a new condition of use sought by the 505(b)(2) applicant.
Abbreviated New Drug Applications
The Hatch-Waxman amendments to the FDCA established a statutory procedure for submission and FDA review and approval of ANDAs for generic versions of listed drugs. An ANDA is a comprehensive submission that contains, among other things, data and information pertaining to the API, drug product formulation, specifications and stability of the generic drug, as well as analytical methods, manufacturing process validation data and quality control procedures. Premarket applications for generic drugs are termed abbreviated because they generally do not include clinical data to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. However, a generic manufacturer is typically required to conduct bioequivalence studies of its test product against the listed drug. The bioequivalence studies for orally administered, systemically available drug products assess the rate and extent to which the API is absorbed into the bloodstream from the drug product and becomes available at the site of action. Bioequivalence is established when there is an absence of a significant difference in the rate and extent for absorption of the generic product and the reference listed drug. For some drugs, other means of demonstrating bioequivalence may be required by the FDA, especially where rate or extent of absorption are difficult or impossible to measure. The FDA will approve the generic product as suitable for an ANDA application if it finds that the generic product does not raise new questions of safety and effectiveness as compared to the reference listed drug. A product is not eligible for ANDA approval if the FDA determines that it is not bioequivalent to the reference listed drug, if it is intended for a different use, or if it is not subject to, and requires, an approved Suitability Petition.
Orange Book Listing
In seeking approval for a drug through an NDA, including a 505(b)(2) NDA, applicants are required to list with the FDA certain patents whose claims cover the applicant’s product. Upon approval of an NDA, each of the patents listed in the application for the drug is then published in the Orange Book. Any applicant who files an ANDA seeking approval of a generic equivalent version of a drug listed in the Orange Book or a 505(b)(2) NDA referencing a drug listed in the Orange Book must certify to the FDA (i) that there is no patent listed with the FDA as covering the relevant branded product, (ii) that any patent listed as covering the branded product has expired, (iii) that the patent listed as covering the branded product will expire prior to the marketing of the generic product, in which case the ANDA will not be finally approved by the FDA until the expiration of such patent or (iv) that any patent listed as covering the branded drug is invalid or will not be infringed by the manufacture, sale or use of the generic product for which the ANDA is submitted. A notice of the Paragraph IV certification must be provided to each owner of the patent that is the subject of the certification and to the holder of the approved NDA to which the ANDA or 505(b)(2) application refers. The applicant may also elect to submit a “section viii” statement certifying that its proposed label does not contain (or carves out) any language regarding the patented method-of-use rather than certify to a listed method-of-use patent.
If the reference NDA holder and patent owners assert a patent challenge directed to one of the Orange Book listed patents within 45 days of the receipt of the Paragraph IV certification notice, the FDA is prohibited from approving the application until the earlier of 30 months from the receipt of the Paragraph IV certification, expiration of the patent, settlement of the lawsuit or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the applicant. The ANDA or 505(b)(2) application also will not be approved until any applicable non-patent exclusivity listed in the Orange Book for the branded reference drug has expired as described in further detail below.
65
Non-Patent Exclusivity
In addition to patent exclusivity, the holder of the NDA for the listed drug may be entitled to a period of non-patent exclusivity, during which the FDA cannot approve an ANDA or 505(b)(2) application that relies on the listed drug.
For example, for listed drugs that were considered new chemical entities at the time of approval, an ANDA or 505(b)(2) application referencing that drug may not be filed with the FDA until the expiration of five years after approval of that drug, unless the submission is accompanied by a Paragraph IV certification, in which case the applicant may submit its application four years following the original product approval.
A drug, including one approved under Section 505(b)(2), may obtain a three-year period of exclusivity for a particular condition of approval, or change to a marketed product, such as a new formulation for a previously approved product, if one or more new clinical studies (other than bioavailability or bioequivalence studies) was essential to the approval of the application and was conducted/sponsored by the applicant. In addition, drugs approved for diseases for which the patient population is sufficiently small, or orphan indications, are entitled to a seven-year data exclusivity period.
Pricing and Reimbursement
Successful commercialization of our products depends, in part, on the availability of governmental and third-party payor reimbursement for the cost of our products. Government authorities and third-party payors increasingly are challenging the price of medical products and services. On the government side, there is a heightened focus, at both the federal and state levels, on decreasing costs and reimbursement rates for Medicaid, Medicare and other government insurance programs. This has led to an increase in federal and state legislative initiatives related to drug prices, which could significantly influence the purchase of pharmaceutical products, resulting in lower prices and changes in product demand. If enacted, these changes could lead to reduced payments to pharmaceutical manufacturers. Many states have also created preferred drug lists and include drugs on those lists only when the manufacturers agree to pay a supplemental rebate. If our current products or future product candidates are not included on these preferred drug lists, physicians may not be inclined to prescribe them to their Medicaid patients, thereby diminishing the potential market for our products.
In addition, third-party payors have been imposing additional requirements and restrictions on coverage and limiting reimbursement levels for pharmaceutical products. Third-party payors may require manufacturers to provide them with predetermined discounts from list prices and limit coverage to specific pharmaceutical products on an approved list, or formulary, which might not include all of the FDA-approved pharmaceutical products for particular indications. Third-party payors may challenge the price and examine the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of pharmaceutical products in addition to their safety and efficacy. Manufacturers may need to conduct expensive pharmaco-economic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of pharmaceutical products in addition to the costs required to obtain the FDA approvals. Adequate third-party reimbursement may not be available to enable manufacturers to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on their investment in drug development.
Healthcare Reform
In the United States, there have been a number of federal and state proposals during the last several years regarding the pricing of pharmaceutical products, government control and other changes to the healthcare system of the United States. It is uncertain what other legislative proposals may be adopted or what actions federal, state, or private payors may take in response to any healthcare reform proposals or legislation. We cannot predict the effect such reforms may have on our business, and no assurance can be given that any such reforms will not have a material adverse effect.
By way of example, in March 2010, the Affordable Care Act, or ACA, was signed into law, which, among other things, includes changes to the coverage and payment for drug products under government health care programs. The law includes measures that (i) significantly increase Medicaid rebates through both the expansion of the program and significant increases in rebates, (ii) substantially expand the Public Health System (340B) program to allow other entities to purchase prescription drugs at substantial discounts, (iii) extend the Medicaid rebate rate to a significant portion of Managed Medicaid enrollees, (iv) assess a rebate on Medicaid Part D spending in the coverage gap for branded and authorized generic prescription drugs, and (v) levy a significant excise tax on the industry to fund the healthcare reform.
66
In addition to the changes brought about by the ACA, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted, including aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year and reduced payments to several types of Medicare providers. Moreover, there has recently been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which manufacturers set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to product pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products. At the federal level, the Trump Administration’s budget proposal for fiscal year 2019 contains further drug price control measures that could be enacted during the 2019 budget process or in other future legislation, including, for example, measures to permit Medicare Part D plans to negotiate the price of certain drugs under Medicare Part B, to allow some states to negotiate drug prices under Medicaid and to eliminate cost sharing for generic drugs for low-income patients. While any proposed measures will require authorization through additional legislation to become effective, Congress and the Trump Administration have each indicated an intent to continue to seek new legislative or administrative measures to control drug costs. At the state level, legislatures have increasingly passed legislation and implemented regulations designed to control pharmaceutical product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing.
Healthcare Regulations
Pharmaceutical companies are subject to various federal and state laws that are intended to combat health care fraud and abuse and that govern certain of our business practices, especially our interactions with third-party payors, healthcare providers, patients, customers and potential customers through sales and marketing or research and development activities. These include anti-kickback laws, false claims laws, sunshine laws, privacy laws and FDA regulation of advertising and promotion of pharmaceutical products.
Anti-kickback laws, including the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, make it a criminal offense knowingly and willfully to offer, pay, solicit, or receive any remuneration to induce or reward referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service reimbursable by, a federal health care program (including our products). The federal Anti-Kickback Statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand and prescribers, purchasers and formulary managers on the other. Although there are several statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting certain common activities from prosecution, the exceptions and safe harbors are drawn narrowly, and practices that involve remuneration intended to induce prescribing, purchasing or recommending may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exception or safe harbor. In addition, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it to have committed a violation. Moreover, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the False Claims Act. The penalties for violating the federal Anti-Kickback Statute include administrative civil money penalties, imprisonment for up to five years, fines of up to $25,000 per violation and possible exclusion from federal healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid.
The federal civil and criminal false claims laws, including the civil False Claims Act, prohibit knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment to the federal government (including Medicare and Medicaid) that are false or fraudulent (and, under the Federal False Claims Act, a claim is deemed false or fraudulent if it is made pursuant to an illegal kickback). Manufacturers can be held liable under these laws if they are deemed to “cause” the submission of false or fraudulent claims by, for example, providing inaccurate billing or coding information to customers or promoting a product off-label. Actions under the False Claims Act may be brought by the Attorney General or as a qui tam action by a private individual in the name of the government. Violations of the False Claims Act can result in significant monetary penalties, including fines ranging from $11,181 to $22,363 for each false claim, and treble damages. The federal government is using the False Claims Act, and the accompanying threat of significant liability, in its investigation and prosecution of pharmaceutical companies throughout the country, for example, in connection with the promotion of products for unapproved uses and other improper sales and marketing practices. The government has obtained multi-million and multi-billion dollar settlements under the False Claims Act in addition to individual criminal convictions under applicable criminal statutes. In addition, companies have been forced to implement extensive corrective action plans and have often become subject to consent decrees or corporate integrity agreements, severely restricting the manner in which they conduct their business. Given the significant size of actual and potential settlements, it is expected that the government will continue to devote substantial resources to investigating healthcare providers’ and manufacturers’ compliance with applicable fraud and abuse laws.
67
The Federal Civil Monetary Penalties Law prohibits, among other things, the offering or transferring of remuneration to a Medicare or Medicaid beneficiary that the person knows or should know is likely to influence the beneficiary’s selection of a particular supplier of Medicare or Medicaid payable items or services. Noncompliance can result in civil money penalties of up to $15,270 for each wrongful act, assessment of three times the amount claimed for each item or service and exclusion from the federal healthcare programs.
Federal criminal statutes prohibit, among other actions, knowingly and willfully executing or attempting to execute a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program, including private third-party payors, knowingly and willfully embezzling or stealing from a healthcare benefit program, willfully obstructing a criminal investigation of a healthcare offense, and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making any materially false, fictitious or fraudulent statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Like the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, the ACA amended the intent standard for certain healthcare fraud statutes under HIPAA such that a person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation.
Analogous state and foreign laws and regulations, including state anti-kickback and false claims laws, may apply to products and services reimbursed by non-governmental third-party payors, including commercial payors. Additionally, there are state laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government or that otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers as well as state and foreign laws that require drug manufacturers to report marketing expenditures or pricing information.
Sunshine laws, including the Federal Open Payments law enacted as part of the ACA, require pharmaceutical manufacturers to disclose payments and other transfers of value to physicians and certain other health care providers or professionals, and in the case of some state sunshine laws, restrict or prohibit certain such payments. Pharmaceutical manufacturers are required to submit reports to the government by the 90th day of each calendar year. Failure to submit the required information may result in civil monetary penalties of up to an aggregate of $165,786 per year (or up to an aggregate of $1.105 million per year for “knowing failures”) for all payments, transfers of value or ownership or investment interests not reported in an annual submission, and may result in liability under other federal laws or regulations. Certain states and foreign governments require the tracking and reporting of gifts, compensation and other remuneration to physicians.
Privacy laws, such as the privacy regulations implemented under HIPAA, restrict covered entities from using or disclosing protected health information. Covered entities commonly include physicians, hospitals and health insurers from which we may seek to acquire data to aid in our research, development, sales and marketing activities. Although pharmaceutical manufacturers are not covered entities under HIPAA, our ability to acquire or use protected health information from covered entities may be affected by privacy laws. Specifically, HIPAA, as amended by HITECH, and their respective implementing regulations, including the final omnibus rule published on January 25, 2013, imposes specified requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information. Among other things, HITECH makes HIPAA’s privacy and security standards directly applicable to “business associates,” defined as independent contractors or agents of covered entities that create, receive, maintain or transmit protected health information in connection with providing a service for or on behalf of a covered entity. HITECH also increased the civil and criminal penalties that may be imposed against covered entities, business associates and possibly other persons, and gave state attorneys general new authority to file civil actions for damages or injunctions in federal courts to enforce the federal HIPAA laws and seek attorney’s fees and costs associated with pursuing federal civil actions. In addition, state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways, thus complicating compliance efforts.
68
The FDA regulates the sale and marketing of prescription drug products and, among other things, prohibits pharmaceutical manufacturers from making false or misleading statements and from promoting products for unapproved uses. There has been an increase in government enforcement efforts at both the federal and state level. Numerous cases have been brought against pharmaceutical manufacturers under the Federal False Claims Act, alleging, among other things, that certain sales or marketing-related practices violate the Anti-Kickback Statute or the FDA’s regulations, and many of these cases have resulted in settlement agreements under which the companies were required to change certain practices, pay substantial fines and operate under the supervision of a federally appointed monitor for a period of years. Due to the breadth of these laws and their implementing regulations and the absence of guidance in some cases, it is possible that our practices might be challenged by government authorities. Violations of fraud and abuse laws may be punishable by civil and criminal sanctions including fines, civil monetary penalties, as well as the possibility of exclusion of our products from payment by federal health care programs.
Government Price Reporting
Government regulations regarding reporting and payment obligations are complex, and we are continually evaluating the methods we use to calculate and report the amounts owed with respect to Medicaid and other government pricing programs. Our calculations are subject to review and challenge by various government agencies and authorities, and it is possible that any such review could result either in material changes to the method used for calculating the amounts owed to such agency or the amounts themselves. Because the process for making these calculations, and our judgments supporting these calculations, involve subjective decisions, these calculations are subject to audit. In the event that a government authority challenges or finds ambiguity with regard to our report of payments, such authority may impose civil and criminal sanctions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. From time to time we conduct routine reviews of our government pricing calculations. These reviews may have an impact on government price reporting and rebate calculations used to comply with various government regulations regarding reporting and payment obligations.
Many governments and third-party payors reimburse the purchase of certain prescription drugs based on a drug’s AWP. In the past several years, state and federal government agencies have conducted ongoing investigations of manufacturers’ reporting practices with respect to AWP, which they have suggested have led to excessive payments by state and federal government agencies for prescription drugs. We and numerous other pharmaceutical companies have been named as defendants in various state and federal court actions alleging improper or fraudulent practices related to the reporting of AWP.
Drug Pedigree Laws
State and federal governments have proposed or passed various drug pedigree laws which can require the tracking of all transactions involving prescription drugs from the manufacturer to the pharmacy (or other dispensing) level. Companies are required to maintain records documenting the chain of custody of prescription drug products beginning with the purchase of such products from the manufacturer. Compliance with these pedigree laws requires implementation of extensive tracking systems as well as heightened documentation and coordination with customers and manufacturers. While we fully intend to comply with these laws, there is uncertainty about future changes in legislation and government enforcement of these laws. Failure to comply could result in fines or penalties, as well as loss of business that could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
Federal Regulation of Patent Litigation Settlements and Authorized Generic Arrangements
As part of the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003, companies are required to file with the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) and the U.S. Department of Justice (the “DOJ”) certain types of agreements entered into between brand and generic pharmaceutical companies related to the settlement of patent litigation or manufacture, marketing and sale of generic versions of branded drugs. This requirement could affect the manner in which generic drug manufacturers resolve intellectual property litigation and other disputes with brand pharmaceutical companies and could result generally in an increase in private-party litigation against pharmaceutical companies or additional investigations or proceedings by the FTC or other governmental authorities.
Other
The U.S. federal government, various states and localities have laws regulating the manufacture and distribution of pharmaceuticals, as well as regulations dealing with the substitution of generic drugs for branded drugs. Our operations are also subject to regulation, licensing requirements and inspection by the states and localities in which our operations are located or in which we conduct business.
69
Certain of our activities are also subject to FTC enforcement actions. The FTC also enforces a variety of antitrust and consumer protection laws designed to ensure that the nation’s markets function competitively, are vigorous, efficient and free of undue restrictions. Federal, state, local and foreign laws of general applicability, such as laws regulating working conditions, also govern us.
In addition, we are subject to numerous and increasingly stringent federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations concerning, among other things, the generation, handling, storage, transportation, treatment and disposal of toxic and hazardous substances, the discharge of pollutants into the air and water and the cleanup of contamination. We are required to maintain and comply with environmental permits and controls for some of our operations, and these permits are subject to modification, renewal and revocation by the issuing authorities. Our environmental capital expenditures and costs for environmental compliance may increase in the future as a result of changes in environmental laws and regulations or increased manufacturing activities at any of our facilities. We could incur significant costs or liabilities as a result of any failure to comply with environmental laws, including fines, penalties, third-party claims and the costs of undertaking a clean-up at a current or former site or at a site to which our wastes were transported. In addition, we have grown in part by acquisition, and our diligence may not have identified environmental impacts from historical operations at sites we have acquired in the past or may acquire in the future.
Scientific Advisory Board
Ravi Mehta, M.D.
Dr. Mehta is a Professor Emeritus of Medicine in the Department of Medicine at University of California San Diego where he directs the UCSD Masters in Clinical Research Program. He is an internationally recognized expert in the field of acute kidney injury (AKI) and continuous renal replacement therapies (CRRT). He holds a patent for “Continuous Hemodialysis Using Citrate”. He chairs the annual International AKI and CRRT Conference in San Diego that is now in its 25th year. He chaired the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) Committee on AKI, is a founding member of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) and the Acute Kidney Injury network (AKIN), a member of the KDIGO Guidelines in AKI committee and served as the director of the ISN 0 by 25 initiative to eliminate preventable deaths from AKI by 2025. He has coordinated and led several multinational efforts for determining best approaches for managing AKI and CRRT. These have included the IHD vs CRRT trial, The PICARD network, the DIRECT study evaluating the genetic determinants of drug induced nephrotoxicity and the ISN 0by25 initiative. He has more than 200 original research publications, 100 reviews and book chapters. He has served on the NIH NIDDK study section and special emphasis panels and on editorial boards of the Journal of American Society of Nephrology, Kidney International and CJASN. He has been on the program committee of the ISN and contributed to the annual meetings of the American Society of Nephrology, National kidney Foundation and ISICEM. He has coordinated the development of consensus recommendations including the RIFLE and AKIN diagnostic and staging criteria for AKI. He has been recognized as one of the Best Doctors in San Diego and the US for several years. In 2008 he was recognized by the American Nephrologists of Indian Origin and in March 2009 he was elected as a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in the UK. He received the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) Bywaters Award for lifetime achievement in AKI in April 2011. He received the M.B.B.S. degree (1976) from the Government Medical School in Amritsar, India, and the M.D. (1979) and D.M. (1981) degrees from the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India. He subsequently completed a nephrology fellowship at the University of Rochester in Rochester New York and obtained his boards in Internal Medicine (1986) and Nephrology (1988). He has been on the faculty at San Diego since 1988.
Suneel Gupta, Ph.D.
Dr. Gupta is currently the Chief Development Officer at Protagonist. Previously, he was Chief Scientific Officer at Impax Pharmaceuticals, having joined them in 2008 and before that Dr. Gupta previously was with ALZA Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, for nearly 20 years. There, he was responsible for the strategic vision and execution of clinical research and development as Senior Vice President and distinguished research fellow. Dr Gupta’s research interest focuses on the influence of rate and route of drug delivery to discover new indications, as well as maximize clinical utility and/or effectiveness. With extensive experience in the development of drug delivery-based products across many therapeutic areas, Dr. Gupta has made significant contributions to the development of several therapeutics including Duragesic®, Durotap®, Nicoderm®, Testoderm®, Effidac®, Covera-HS®, Ditropan-XL®, Concerta®, Ionsys®, Jurnista®, Invega® and Priligy®. Before ALZA, he worked at Ciba Geigy (India) where he was responsible for scale-up and manufacturing of several products. Dr. Gupta received his PhD from the University of Manchester and was a Postdoctoral Fellow at UCSF. He is a coauthor on more than 200 research publications and co-inventor on more than 40 patents.
Employees and Labor Relations
As of the date of this prospectus, we have one full time employee. We have no collective bargaining agreements with our employee, and none are represented by labor unions. We consider our current relations with our employee to be good.
Facilities
Our principal address is 5150 El Camino Real, Suite A-32, Los Altos, CA 94022. We believe our facilities are adequate to meet our current needs, although we may seek to negotiate new leases or evaluate additional or alternate space for our operations. We believe appropriate alternative space would be readily available on commercially reasonable terms.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time we may be involved in claims that arise during the ordinary course of business. Although the results of litigation and claims cannot be predicted with certainty, we do not currently have any pending litigation to which we are a party or to which our property is subject that we believe to be material. Regardless of the outcome, litigation can be costly and time consuming, and it can divert management’s attention from important business matters and initiatives, negatively impacting our overall operations.
70
Directors and Executive Officers
The following table sets forth the name, age and position of each of our executive officers, key employee, consultants and directors as of September 14, 2020.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D. | 47 | Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman of the Board of Directors | ||
| Keith Ward, Ph.D. | 50 | Executive Vice President and Chief Development Officer | ||
| Pramod Gupta, M.D. | 60 | Executive Vice President, Pharmaceutical and Business Operations | ||
| John Ryan, M.D., Ph.D. | 77 | Director | ||
| Sandeep Laumas, M.D. | 52 | Director |
Shalabh Gupta, M.D. Shalabh Gupta, our founder, has served as our Chief Executive Officer, President and director since August 2016. Since June 2013, Dr. Gupta has also served as the founder and Chief Executive Officer of Globavir Biosciences, Inc., a company focused on commercializing novel therapeutics and powerful diagnostics for treating global infectious disease. Dr. Gupta has also served in various other capacities including founder and Chief Executive Officer of Biocycive Inc.; Strategy, Genentech Commercial at Genentech, Inc.; Equity Research, Pharmaceuticals at UBS Investment Bank; Attending Physician at NYU Medical Center; clinical faculty member at NYU School of Medicine; and Equity Research, Biotechnology at Rodman & Renshaw, LLC. In addition, he has served on the board of directors of Beall Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship since 2018 and on the commercial advisory board of the University of Maryland Medical Center since 2011. Dr. Gupta has also served as an advisor to SPARK, Stanford University School of Medicine since 2012, a charter member of TiE, a not-for-profit network of entrepreneurs fostering entrepreneurship, mentoring and education, since 2013 and a member of Founders Network, a private community of tech startup founders since 2013. Dr. Gupta previously served on the board of directors of Phenomenome Discoveries Inc. and was a Fellow at the Startup Leadership Program, a medical advisor Synageva BioPharma Corporation (formerly known as AviGenics) and an advisor to NYU Langone Medical Center (Office of Technology Transfer). Dr. Gupta received his MPA in health care finance and management from NYU Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service, and his medical degree from Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research, India. Furthermore, Dr. Gupta completed his internship in Internal Medicine, and medical residency in physical medicine and rehabilitation and a research fellowship in cardiopulmonary rehabilitation from New York University (“NYU”) School of Medicine and New York University. He practiced medicine from 2000 to 2008 at NYU’s various hospitals first during his medical training (2000-2004) and then as an attending physician (2004-2008). Dr. Gupta also served as a faculty member at NYU School of Medicine. In the past, Dr. Gupta was a board-certified physician, and he currently holds a license from the California State Medical Board. While working as a stock analyst on Wall Street, Dr. Gupta held Series 7, 63, 86 and 87 licenses. We believe Dr. Gupta is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his background as a physician and as a biotechnology executive and his extensive experience in both in-licensing technologies from academic institutions and biotechnology companies as well as out-licensing technologies to larger organizations in addition to his former experience on Wall Street.
Keith Ward, Ph.D. Keith Ward has served as our Chief Development Officer since May 2020 in a consulting role. Dr. Ward is a life sciences executive with over 25 years of experience in the biotech and pharmaceutical industry. In addition to his role at Unicycive, Dr. Ward serves in leadership and Board positions for several emerging biotech and pharma companies. Prior to joining Unicycive, Dr. Ward served as Executive Vice President and Chief Development Officer for Reata Pharmaceuticals, from July 2011 through March 2019 and led research and development, clinical operations, regulatory affairs, manufacturing, and project management. Before that, Dr. Ward developed ophthalmic pharmaceuticals and medical devices as Global Vice President of Pharmaceutical R&D for Bausch & Lomb from May, 2005 to June, 2011. Dr. Ward has also held positions of increasing responsibility within GlaxoSmithKline and SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Ward earned a B.S. in Toxicology with a minor in Chemistry from Northeast Louisiana University and a Ph.D. in Toxicology from The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
71
Pramod Gupta, M.D. Dr. Gupta has been our Executive Vice President, Pharmaceutical and Business Operations since September 2020 in a consulting role. Dr. Gupta is a pharmaceutical executive with 30 years’ experience at large as well as small companies. He has extensive experience in drug development, regulatory requirements and drug approvals globally. He has led development/approval/launch of over 40 products by leveraging external partnerships/technologies/business solutions. Previously Dr. Gupta served as the Senior Vice President at Spectrum Pharmaceuticals from January 2011 to April 2018, Vice President at Bausch & Lomb from May 2005 to August 2009, and at positions of increasing responsibilities at Baxter, TAP Pharmaceuticals and Abbott Laboratories. He has published more than 50 scientific papers and 2 scientific books, and holds 14 patents. He completed his PhD from the University of Otago New Zealand.
John Ryan, M.D., Ph.D. John Ryan has served as our director since 2018. Since 2011, Dr. Ryan has served as Executive Vice President, Chief Medical Officer of Kadmon Holdings, Inc., a biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development and commercialization of small molecules and biologics. From 2009 until 2011, Dr. Ryan served as Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer of Cerulean Pharma, Inc., a publicly traded pharmaceutical company, and from 2006 until 2009, he served as Chief Medical Officer at Aveo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: AVEO), a biopharmaceutical company seeking to advance targeted medicines for oncology and other unmet medical needs. From 1995 until 2006, Dr. Ryan served as Senior Vice President of Translational Research at Wyeth (formerly Genetics Institute), where he served as head of the Department of Experimental Medicine. Dr. Ryan also served as an Executive Director of Clinical Research at Merck Research Laboratories from 1989 to 1995 and he previously served on the scientific advisory boards of ArQule, Inc. and Expression Analysis, Inc. Dr. Ryan has also been a director of Globavir Biosciences, Inc. since 2014. Dr. Ryan received his B.S. and his Ph.D. from Yale University. Dr. Ryan received his M.D. from the University of California, San Diego. We believe Dr. Ryan is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his clinical background and extensive experience in running clinical development programs and getting drugs through the FDA approval process.
Sandeep Laumas, M.D. Sandeep Laumas has served as our director since 2018. Since 2014, Dr. Laumas has served on the board of directors of private and publicly traded biotechnology companies. In 2008, Dr. Laumas founded Bearing Circle Capital, an investment vehicle and has served as its Managing Director since such time. Dr. Laumas began his career at Goldman Sachs & Co. in 1996 as an equity analyst in the healthcare investment banking division working on mergers & acquisitions and corporate finance transactions before transitioning to the healthcare equity research division. After leaving Goldman Sachs in 2000, Dr. Laumas moved to the buy side as an analyst at Balyasny Asset Management from 2001 to 2003. Dr. Laumas was a Managing Director of North Sound Capital from 2003 to 2007, where he was responsible for the global healthcare investment portfolio. Dr. Laumas has served as a member of the board of directors of private and public healthcare companies including, Parkway Holdings Ltd. (2010), SRL Ltd. (2011-2012), 9 Meters Biopharma, Inc. (2018-present) and BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc. (2017-present). Dr. Laumas has also been a director of Globavir Biosciences, Inc. since 2015. Dr. Laumas received his A.B. in Chemistry from Cornell University in 1990, M.D. from Albany Medical College in 1995 with a research year at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and completed his medical internship in 1996 from the Yale University School of Medicine. We believe Dr. Laumas is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because his vast industry perspective in both public and private investments and financial transactions in the healthcare arena.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships among any of our executive officers or directors.
Director Independence
Prior to the consummation of this offering, our board of directors undertook a review of the independence of our directors and considered whether any director has a relationship with us that could compromise that director’s ability to exercise independent judgment in carrying out that director’s responsibilities. Our board of directors Dr. Laumas and Dr. Ryan have affirmatively determined that they both are “independent director,” as defined under the Nasdaq rules.
Committees of Our Board of Directors
Our board of directors directs the management of our business and affairs, as provided by Delaware law, and conducts its business through meetings of the board of directors and its standing committees. We will have a standing audit committee, compensation committee and nominating and corporate governance committee. In addition, from time to time, special committees may be established under the direction of the board of directors when necessary to address specific issues.
72
Audit Committee
Our audit committee is responsible for, among other things:
| ● | approving and retaining the independent auditors to conduct the annual audit of our financial statements; |
| ● | reviewing the proposed scope and results of the audit; |
| ● | reviewing and pre-approving audit and non-audit fees and services; |
| ● | reviewing accounting and financial controls with the independent auditors and our financial and accounting staff; |
| ● | reviewing and approving transactions between us and our directors, officers and affiliates; |
| ● | establishing procedures for complaints received by us regarding accounting matters; |
| ● | overseeing internal audit functions, if any; and |
| ● | preparing the report of the audit committee that the rules of the SEC require to be included in our annual meeting proxy statement. |
Upon the consummation of this offering, our audit committee consists of Dr. Sandeep Laumas and Dr. John Ryan with John Ryan serving as chair. Our board of directors has affirmatively determined that each meet the definition of “independent director” under the Nasdaq rules, and that they meet the independence standards under Rule 10A-3. Each member of our audit committee meets the financial literacy requirements of the Nasdaq rules. In addition, our board of directors has determined that will qualify as an “audit committee financial expert,” as such term is defined in Item 407(d)(5) of Regulation S-K. Our board of directors will adopt a written charter for the audit committee, which will be available on our principal corporate website at http://www.unicycive.com concurrently with the consummation of this offering.
Compensation Committee
Our compensation committee will be responsible for, among other things:
| ● | reviewing and recommending the compensation arrangements for management, including the compensation for our president and chief executive officer; |
| ● | establishing and reviewing general compensation policies with the objective to attract and retain superior talent, to reward individual performance and to achieve our financial goals; |
| ● | administering our stock incentive plans; and |
| ● | preparing the report of the compensation committee that the rules of the SEC require to be included in our annual meeting proxy statement. |
Upon the consummation of this offering, our compensation committee will consist of , with serving as chair. Our board has determined that are independent directors under Nasdaq rules. Our board of directors will adopt a written charter for the compensation committee, which will be available on our principal corporate website at http://www.unicycive.com concurrently with the consummation of this offering.
73
Nominating and Governance Committee
Our nominating and governance committee will be responsible for, among other things:
| ● | nominating members of the board of directors; |
| ● | developing a set of corporate governance principles applicable to our company; and |
| ● | overseeing the evaluation of our board of directors. |
Upon the consummation of this offering, our nominating and corporate governance committee will consist of , , and , with serving as chair. Our board has determined that are independent directors under Nasdaq rules. Our board of directors will adopt a written charter for the nominating and governance committee, which will be available on our principal corporate website at http://www.unicycive.com concurrently with the consummation of this offering.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Prior to the completion of this offering, we will adopt a written code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions. A copy of the code will be posted on our website, www.unicycive.com. In addition, we intend to post on our website all disclosures that are required by law or the Nasdaq rules concerning any amendments to, or waivers from, any provision of the code.
Limitations on Liability and Indemnification Matters
Upon the closing of this offering, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation will contain provisions that limit the liability of our current and former directors for monetary damages to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Delaware law provides that directors of a corporation will not be personally liable for monetary damages for any breach of fiduciary duties as directors, except liability for:
| ● | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders; |
| ● | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| ● | unlawful payments of dividends or unlawful stock repurchases or redemptions as provided in Section 174 of the Delaware General Corporation Law; or |
| ● | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
This limitation of liability does not apply to liabilities arising under federal securities laws and does not affect the availability of equitable remedies such as injunctive relief or rescission.
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation to be in effect upon the closing of this offering will provide that we are authorized to indemnify our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be in effect upon the closing of this offering will provide that we are required to indemnify our directors and executive officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Our Amended and Restated Bylaws will also provide that, upon satisfaction of certain conditions, we are required to advance expenses incurred by a director or executive officer in advance of the final disposition of any action or proceeding, and permit us to secure insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in that capacity regardless of whether we would otherwise be permitted to indemnify him or her under the provisions of Delaware law. Our Amended and Restated Bylaws will also provide our board of directors with discretion to indemnify our other officers and employees when determined appropriate by our board of directors. We expect to enter into agreements to indemnify our directors, executive officers and other employees as determined by the board of directors. With certain exceptions, these agreements provide for indemnification for related expenses, including, among other things, attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines and settlement amounts incurred by any of these individuals in any action or proceeding. We believe that these provisions and agreements are necessary to attract and retain qualified persons as directors and officers. We also maintain and intend to continue to maintain obtain customary directors’ and officers’ liability insurance upon consummation of this offering.
The limitation of liability and indemnification provisions in our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws to be in effect upon the closing of this offering may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against our directors for breach of their fiduciary duty. They may also reduce the likelihood of derivative litigation against our directors and officers, even though an action, if successful, might benefit us and other stockholders. Further, a stockholder’s investment may be adversely affected to the extent that we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers as required by these indemnification provisions. At present, there is no pending litigation or proceeding involving any of our directors, officers or employees for which indemnification is sought, and we are not aware of any threatened litigation that may result in claims for indemnification.
74
EXECUTIVE AND DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
Summary Compensation Table
The following table presents the compensation awarded to, earned by or paid to each of our named executive officers for each of the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary(1) ($) | Bonus ($) | Stock awards ($) | Option awards (2) ($) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) | Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) | All Other Compensation(3) ($) | Total ($) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D., | 2019 | 262,500 | 50,000 | - | 2,288 | 314,788 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer | 2018 | 145,833 | 20,833 | 20,146 | 186,812 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents salary and bonus earned, but not all paid. |
| (2) | Reflects the aggregate grant date fair value computed in accordance with ASC Topic 718. These amounts do not necessarily correspond to the actual value that may be recognized by the Named Executive Officers. |
Outstanding Equity Awards at December 31, 2019
The following table provides information regarding awards held by each of our named executive officers that were outstanding as of December 31, 2019. There were no other equity awards outstanding as of December 31, 2019.
| Name | Number
of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) (Exercisable) |
Number
of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) (Unexercisable) |
Option Exercise Price ($) |
Option Expiration Date | ||||||||||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D., | 495,833 | 904,167 | 0.0033 | 07/25/2028 | ||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||||||||||||||
Non-Employee Director Compensation
None of our non-employee directors were compensated in cash for their services to us during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019.
Employment Agreements
We have entered into the following employment agreements with our Named Executive Officers:
Gupta Employment Agreement
We entered into an employment agreement with Shalabh Gupta, our Chief Executive Officer, on September 28, 2018 (the “Gupta Employment Agreement”), pursuant to which Dr. Gupta serves as our Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman. Pursuant to the Gupta Employment Agreement, Dr. Gupta shall (i) receive a base salary of $350,000 per year, which base salary shall increase to $495,000 upon the earlier of (A) the date upon which we sell equity securities (or securities convertible into equity securities) in one or a series of related transactions of more than $2 million (the “Employment Agreement Financing Event”) and (B) the date upon which a registration statement is declared effective by the SEC and our securities become subject to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act and (ii) an annual bonus of $50,000 upon the achievement of certain objectives to be determined by the Company’s board of directors; provided, however, after the occurrence of an Employment Agreement Financing Event, Dr. Gupta shall be eligible to receive an annual bonus between 30% to 50% of his then base salary. In addition, Dr. Gupta shall be eligible to participate in our equity incentive plans as well as all rights and benefits for which he shall be eligible under any benefit or other plans as we shall make available to our executive officers from time to time.
If Dr. Gupta’s employment is terminated as a result of an Involuntary Termination (as defined in the Gupta Employment Agreement) within two months prior to or within one year following a Change in Control (as defined in the Gupta Employment Agreement) (such period, the “Change in Control Period”), Dr. Gupta shall receive (i) 18 months of his then base salary; (ii) his annual target bonus for the year during which the termination occurs on a pro rata basis and (iii) COBRA benefits for a period of 18 months following termination. In addition, (i) any unvested stock options or other equity awards held by Dr. Gupta shall accelerate and vest in full; and (ii) any outstanding and vested stock options and stock appreciation rights will remain exercisable until the 12 month anniversary of his termination date.
75
In the event that the proposed Change in Control is terminated prior to consummation, any unvested portion of Dr. Gupta’s equity awards will automatically be forfeited permanently without having vested. If Dr. Gupta’s employment with us is terminated as a result of an Involuntary Termination outside of the Change in Control Period, Dr. Gupta shall receive (i) 12 months of his then base salary; (ii) his annual target bonus for the year during which the termination occurs on a pro rata basis and (iii) COBRA benefits for a period of 12 months following termination. In addition, (i) any unvested stock options or other equity awards held by Dr. Gupta shall accelerate and vest in full; and (ii) any outstanding and vested stock options and stock appreciation rights will remain exercisable until the 12 month anniversary of his termination date. In the event Dr. Gupta’s employment is terminated for Cause (as defined in the Gupta Employment Agreement), Dr. Gupta shall receive (i) base salary up to and through the date of termination, (ii) any earned but unpaid bonus through the date of termination, (iii) any expense reimbursement amounted owed to Dr. Gupta through the date of termination; and (iv) any stock options, to the extent such options have vested, may be retained by Dr. Gupta subject to the terms and conditions of such award (the “Severance Benefits”). Pursuant to the Gupta Employment Agreement, any termination benefits described therein shall be subject to Dr. Gupta’s execution of a release of all claims against us. Dr. Gupta may terminate the Gupta Employment Agreement upon 60 days prior written notice, and upon such termination, Dr. Gupta shall receive the Severance Benefits.
Upon the closing of the offering contemplated by this registration statement, we will enter into an amended and restated employment agreement with Shalabh Gupta. The form of the amended and restated employment agreement is filed herewith as Exhibit 10.20.
2018 Equity Incentive Plan
The following is a summary of the material features of our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2018 Plan”). This summary is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the 2018 Plan, a copy of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
Authorized Shares. Our board of directors adopted the 2018 Plan pursuant to which we have reserved 2,000,000 shares of common stock for issuance thereunder.
Types of Awards. The 2018 Plan provides for the issuance of incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”), restricted stock and restricted stock units (“RSUs”).
Administration. The 2018 Plan will be administered by our board of directors or a Committee (as defined in the 2018 Plan) (the “2018 Plan administrator”). The 2018 Plan administrator will have the authority, in its discretion to, among other things, determine the Fair Market Value (as defined in the 2018 Plan); to select the Service Providers (as defined in the 2018 Plan) to whom awards may be granted; to determine the terms and conditions of any award; to modify or amend each award; and to make all other determinations deemed necessary or advisable for administering the 2018 Plan.
Restricted Stock and Restricted Stock Units. Restricted stock and RSUs may be granted under the 2018 Plan. The plan administrator will determine the purchase price, vesting schedule and performance goals, if any, and any other conditions that apply to a grant of restricted stock and RSUs. Unless the applicable award agreement provides otherwise, participants with restricted stock will generally have all of the rights of a stockholder.
Options. Incentive stock options and non-statutory stock options may be granted under the 2018 Plan. An “incentive stock option” means an option intended to qualify for tax treatment applicable to incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Internal Revenue Code”). A “non-statutory stock option” is an option that is not subject to statutory requirements and limitations required for certain tax advantages that are allowed under specific provisions of the Internal Revenue Code. Each option granted under the 2018 Plan will be designated as a non-qualified stock option or an incentive stock option.
The exercise period of an option may not exceed ten years from the date of grant (five years in the case of incentive stock options granted to 10% stockholders) and the exercise price may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the date the option is granted (110% of fair market value in the case of incentive stock options granted to 10% stockholders). The exercise price for shares of common stock subject to an option may be paid as determined by the 2018 Plan administrator in its sole discretion. The option holder will have no rights to dividends, voting rights or other rights of a stockholder with respect to the shares of common stock subject to an option until the option holder has given written notice of exercise and paid the exercise price and applicable withholding taxes and the shares of common stock have been issued to such option holder.
Stock Appreciation Rights. A SAR will entitle its holder to receive, at the time of exercise, an amount per share up to the excess of the fair market value (at the date of exercise) of a share of common stock over the base price of the SAR (which shall be no less than 100% of the fair market value of the related shares of common stock on the date of grant) multiplied by the number of shares in respect of which the SAR is being exercised. The exercise period of a SAR may not exceed ten years from the date of grant.
The holder of a SAR will have no rights to dividends, voting rights or other rights of a stockholder with respect to the shares of common stock subject to the SAR until the holder has given written notice of exercise and paid the exercise price and applicable withholding taxes and the shares of common stock have been issued to such SAR holder. The exercise price for a SAR may be paid as determined by the 2018 Plan administrator in its sole discretion.
Tax Withholding
Each participant will be required to make arrangements satisfactory to the 2018 Plan administrator regarding payment of up to the maximum statutory tax rates in the participant’s applicable jurisdiction with respect to any award granted under the 2018 Plan, as determined by us. We have the right, to the extent permitted by applicable law, to deduct any such taxes from any payment of any kind otherwise due to the participant.
76
2019 Stock Option Plan
The following is a summary of the material features of our 2019 Stock Option Plan (the “2019 Plan”). This summary is qualified in its entirety by the full text of the 2019 Plan, a copy of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
Authorized Shares. Our board of directors adopted the 2019 Plan pursuant to which we have reserved 1,500,000 shares of common stock for issuance thereunder.
Types of Awards. The 2019 Plan provides for the issuance of incentive stock options and non-statutory stock options.
Administration. The 2019 Plan will be administered by our board of directors or a Committee (as defined in the 2019 Plan) (the “2019 Plan administrator”). The 2019 Plan administrator will have the authority, in its discretion to, among other things, determine the Fair Market Value (as defined in the 2019 Plan); to select the Service Providers (as defined in the 2019 Plan) to whom awards may be granted; to determine the terms and conditions of any award; to modify or amend each award; and to make all other determinations deemed necessary or advisable for administering the 2019 Plan.
Options. Incentive stock options and non-statutory stock options may be granted under the 2019 Plan. An “incentive stock option” means an option intended to qualify for tax treatment applicable to incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Internal Revenue Code”). A “non-statutory stock option” is an option that is not subject to statutory requirements and limitations required for certain tax advantages that are allowed under specific provisions of the Internal Revenue Code. Each option granted under the 2019 Plan will be designated as a non-qualified stock option or an incentive stock option.
The exercise period of an option may not exceed ten years from the date of grant (five years in the case of incentive stock options granted to 10% stockholders) and the exercise price may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the date the option is granted (110% of fair market value in the case of incentive stock options granted to 10% stockholders). The exercise price for shares of common stock subject to an option may be paid as determined by the 2019 Plan administrator in its sole discretion. The option holder will have no rights to dividends, voting rights or other rights of a stockholder with respect to the shares of common stock subject to an option until the option holder has given written notice of exercise and paid the exercise price and applicable withholding taxes and the shares of common stock have been issued to such option holder.
Tax Withholding
Each participant will be required to make arrangements satisfactory to the 2019 Plan administrator regarding payment of up to the maximum statutory tax rates in the participant’s applicable jurisdiction with respect to any award granted under the 2019 Plan, as determined by us. We have the right, to the extent permitted by applicable law, to deduct any such taxes from any payment of any kind otherwise due to the participant.
77
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS
The following includes a summary of transactions during our fiscal years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 to which we have been a party, including transactions in which the amount involved in the transaction exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years, and in which any of our directors, executive officers or, to our knowledge, beneficial owners of more than 5% of our capital stock or any member of the immediate family of any of the foregoing persons had or will have a direct or indirect material interest, other than equity and other compensation, termination, change in control and other arrangements, which are described elsewhere in this prospectus. We are not otherwise a party to a related party transaction, and no transaction is currently proposed, in which the amount of the transaction exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years and in which a related person had or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
Service Agreement with Globavir Biosciences, Inc.
On July 1, 2017, we entered into a Service Agreement with Globavir Biosciences, Inc. (“Globavir”), as amended on April 6, 2020, pursuant to which Globavir provides us (i) with access to and use of certain office space; (ii) administrative office services and equipment; (iii) access to and use of consulting services of Globavir’s employees in connection with our drug development programs; and (iv) such other administrative and consulting services as are agreed upon by us and Globavir from time to time. Pursuant to the Service Agreement, we paid Globavir $50,000 per month through December 31, 2019 and $10,000 per month commencing on January 1, 2020. The Service Agreement shall continue until December 31, 2020 (the “Initial Term”) unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms thereof. Unless terminated, the Service Agreement shall automatically renew for successive one month periods after the termination of the Initial Term. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, $108,000 and $111,000, respectively, is owed by us for such services. Our Chief Executive Officer is the Chief Executive Officer and majority stockholder of Globavir.
Related Person Transaction Policy
Prior to this offering, we have not had a formal policy regarding approval of transactions with related parties. Upon consummation of this offering, we shall adopt a related person transaction policy that sets forth our procedures for the identification, review, consideration and approval or ratification of related person transactions. The policy will become effective immediately upon the execution of the underwriting agreement for this offering. For purposes of our policy only, a related person transaction is a transaction, arrangement or relationship, or any series of similar transactions, arrangements or relationships, in which we and any related person are, were or will be participants in which the amount involved exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end. Transactions involving compensation for services provided to us as an employee or director are not covered by this policy. A related person is any executive officer, director or beneficial owner of more than 5% of any class of our voting securities, including any of their immediate family members and any entity owned or controlled by such persons.
78
Under the policy, if a transaction has been identified as a related person transaction, including any transaction that was not a related person transaction when originally consummated or any transaction that was not initially identified as a related person transaction prior to consummation, our management must present information regarding the related person transaction to our audit committee, or, if audit committee approval would be inappropriate, to another independent body of our board of directors, for review, consideration and approval or ratification. The presentation must include a description of, among other things, the material facts, the interests, direct and indirect, of the related persons, the benefits to us of the transaction and whether the transaction is on terms that are comparable to the terms available to or from, as the case may be, an unrelated third party or to or from employees generally. Under the policy, we will collect information that we deem reasonably necessary from each director, executive officer and, to the extent feasible, significant stockholder to enable us to identify any existing or potential related-person transactions and to effectuate the terms of the policy. In addition, under our code of business conduct and ethics, our employees and directors will have an affirmative responsibility to disclose any transaction or relationship that reasonably could be expected to give rise to a conflict of interest. In considering related person transactions, our audit committee, or other independent body of our board of directors, will take into account the relevant available facts and circumstances including, but not limited to:
| ● | the risks, costs and benefits to us; |
| ● | the impact on a director’s independence in the event that the related person is a director, immediate family member of a director or an entity with which a director is affiliated; |
| ● | the availability of other sources for comparable services or products; and |
| ● | the terms available to or from, as the case may be, unrelated third parties or to or from employees generally. |
The policy requires that, in determining whether to approve, ratify or reject a related person transaction, our audit committee, or other independent body of our board of directors, must consider, in light of known circumstances, whether the transaction is in, or is not inconsistent with, our best interests and those of our stockholders, as our audit committee, or other independent body of our board of directors, determines in the good faith exercise of its discretion.
79
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of September 14, 2020 by:
| ● | each of our named executive officers; |
| ● | each of our directors; |
| ● | all of our current directors and named executive officers as a group; and |
| ● | each stockholder known by us to own beneficially more than 5% of our common stock. |
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC and includes voting or investment power with respect to the securities. Shares of common stock that may be acquired by an individual or group within 60 days of September 14, 2020, pursuant to the exercise of options or warrants, vesting of common stock or conversion of convertible debt, are deemed to be outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of such individual or group, but are not deemed to be outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person shown in the table. Percentage of ownership is based on 36,534,840 shares of common stock issued and outstanding as of September 14, 2020.
Except as indicated in footnotes to this table, we believe that the stockholders named in this table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock shown to be beneficially owned by them, based on information provided to us by such stockholders. Unless otherwise indicated, the address for each director and executive officer listed is: c/o Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc., 5150 El Camino Real, Suite A-32, Los Altos, CA 94022.
| Number of Shares Beneficially Owned | Percentage of Common Stock Beneficially Owned | |||||||||||
| Name of Beneficial Owner | Prior to Offering | Before Offering | After Offering | |||||||||
| Directors and Named Executive Officers: | ||||||||||||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D. | 24,623,578 | (1) | 67.40 | % | % | |||||||
| John Ryan, M.D., Ph.D. | 327,083 | (2) | * | % | % | |||||||
| Sandeep Laumas, M.D. | 482,083 | (3) | 1.32 | % | % | |||||||
| Pramod Gupta, Ph.D. | 56,250 | (4) | * | % | % | |||||||
| Keith Ward, Ph.D. | 38,542 | (5) | * | % | % | |||||||
| All current named executive officers and directors as a group (5 persons) | 25,527,536 | 69.73 | % | % | ||||||||
| 5% or Greater Stockholders | ||||||||||||
| * | less than 1% |
| (1) | Includes an aggregate of (i) 23,836,078 shares of common stock held by Dr. Gupta and/or entities controlled by Dr. Gupta; (ii) 729,167 shares of common stock underlying vested options to purchase shares of common stock; and (iii) 58,333 shares of common stock that will vest within 60 days of September 14, 2020. |
| (2) | Includes an aggregate of (i) 300,000 shares of common stock held by Dr. Ryan (ii) 25,000 shares of common stock underlying vested options to purchase shares of common stock; and (iii) 2,083 shares of common stock that will vest within 60 days of September 14, 2020. |
| (3) | Includes an aggregate of (i) 455,000 shares of common stock held by Dr. Laumas and/or entities controlled by Dr. Laumas; (ii) 25,000 shares of common stock underlying vested options to purchase shares of common stock; and (iii) 2,083 shares of common stock that will vest within 60 days of September 14, 2020. |
| (4) | Includes an aggregate of (i) 56,250 shares of common stock that will vest within 60 days of September 14, 2020. |
| (5) | Includes an aggregate of (i) 38,342 shares of common stock that will vest within 60 days of September 14, 2020. |
80
General
Our authorized capital stock consists of 200,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share, and 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share.
As of September 14, 2020 there were 36,534,840 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding held by 126 holders of record.
The following description of our capital stock and provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon the completion of this offering is only a summary. You should also refer to our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, a copy of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and our Amended and Restated Bylaws, a copy of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Common Stock
We are authorized to issue up to a total of 200,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share. Holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders. Holders of our common stock have no cumulative voting rights.
Further, holders of our common stock have no preemptive or conversion rights or other subscription rights. Upon our liquidation, dissolution or winding-up, holders of our common stock are entitled to share in all assets remaining after payment of all liabilities and the liquidation preferences of any of our outstanding shares of preferred stock. Subject to preferences that may be applicable to any outstanding shares of preferred stock, holders of our common stock are entitled to receive dividends, if any, as may be declared from time to time by our board of directors out of our assets which are legally available. Each outstanding share of our common stock is, and all shares of common stock to be issued in this offering when they are paid for will be, fully paid and non-assessable.
The holders of a majority of the shares of our capital stock, represented in person or by proxy, are necessary to constitute a quorum for the transaction of business at any meeting. If a quorum is present, an action by stockholders entitled to vote on a matter is approved if the number of votes cast in favor of the action exceeds the number of votes cast in opposition to the action, with the exception of the election of directors, which requires a plurality of the votes cast.
Preferred Stock
Our board of directors will have the authority, without further action by the stockholders, to issue up to 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series and to fix the designations, powers, preferences, privileges, and relative participating, optional, or special rights as well as the qualifications, limitations, or restrictions of the preferred stock, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, and liquidation preferences, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of the common stock. Our board of directors, without stockholder approval, will be able to issue convertible preferred stock with voting, conversion, or other rights that could adversely affect the voting power and other rights of the holders of common stock. Preferred stock could be issued quickly with terms calculated to delay or prevent a change of control or make removal of management more difficult. Additionally, the issuance of preferred stock may have the effect of decreasing the market price of our common stock, and may adversely affect the voting and other rights of the holders of common stock. At present, we have no plans to issue any shares of preferred stock following this offering.
81
Options
Our 2018 Plan provides for us to sell or issue shares of common stock or restricted shares of common stock, or to grant incentive stock options or nonqualified stock options, SARs and RSU awards for the purchase of shares of common stock to certain service providers. As of September 14, 2020, options to purchase 1,925,000 common shares were outstanding under our 2018 Plan. For additional information regarding the terms of the 2018 Plan, see “Executive and Director Compensation—2018 Equity Incentive Plan.”
Our 2019 Plan provides for us to grant incentive stock options or nonqualified stock options for the purchase of shares of common stock to certain service providers. As of September 14, 2020, options to purchase 1,455,000 common shares were outstanding under our 2019 Plan. For additional information regarding the terms of the 2019 Plan, see “Executive and Director Compensation—2019 Stock Option Plan.”
Exclusive Forum
Our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering provides that unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the State of Delaware is the sole and exclusive forum for: (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of us, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director, officer or other employee of our Company to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation or our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering, or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers, employees or agents governed by the internal affairs doctrine, except for, as to each of (i) through (iv) above, any claim as to which the Court of Chancery determines that there is an indispensable party not subject to the jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery (and the indispensable party does not consent to the personal jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery within ten days following such determination), which is vested in the exclusive jurisdiction of a court or forum other than the Court of Chancery, or for which the Court of Chancery does not have subject matter jurisdiction.
Additionally, our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon completion of this offering provide that unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock are deemed to have notice of and consented to this provision.
Anti-Takeover Provisions of Delaware Law, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and our Amended and Restated Bylaws
Delaware Law
We are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the DGCL. In general, Section 203 prohibits a publicly traded Delaware corporation from engaging in a business combination with an interested stockholder for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person became an interested stockholder, unless the business combination is approved in a prescribed manner. A business combination includes mergers, asset sales or other transactions resulting in a financial benefit to the stockholder. An interested stockholder is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns (or within three years, did own) 15% or more of the corporation’s voting stock, subject to certain exceptions. The statute could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of our Company.
Board of Directors Vacancies
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon the completion of this offering authorize only our board of directors to fill vacant directorships. In addition, the number of directors constituting our board of directors may be set only by resolution of the majority of the incumbent directors.
Special Meeting of Stockholders
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon the completion of this offering further provide that special meetings of our stockholders may be called by a majority of the board of directors, the Chief Executive Officer, or the Chairman of the board of directors.
82
Advance Notice Requirements for Stockholder Proposals and Director Nominations
Our Amended and Restated Bylaws to be effective upon the completion of this offering provide that stockholders seeking to bring business before our annual meeting of stockholders, or to nominate candidates for election as directors at our annual meeting of stockholders, must provide timely notice of their intent in writing. To be timely, a stockholder’s notice must be delivered to the secretary at our principal executive offices not later than the close of business on the 90th day nor earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to the first anniversary of the preceding year’s annual meeting; provided, however, that in the event the date of the annual meeting is more than 30 days before or more than 60 days after such anniversary date, or if no annual meeting was held in the preceding year, notice by the stockholder to be timely must be so delivered not earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to such annual meeting and not later than the close of business on the later of the 90th day prior to such annual meeting or the 10th day following the day on which a public announcement of the date of such meeting is first made by us. These provisions may preclude our stockholders from bringing matters before our annual meeting of stockholders or from making nominations for directors at our annual meeting of stockholders.
Authorized but Unissued Shares
Our authorized but unissued shares of common stock and preferred stock are available for future issuance without stockholder approval and may be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings to raise additional capital, corporate acquisitions and employee benefit plans. The existence of authorized but unissued and unreserved common stock and preferred stock could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of us by means of a proxy contest, tender offer, merger or otherwise. If we issue such shares without stockholder approval and in violation of limitations imposed by the Nasdaq Capital Market or any stock exchange on which our stock may then be trading, our stock could be delisted.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our common stock is Philadelphia Stock Transfer, 2320 Haverford Rd, Suite 230, Ardmore, PA 19003.
Stock Market Listing
We have applied to have our shares of common stock listed for trading on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “UNCY.” No assurance can be given that such listing will be approved.
83
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock, and a liquid trading market for our common stock may not develop or be sustained after this offering. Future sales of substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market, or the anticipation of these sales, could materially and adversely affect market prices prevailing from time to time, and could impair our ability to raise capital through sales of equity or equity-related securities.
Only a limited number of shares of our common stock will be available for sale in the public market for a period of several months after completion of this offering due to contractual and legal restrictions on resale described below. Nevertheless, sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market after such restrictions lapse, or the perception that those sales may occur, could materially and adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock. Although we have applied to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Capital Market, we cannot assure you that there will be an active market for our common stock.
Of the shares to be outstanding immediately after the completion of this offering, we expect that the shares to be sold in this offering and the shares of common stock sold by the selling stockholders will be freely tradable without restriction under the Securities Act unless purchased by our “affiliates,” as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. Certain of the remaining shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering will be subject to a -day lock-up period under the lock-up agreements as described below. These restricted securities may be sold in the public market only if registered or pursuant to an exemption from registration, such as Rule 144 or Rule 701 under the Securities Act.
Rule 144
Affiliate Resales of Restricted Securities
Affiliates of ours must generally comply with Rule 144 if they wish to sell any shares of our common stock in the public market, whether or not those shares are “restricted securities.” “Restricted securities” are any securities acquired from us or one of our affiliates in a transaction not involving a public offering. All shares of our common stock issued prior to the closing of the offering made hereby, are considered to be restricted securities. The shares of our common stock sold in this offering are not considered to be restricted securities.
Non-Affiliate Resales of Restricted Securities
Any person or entity who is not an affiliate of ours and who has not been an affiliate of ours at any time during the three months preceding a sale is only required to comply with Rule 144 in connection with sales of restricted shares of our common stock. Subject to the lock-up agreements described below, those persons may sell shares of our common stock that they have beneficially owned for at least one year without any restrictions under Rule 144 immediately following the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Further, beginning 90 days after the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, a person who is not an affiliate of ours at the time such person sells shares of our common stock, and has not been an affiliate of ours at any time during the three months preceding such sale, and who has beneficially owned such shares of our common stock for at least six months but less than a year, is entitled to sell such shares so long as there is adequate current public information, as defined in Rule 144, available about us.
Resales of restricted shares of our common stock by non-affiliates are not subject to the manner of sale, volume limitation or notice filing provisions of Rule 144, described above.
Rule 701
Rule 701 generally allows a stockholder who purchased shares of our common stock pursuant to a written compensatory plan or contract and who is not deemed to have been an affiliate of ours during the immediately preceding 90 days to sell these shares in reliance upon Rule 144, but without being required to comply with the public information, holding period, volume limitation, or notice provisions of Rule 144.
Rule 701 also permits affiliates of ours to sell their Rule 701 shares under Rule 144 without complying with the holding period requirements of Rule 144. All holders of Rule 701 shares, however, are required to wait until 90 days after the date of this prospectus before selling such shares pursuant to Rule 701 and until expiration of the -day lock-up period described below.
Equity Incentive Awards
We intend to file a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act after the closing of this offering to register the shares of common stock that are issuable pursuant to our 2019 Plan and 2018 Plan. The registration statement is expected to be filed and become effective as soon as practicable after the completion of this offering. Accordingly, shares registered under the registration statement will be available for sale in the open market following its effective date, subject to Rule 144 volume limitations and the lock-up arrangement described above, if applicable.
84
MATERIAL
U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES TO
NON-U.S. HOLDERS OF OUR COMMON STOCK
The following is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to non-U.S. holders (as defined below) of the ownership and disposition of our common stock but does not purport to be a complete analysis of all the potential tax considerations relating thereto. This summary is based upon the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder, administrative rulings and judicial decisions, all as of the date hereof. These authorities may be changed, possibly retroactively, so as to result in U.S. federal income tax consequences different from those set forth below. No ruling on the U.S. federal, state, or local tax considerations relevant to our operations or to the purchase, ownership or disposition of our shares, has been requested from the IRS or other tax authority. No assurance can be given that the IRS would not assert, or that a court would not sustain, a position contrary to any of the tax consequences described below.
This summary also does not address the tax considerations arising under the laws of any non-U.S., state or local jurisdiction, or under U.S. federal gift and estate tax laws, except to the limited extent set forth below. In addition, this discussion does not address tax considerations applicable to an investor’s particular circumstances or to investors that may be subject to special tax rules, including, without limitation:
| ● | banks, insurance companies or other financial institutions, regulated investment companies or real estate investment trusts; |
| ● | persons subject to the alternative minimum tax or Medicare contribution tax on net investment income; |
| ● | tax-exempt organizations or governmental organizations; |
| ● | controlled foreign corporations, passive foreign investment companies and corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax; |
| ● | brokers or dealers in securities or currencies; |
| ● | traders in securities that elect to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for their securities holdings; |
| ● | persons that own, or are deemed to own, more than five percent of our capital stock (except to the extent specifically set forth below); |
| ● | U.S. expatriates and certain former citizens or long-term residents of the U.S.; |
| ● | partnerships or entities classified as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes or other pass-through entities (and investors therein); |
| ● | persons who hold our common stock as a position in a hedging transaction, “straddle,” “conversion transaction” or other risk reduction transaction or integrated investment; |
| ● | persons who hold or receive our common stock pursuant to the exercise of any employee stock option or otherwise as compensation; |
| ● | persons who do not hold our common stock as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Internal Revenue Code; or |
| ● | persons deemed to sell our common stock under the constructive sale provisions of the Internal Revenue Code. |
You are urged to consult your tax advisor with respect to the application of the U.S. federal income tax laws to your particular situation, as well as any tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock arising under the U.S. federal estate or gift tax rules or under the laws of any state, local, non-U.S., or other taxing jurisdiction or under any applicable tax treaty.
85
Non-U.S. Holder Defined
For purposes of this discussion, you are a non-U.S. holder (other than a partnership) if you are any holder other than:
| ● | an individual citizen or resident of the U.S. (for U.S. federal income tax purposes); |
| ● | a corporation or other entity taxable as a corporation created or organized in the U.S. or under the laws of the U.S., any state thereof, or the District of Columbia, or other entity treated as such for U.S. federal income tax purposes; |
| ● | an estate whose income is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or |
| ● | a trust (x) whose administration is subject to the primary supervision of a U.S. court and which has one or more “U.S. persons” (within the meaning of Section 7701(a)(30) of the Internal Revenue Code) who have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (y) which has made a valid election to be treated as a U.S. person. |
In addition, if a partnership or entity classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner generally will depend on the status of the partner and upon the activities of the partnership. Accordingly, partnerships that hold our common stock, and partners in such partnerships, should consult their tax advisors.
Distributions
As described in “Dividend Policy,” we have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock and do not anticipate paying any dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. However, if we do make distributions on our common stock, those payments will constitute dividends for U.S. tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. To the extent those distributions exceed both our current and our accumulated earnings and profits, they will constitute a return of capital and will first reduce your basis in our common stock, but not below zero, and then will be treated as gain from the sale of stock as described below under “— Gain on Disposition of Common Stock.”
Subject to the discussion below on effectively connected income, backup withholding and foreign accounts, any dividend paid to you generally will be subject to U.S. withholding tax either at a rate of 30% of the gross amount of the dividend or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. In order to receive a reduced treaty rate, you must provide us with an IRS Form W-8BEN, IRS Form W-8BEN-E or other appropriate version of IRS Form W-8 certifying qualification for the reduced rate. A non-U.S. holder of shares of our common stock eligible for a reduced rate of U.S. withholding tax pursuant to an income tax treaty may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by timely filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS. If the non-U.S. holder holds the stock through a financial institution or other agent acting on the non-U.S. holder’s behalf, the non-U.S. holder will be required to provide appropriate documentation to the agent, which then will be required to provide certification to us or our paying agent, either directly or through other intermediaries.
Dividends received by you that are effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by you in the U.S.) are generally exempt from such withholding tax. In order to obtain this exemption, you must provide us with an IRS Form W-8ECI or other applicable IRS Form W-8 properly certifying such exemption. Such effectively connected dividends, although not subject to withholding tax, are taxed at the same graduated rates applicable to U.S. persons, net of certain deductions and credits. In addition, if you are a corporate non-U.S. holder, dividends you receive that are effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business may also be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of 30% or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. You should consult your tax advisor regarding any applicable tax treaties that may provide for different rules.
86
Gain on Disposition of Common Stock
Subject to the discussion below regarding backup withholding and foreign accounts, you generally will not be required to pay U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other disposition of our common stock unless:
| ● | the gain is effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the gain is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by you in the U.S.); |
| ● | you are a non-resident alien individual who is present in the U.S. for a period or periods aggregating 183 days or more during the taxable year in which the sale or disposition occurs and certain other conditions are met; or |
| ● | our common stock constitutes a U.S. real property interest by reason of our status as a “U.S. real property holding corporation,” (“USRPHC”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes at any time within the shorter of (i) the five-year period preceding your disposition of our common stock, or (ii) your holding period for our common stock. |
We believe that we are not currently and will not become a USRPHC for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and the remainder of this discussion so assumes. However, because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends on the fair market value of our U.S. real property relative to the fair market value of our other business assets, there can be no assurance that we will not become a USRPHC in the future. Even if we become a USRPHC, however, as long as our common stock is regularly traded on an established securities market, such common stock will be treated as U.S. real property interests only if you actually or constructively hold more than five percent of such regularly traded common stock at any time during the shorter of the five-year period preceding your disposition of, or your holding period for, our common stock.
If you are a non-U.S. holder described in the first bullet above, you will be required to pay tax on the net gain derived from the sale under regular graduated U.S. federal income tax rates, and a corporate non-U.S. holder described in the first bullet above also may be subject to the branch profits tax at a 30% rate, or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. If you are an individual non-U.S. holder described in the second bullet above, you will be required to pay a flat 30% tax (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on the gain derived from the sale, which gain may be offset by U.S. source capital losses for the year (provided you have timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses). You should consult any applicable income tax or other treaties that may provide for different rules.
Federal Estate Tax
Our common stock beneficially owned by an individual who is not a citizen or resident of the U.S. (as defined for U.S. federal estate tax purposes) at the time of their death will generally be includable in the decedent’s gross estate for U.S. federal estate tax purposes, unless an applicable estate tax treaty provides otherwise. The test for whether an individual is a resident of the U.S. for U.S. federal estate tax purposes differs from the test used for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Some individuals, therefore, may be non-U.S. holders for U.S. federal income tax purposes, but not for U.S. federal estate tax purposes, and vice versa.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Generally, we must report annually to the IRS the amount of dividends paid to you, your name and address and the amount of tax withheld, if any. A similar report will be sent to you. Pursuant to applicable income tax treaties or other agreements, the IRS may make these reports available to tax authorities in your country of residence.
Payments of dividends or of proceeds on the disposition of stock made to you may be subject to information reporting and backup withholding at a current rate of 28% unless you establish an exemption, for example, by properly certifying your non-U.S. status on an IRS Form W-8BEN, IRS Form W-8BEN-E or another appropriate version of IRS Form W-8.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax; rather, the U.S. federal income tax liability of persons subject to backup withholding will be reduced by the amount of tax withheld. If withholding results in an overpayment of taxes, a refund or credit may generally be obtained from the IRS, provided that the required information is furnished to the IRS in a timely manner.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance
The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (“FATCA”) imposes withholding tax at a rate of 30% on dividends on and gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock paid to “foreign financial institutions” (as specially defined under these rules), unless such institution enters into an agreement with the U.S. government to withhold on certain payments and to collect and provide to the U.S. tax authorities substantial information regarding the U.S. account holders of such institution (which includes certain equity and debt holders of such institution, as well as certain account holders that are foreign entities with U.S. owners) or otherwise establishes an exemption. FATCA also generally imposes a U.S. federal withholding tax of 30% on dividends on and gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock paid to a “non-financial foreign entity” (as specially defined for purposes of these rules) unless such entity provides the withholding agent with a certification identifying certain substantial direct and indirect U.S. owners of the entity, certifies that there are none or otherwise establishes an exemption. The withholding provisions under FATCA generally apply to dividends on our common stock, and under current transition rules, are expected to apply with respect to the gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock on or after January 1, 2019. An intergovernmental agreement between the U.S. and an applicable foreign country may modify the requirements described in this paragraph. Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the possible implications of this legislation on their investment in our common stock.
Each prospective investor should consult its tax advisor regarding the particular U.S. federal, state and local and non-U.S. tax consequences of purchasing, holding and disposing of our common stock, including the consequences of any proposed change in applicable laws.
87
is acting as the representative of the underwriters and the book-running manager of this offering. Under the terms of an underwriting agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement, each of the underwriters named below has severally agreed to purchase from us the respective number of shares of common stock shown opposite its name below:
Underwriters |
Number
of Shares |
|||
The underwriting agreement provides that the underwriters’ obligation to purchase shares of common stock depends on the satisfaction of the conditions contained in the underwriting agreement including:
| ● | the representations and warranties made by us to the underwriters are true; |
| ● | there is no material change in our business or the financial markets; and |
| ● | we deliver customary closing documents to the underwriters. |
Commissions and Expenses
The following table summarizes the underwriting discounts and commissions we will pay to the underwriters. These amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares. The underwriting fee is the difference between the initial price to the public and the amount the underwriters pay to us for the shares.
| No Exercise | Full Exercise | |||||||
| Per Share | $ | $ | ||||||
| Total | $ | $ | ||||||
The representatives have advised us that the underwriters propose to offer the shares of common stock directly to the public at the public offering price on the cover of this prospectus and to selected dealers, which may include the underwriters, at such offering price less a selling concession not in excess of $ per share. After the offering, the representatives may change the offering price and other selling terms.
The expenses of this offering that are payable by us are estimated to be approximately $ (excluding estimated underwriting discounts and commissions). We have also agreed to reimburse the underwriters for certain of their expenses, in an amount up to $ , incurred in connection with review by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. of the terms of this offering, as set forth in the underwriting agreement.
Option to Purchase Additional Shares
We have granted the underwriters an option exercisable for days after the date of this prospectus, to purchase, from time to time, in whole or in part, up to an aggregate of shares from us at the public offering price less underwriting discounts and commissions. To the extent that this option is exercised, each underwriter will be obligated, subject to certain conditions, to purchase its pro rata portion of these additional shares based on the underwriter’s percentage underwriting commitment in this offering as indicated in the table at the beginning of this Underwriting Section.
88
Lock-Up Agreements
We, all of our directors, executive officers, and holders of all of our outstanding stock have agreed that, for a period of days after the date of this prospectus subject to certain limited exceptions, we and they will not directly or indirectly, without the prior written consent of , (i) offer for sale, sell, pledge, or otherwise dispose of (or enter into any transaction or device that is designed to, or could be expected to, result in the disposition by any person at any time in the future of) any shares of common stock (including, without limitation, shares of common stock that may be deemed to be beneficially owned by us or them in accordance with the rules and regulations of the SEC and shares of common stock that may be issued upon exercise of any options or warrants) or securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for common stock, (ii) enter into any swap or other derivatives transaction that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic benefits or risks of ownership of shares of common stock, whether any such transaction described in clause (i) or (ii) above is to be settled by delivery of common stock or other securities, in cash or otherwise, (iii) make any demand for or exercise any right or file or cause to be filed a registration statement, including any amendments thereto, with respect to the registration of any shares of common stock or securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for common stock or any of our other securities, or (iv) publicly disclose the intention to do any of the foregoing.
, in its sole discretion, may release the common stock and other securities subject to the lock-up agreements described above in whole or in part at any time. When determining whether or not to release common stock and other securities from lock-up agreements, will consider, among other factors, the holder’s reasons for requesting the release, the number of shares of common stock and other securities for which the release is being requested and market conditions at the time.
Offering Price Determination
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. The initial public offering price was negotiated between the representative and us. In determining the initial public offering price of our common stock, the representative considered:
| ● | the history and prospects for the industry in which we compete; |
| ● | our financial information; |
| ● | the ability of our management and our business potential and earning prospects; |
| ● | the prevailing securities markets at the time of this offering; and |
| ● | the recent market prices of, and the demand for, publicly traded shares of generally comparable companies. |
Indemnification
We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, and to contribute to payments that the underwriters may be required to make for these liabilities.
Stabilization, Short Positions and Penalty Bids
The representatives may engage in stabilizing transactions, short sales and purchases to cover positions created by short sales, and penalty bids or purchases for the purpose of pegging, fixing or maintaining the price of the common stock, in accordance with Regulation M under the Exchange Act:
| ● | Stabilizing transactions permit bids to purchase the underlying security so long as the stabilizing bids do not exceed a specified maximum. |
89
| ● | A short position involves a sale by the underwriters of shares in excess of the number of shares the underwriters are obligated to purchase in the offering, which creates the syndicate short position. This short position may be either a covered short position or a naked short position. In a covered short position, the number of shares involved in the sales made by the underwriters in excess of the number of shares they are obligated to purchase is not greater than the number of shares that they may purchase by exercising their option to purchase additional shares. In a naked short position, the number of shares involved is greater than the number of shares in their option to purchase additional shares. The underwriters may close out any short position by either exercising their option to purchase additional shares and/or purchasing shares in the open market. In determining the source of shares to close out the short position, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the price of shares available for purchase in the open market as compared to the price at which they may purchase shares through their option to purchase additional shares. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there could be downward pressure on the price of the shares in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in the offering. |
| ● | Syndicate covering transactions involve purchases of the common stock in the open market after the distribution has been completed in order to cover syndicate short positions. |
| ● | Penalty bids permit the representatives to reclaim a selling concession from a syndicate member when the common stock originally sold by the syndicate member is purchased in a stabilizing or syndicate covering transaction to cover syndicate short positions. |
These stabilizing transactions, syndicate covering transactions and penalty bids may have the effect of raising or maintaining the market price of our common stock or preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the common stock. As a result, the price of the common stock may be higher than the price that might otherwise exist in the open market. These transactions may be effected on The Nasdaq Capital Market or otherwise and, if commenced, may be discontinued at any time.
Neither we nor any of the underwriters make any representation or prediction as to the direction or magnitude of any effect that the transactions described above may have on the price of the common stock. In addition, neither we nor any of the underwriters make any representation that the representatives will engage in these stabilizing transactions or that any transaction, once commenced, will not be discontinued without notice.
Electronic Distribution
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available on the Internet sites or through other online services maintained by one or more of the underwriters and/or selling group members participating in this offering, or by their affiliates. In those cases, prospective investors may view offering terms online and, depending upon the particular underwriter or selling group member, prospective investors may be allowed to place orders online. The underwriters may agree with us to allocate a specific number of shares for sale to online brokerage account holders. Any such allocation for online distributions will be made by the representatives on the same basis as other allocations.
Other than the prospectus in electronic format, the information on any underwriter’s or selling group member’s web site and any information contained in any other web site maintained by an underwriter or selling group member is not part of the prospectus or the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, has not been approved and/or endorsed by us or any underwriter or selling group member in its capacity as underwriter or selling group member and should not be relied upon by investors.
Listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market
We intend to apply to have our common stock listed on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “UNCY.”
Discretionary Sales
The underwriters have informed us that they do not expect to sell more than 5% of the common stock in the aggregate to accounts over which they exercise discretionary authority.
90
Stamp Taxes
If you purchase shares of common stock offered in this prospectus, you may be required to pay stamp taxes and other charges under the laws and practices of the country of purchase, in addition to the offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus.
Other Relationships
The underwriters and certain of their affiliates are full service financial institutions engaged in various activities, which may include securities trading, commercial and investment banking, financial advisory, investment management, investment research, principal investment, hedging, financing and brokerage activities. The underwriters and certain of their affiliates have, from time to time, performed, and may in the future perform, various commercial and investment banking and financial advisory services for the issuer and its affiliates, for which they received or may in the future receive customary fees and expenses.
In the ordinary course of their various business activities, the underwriters and certain of their affiliates may make or hold a broad array of investments and actively trade debt and equity securities (or related derivative securities) and financial instruments (including bank loans) for their own account and for the accounts of their customers, and such investment and securities activities may involve securities and/or instruments of the issuer or its affiliates. If the underwriters or their affiliates have a lending relationship with us, they routinely hedge their credit exposure to us consistent with their customary risk management policies. The underwriters and their affiliates may hedge such exposure by entering into transactions which consist of either the purchase of credit default swaps or the creation of short positions in our securities or the securities of our affiliates, including potentially the shares of common stock offered hereby. Any such credit default swaps or short positions could adversely affect future trading prices of the shares of common stock offered hereby. The underwriters and certain of their affiliates may also communicate independent investment recommendations, market color or trading ideas and/or publish or express independent research views in respect of such securities or instruments and may at any time hold, or recommend to clients that they acquire, long and/or short positions in such securities and instruments.
Selling Restrictions
This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell to, or a solicitation of an offer to buy from, anyone in any country or jurisdiction (i) in which such an offer or solicitation is not authorized, (ii) in which any person making such offer or solicitation is not qualified to do so or (iii) in which any such offer or solicitation would otherwise be unlawful. No action has been taken that would, or is intended to, permit a public offer of the shares of common stock or possession or distribution of this prospectus or any other offering or publicity material relating to the shares of common stock in any country or jurisdiction (other than the U.S.) where any such action for that purpose is required. Accordingly, each underwriter has undertaken that it will not, directly or indirectly, offer or sell any shares of common stock or have in its possession, distribute or publish any prospectus, form of application, advertisement or other document or information in any country or jurisdiction except under circumstances that will, to the best of its knowledge and belief, result in compliance with any applicable laws and regulations and all offers and sales of shares of common stock by it will be made on the same terms.
European Economic Area
In relation to each Member State of the European Economic Area which has implemented the Prospectus Directive (each, a “Relevant Member State”) an offer to the public of any common stock which are the subject of the offering contemplated herein may not be made in that Relevant Member State, except that an offer to the public in that Relevant Member State of any common stock may be made at any time under the following exemptions under the Prospectus Directive, if they have been implemented in that Relevant Member State:
| ● | to legal entities which are qualified investors as defined under the Prospectus Directive; |
| ● | by the underwriters to fewer than 100, or, if the Relevant Member State has implemented the relevant provisions of the 2010 PD Amending Directive, 150, natural or legal persons (other than qualified investors as defined in the Prospectus Directive), as permitted under the Prospectus Directive, subject to obtaining the prior consent of the representatives of the underwriters for any such offer; or |
| ● | in any other circumstances falling within Article 3(2) of the Prospectus Directive, |
provided that no such offer of common stock shall result in a requirement for us or any underwriter to publish a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Directive or supplement a prospectus pursuant to Article 16 of the Prospectus Directive.
91
Each person in a Relevant Member State who receives any communication in respect of, or who acquires any common stock under, the offers contemplated here in this prospectus will be deemed to have represented, warranted and agreed to and with each underwriter and us that:
| ● | it is a qualified investor as defined under the Prospectus Directive; and |
| ● | in the case of any common stock acquired by it as a financial intermediary, as that term is used in Article 3(2) of the Prospectus Directive, (i) the common stock acquired by it in the offering have not been acquired on behalf of, nor have they been acquired with a view to their offer or resale to, persons in any Relevant Member State other than qualified investors, as that term is defined in the Prospectus Directive, or in the circumstances in which the prior consent of the representatives of the underwriters has been given to the offer or resale or (ii) where common stock have been acquired by it on behalf of persons in any Relevant Member State other than qualified investors, the offer of such common stock to it is not treated under the Prospectus Directive as having been made to such persons. |
For the purposes of this representation and the provision above, the expression an “offer of common stock to the public” in relation to any common stock in any Relevant Member State means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and any common stock to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase or subscribe for the common stock, as the same may be varied in that Relevant Member State by any measure implementing the Prospectus Directive in that Relevant Member State, the expression “Prospectus Directive” means Directive 2003/71/EC (and amendments thereto, including the 2010 PD Amending Directive, to the extent implemented in the Relevant Member State), and includes any relevant implementing measure in each Relevant Member State and the expression “2010 PD Amending Directive” means Directive 2010/73/EU.
United Kingdom
This prospectus has only been communicated or caused to have been communicated and will only be communicated or caused to be communicated as an invitation or inducement to engage in investment activity (within the meaning of Section 21 of the Financial Services and Markets Act of 2000 (the “FSMA”)) as received in connection with the issue or sale of the common stock in circumstances in which Section 21(1) of the FSMA does not apply to us. All applicable provisions of the FSMA will be complied with in respect to anything done in relation to the common stock in, from or otherwise involving the United Kingdom.
Notice to Residents of Canada
The securities may be sold only to purchasers purchasing, or deemed to be purchasing, as principal that are accredited investors, as defined in National Instrument 45-106 Prospectus Exemptions or subsection 73.3(1) of the Securities Act (Ontario), and are permitted clients, as defined in National Instrument 31-103 Registration Requirements, Exemptions and Ongoing Registrant Obligations. Any resale of the securities must be made in accordance with an exemption from, or in a transaction not subject to, the prospectus requirements of applicable securities laws.
Securities legislation in certain provinces or territories of Canada may provide a purchaser with remedies for rescission or damages if this prospectus (including any amendment thereto) contains a misrepresentation, provided that the remedies for rescission or damages are exercised by the purchaser within the time limit prescribed by the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory. The purchaser should refer to any applicable provisions of the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory for particulars of these rights or consult with a legal advisor.
Pursuant to section 3A.3 (or, in the case of securities issued or guaranteed by the government of a non-Canadian jurisdiction, section 3A.4) of National Instrument 33-105 Underwriting Conflicts (NI 33-105), the underwriters are not required to comply with the disclosure requirements of NI 33-105 regarding underwriter conflicts of interest in connection with this offering.
92
The validity of the issuance of the common stock offered by us in this offering will be passed upon for us by Sheppard, Mullin, Richter & Hampton LLP, New York, New York. Certain legal matters in connection with this offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by .
The financial statements of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 and for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, included in this registration statement, of which this prospectus forms a part, have been audited by Mayer Hoffman McCann P.C., independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon (which includes an explanatory paragraph related to the existence of substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern) appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in auditing and accounting in giving said report.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the common stock offered by this prospectus. This prospectus, which is part of the registration statement, omits certain information, exhibits, schedules and undertakings set forth in the registration statement. For further information pertaining to us and our common stock, reference is made to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules to the registration statement. Statements contained in this prospectus as to the contents or provisions of any documents referred to in this prospectus are not necessarily complete, and in each instance where a copy of the document has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement, reference is made to the exhibit for a more complete description of the matters involved.
You may read and copy all or any portion of the registration statement without charge at the public reference room of the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Copies of the registration statement may be obtained from the SEC at prescribed rates from the public reference room of the SEC at such address. You may obtain information regarding the operation of the public reference room by calling 1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, registration statements and certain other filings made with the SEC electronically are publicly available through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. The registration statement, including all exhibits and amendments to the registration statement, has been filed electronically with the SEC.
Upon completion of this offering, we will become subject to the information and periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, and, accordingly, will be required to file annual reports containing financial statements audited by an independent public accounting firm, quarterly reports containing unaudited financial data, current reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. You will be able to inspect and copy such periodic reports, proxy statements and other information at the SEC’s public reference room, and the website of SEC referred to above.
93
UNICYCIVE THERAPEUTICS, INC.
F-1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the related statements of operations, stockholders’ deficit, and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company has incurred recurring losses and negative cash flows from operations and is dependent on additional financing to fund operations. These conditions raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans regarding these matters are also described in Note 1. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2019.
/s/ Mayer Hoffman McCann P.C.
San Diego, California
September 14, 2020
F-2
Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except for share and per share amounts)
| As of | As of | As of | ||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | ||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 25 | $ | 15 | $ | 1 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 4 | 4 | 27 | |||||||||
| Total current assets | 29 | 19 | 28 | |||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 29 | $ | 19 | $ | 28 | ||||||
| Liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 60 | $ | 322 | $ | 427 | ||||||
| Related party service fee payable | 111 | 108 | 103 | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities | 17 | 13 | 20 | |||||||||
| Convertible notes | 900 | - | - | |||||||||
| Loan from stockholder | 147 | 460 | 762 | |||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 1,235 | 903 | 1,312 | |||||||||
| Long-term liabilities | - | - | 19 | |||||||||
| Total liabilities | 1,235 | 903 | 1,331 | |||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 7) | ||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ deficit: | ||||||||||||
| Preferred stock: $0.001 par value per share—10,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2018 and 2019 and at June 30, 2020 (unaudited), no shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 and 2019 and at June 30, 2020 (unaudited) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value per share - 200,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2018 and 2019 and at June 30, 2020 (unaudited); 33,762,335 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018, 36,361,299 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019, 36,534,840 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2020 (unaudited) | 34 | 36 | 37 | |||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 253 | 2,738 | 3,000 | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (1,493 | ) | (3,658 | ) | (4,340 | ) | ||||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit | (1,206 | ) | (884 | ) | (1,303 | ) | ||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | $ | 29 | $ | 19 | $ | 28 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to the financial statements
F-3
Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except for share and per share amounts)
| Year ended | Year ended | Six Months Ended | Six Months Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | 344 | $ | 795 | $ | 231 | $ | 329 | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 608 | 1,168 | 550 | 349 | ||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 952 | 1,963 | 781 | 678 | ||||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (952 | ) | (1,963 | ) | (781 | ) | (678 | ) | ||||||||
| Other income (expenses): | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (168 | ) | (139 | ) | (118 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||
| Other expenses – Loss on debt conversion | - | (63 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||
| Total other income (expenses) | (168 | ) | (202 | ) | (118 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,120 | ) | $ | (2,165 | ) | $ | (899 | ) | $ | (682 | ) | ||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | ||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding used in computing net loss per share, basic and diluted | 29,010,940 | 34,915,828 | 34,155,838 | 36,433,549 | ||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to the financial statements
F-4
Statements of Stockholders’ Deficit
(in thousands, except share amounts)
| Additional | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Preferred stock | Paid-In | Accumulated | Stockholders’ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2018 | 23,625,000 | $ | 23 | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (373 | ) | $ | (350 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | (1,120 | ) | (1,120 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for cash, net of issuance cost of $16 | 8,521,205 | 10 | - | - | 250 | - | 260 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for acquired IPR&D technology | 1,348,750 | 1 | - | - | 3 | - | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in related-party transaction | 267,380 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | 33,762,335 | $ | 34 | - | $ | - | $ | 253 | $ | (1,493 | ) | $ | (1,206 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | (2,165 | ) | (2,165 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for cash | 1,238,615 | 1 | - | - | 1,165 | - | 1,166 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes into common stock | 1,159,065 | 1 | - | - | 1,101 | - | 1,102 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for anti-dilution clause | 149,762 | - | - | - | 145 | - | 145 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in settlement of accounts payable | 51,522 | - | - | - | 50 | - | 50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | - | - | - | - | 24 | - | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | 36,361,299 | $ | 36 | - | $ | - | $ | 2,738 | $ | (3,658 | ) | $ | (884 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | 33,762,335 | $ | 34 | - | $ | - | $ | 253 | $ | (1,493 | ) | $ | (1,206 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss (unaudited) | - | - | - | - | - | (899 | ) | (899 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for cash (unaudited) | 659,903 | 1 | - | - | 600 | - | 601 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for anti-dilution clause (unaudited) | 51,190 | - | - | - | 49 | - | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2019 (unaudited) | 34,473,428 | $ | 35 | - | $ | - | $ | 902 | $ | (2,392 | ) | $ | (1,455 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | 36,361,299 | $ | 36 | - | $ | - | $ | 2,738 | $ | (3,658 | ) | $ | (884 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss (unaudited) | - | - | - | - | - | (682 | ) | (682 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for cash (unaudited) | 143,020 | 1 | - | - | 141 | - | 142 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense (unaudited) | - | - | - | - | 91 | - | 91 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for anti-dilution clause (unaudited) | 30,521 | - | - | - | 30 | - | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at June 30, 2020 (unaudited) | 36,534,840 | $ | 37 | - | $ | - | $ | 3,000 | $ | (4,340 | ) | $ | (1,303 | ) | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to the financial statements
F-5
Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
| Year ended | Year ended | Six Months Ended | Six Months Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,120 | ) | (2,165 | ) | (899 | ) | (682 | ) | |||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| R&D Expense for issuance of common stock for anti-dilution clause | - | 145 | 49 | 30 | ||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | - | 24 | - | 91 | ||||||||||||
| Convertible debt discount amortization | 112 | 96 | 82 | - | ||||||||||||
| Loss on conversion | - | 63 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Convertible debt non-cash interest | 56 | 43 | 36 | - | ||||||||||||
| Deferred compensation to CEO | 167 | 313 | 201 | 262 | ||||||||||||
| Common stock issued for acquired IPR&D technology | 4 | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Prepaid expense and other current assets | (3 | ) | - | (3 | ) | (23 | ) | |||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 31 | 308 | 9 | 112 | ||||||||||||
| Related party service fee payable | (22 | ) | (3 | ) | (100 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (775 | ) | (1,176 | ) | (625 | ) | (215 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock | 250 | 1,166 | 601 | 142 | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from loan from stockholder | - | 9 | - | 40 | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from convertible notes | 550 | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Repayment of loan from stockholder | - | (9 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from government loan | - | - | - | 19 | ||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 800 | 1,166 | 601 | 201 | ||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash | 25 | (10 | ) | (24 | ) | (14 | ) | |||||||||
| Cash at the beginning of the period | - | 25 | 25 | 15 | ||||||||||||
| Cash at the end of the period | $ | 25 | 15 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Supplemental cash flow information | ||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issuance costs in accounts payable | $ | 11 | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| Settlement of stockholder loan for common stock | 21 | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable settled with issuance of common stock | - | 50 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Common stock issuance in conversion of convertible notes | $ | - | 1,102 | - | - | |||||||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to the financial statements
F-6
Notes to the Financial Statements
(Information as of June 30, 2020 and for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 is unaudited)
| 1. | Organization and Description of Business |
Overview
Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. (“the Company”) was incorporated in the State of Delaware on August 18, 2016. The Company was dormant until July 2017 when it began evaluating a number of drug candidates for in-licensing.
The Company in-licensed the drug candidate UNI-494 from Sphaera Pharma Pte. Ltd, a Singapore-based corporation, (“Sphaera”) (Note 3). UNI-494 is a pro-drug of Nicorandill that is being developed as a treatment for acute kidney injury.
In September 2018, the Company purchased a second drug candidate, Renazorb RZB 012 (“Renazorb”) and its trademark, RENALAN, and various patents from Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Spectrum”) (Note 3). Renazorb is being developed for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases (“CKD”).
The Company continues to evaluate the licensing of additional technologies and drugs, targeting orphan diseases and other renal, liver and other metabolic diseases affecting fibrosis and inflammation.
Liquidity
The Company is subject to risks and uncertainties common to early-stage companies in the biotechnology industry including, but not limited to, development by competitors of new technological innovations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on key personnel, compliance with governmental regulations and the need to obtain additional financing to fund operations. The Company’s product candidates currently under development will require significant additional research and development efforts prior to commercialization. The Company has not generated revenue to date.
The Company has incurred operating losses and negative cash flows from operations since inception and expects to continue to incur negative cash flows from operations for the foreseeable future. As the Company increases its research and development activities, the operating losses are expected to increase. The Company has historically relied on private equity offerings, debt financings and loans from a stockholder to fund its operations. As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company had an accumulated deficit of $4.3 million and $3.7 million, respectively.
The Company expects to continue incurring losses for the foreseeable future and is required to raise additional capital to complete its planned clinical trials, pursue product development initiatives and penetrate markets for the sale of its products. Management believes that the Company will continue to have access to capital resources through possible private equity offerings, debt financings, corporate collaborations or other means. In July and August 2020, the Company received an aggregate of $0.8 million upon the issuance of convertible notes. These funds were used to settle outstanding accounts payable and a loan from the chief executive officer and stockholder. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain additional financing on terms acceptable to the Company, on a timely basis or at all. If the Company is unable to secure additional capital, it may be required to curtail any clinical trials and development of new or existing products and take additional measures to reduce expenses in order to conserve its cash in amounts sufficient to sustain operations and meet its obligations. Based on the Company’s current level of expenditures and given the Company’s cash balance less than $0.1 million as of August 31, 2020, the Company believes that it will need funding by the end of the third quarter 2020 to continue operations, satisfy its obligations and fund the future expenditures that will be required to conduct the clinical and regulatory work to develop its product candidates.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern, which contemplates the realization of assets and the settlement of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business. There is substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for one year after the date that these financial statements are available to be issued, which is not alleviated by management’s plans. The financial statements do not reflect any adjustments relating to the recoverability and reclassification of assets and liabilities that might be necessary from the outcome of this uncertainty.
F-7
| 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Basis of Presentation
The financial statements and accompanying notes have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the periods presented. Management believes that these estimates and assumptions are reasonable; however, actual results may differ and could have a material effect on future results of operations and financial position. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include deferred tax asset valuation allowance, unrecognized tax benefits, stock-based compensation and fair value of Company’s common stock. Actual results may materially differ from those estimates.
Unaudited Interim Financial Information
The accompanying balance sheet as of June 30, 2020 and the related statements of operations, statements of stockholders’ deficit and statements of cash flows for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 are unaudited. In the opinion of management, the unaudited data reflects all adjustments, which include only normal recurring adjustments, necessary for the fair presentation of the Company’s balance sheet as of June 30, 2020 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and June 30, 2019.
The financial data and other information disclosed in these notes as of June 30, 2020 and for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 are also unaudited. The results for the six months ended and as of June 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for the year ending December 31, 2020, any other interim periods or any future year or period.
Segment Information
The Company operates and manages its business as one reportable operating segment. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer, who is the chief operating decision maker, reviews financial information on an aggregate basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance.
Risks and Uncertainties
The Company operates in a dynamic and highly competitive industry and believes that changes in any of the following areas could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s future financial position, results of operations, or cash flows: ability to obtain future financing; advances and trends in new technologies and industry standards; results of clinical trials; regulatory approval and market acceptance of the Company’s products; development of sales channels; certain strategic relationships; litigation or claims against the Company related to intellectual property, product, regulatory, or other matters; and the Company’s ability to attract and retain employees necessary to support its growth.
The Company’s general business strategy may be adversely affected by any such economic downturns (including the current downturn related to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic), volatile business environments and continued unstable or unpredictable economic and market conditions.
Any product candidates developed by the Company will require approvals from the FDA or other international regulatory agencies prior to commercial sales. There can be no assurance that the Company’s current product candidates or any future product candidates will receive the necessary approvals. If the Company is denied approval, approval is delayed or the Company is unable to maintain approval, it could have a materially adverse impact on the Company.
F-8
The Company has expended and will continue to expend substantial funds to complete the research, development and clinical testing of its product candidates. The Company also will be required to expend additional funds to establish commercial-scale manufacturing arrangements and to provide for the marketing and distribution of products that receive regulatory approval. The Company will require additional funds to commercialize its products. The Company is unable to entirely fund these efforts with its current financial resources. If adequate funds are unavailable on a timely basis from operations or additional sources of financing, the Company may have to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate one or more of its research or development programs, which would materially and adversely affect its business, financial condition and operations.
The Company is dependent upon the services of its employees, consultants and other third parties.
Deferred Offering Costs
Deferred offering costs, consisting of legal, accounting and other fees and costs relating to the Company’s planned Initial Public Offering (“IPO”) are capitalized and recorded on the balance sheets. The deferred offering costs will be offset against the proceeds received upon the closing of the planned IPO. In the event that the Company’s plans for an IPO are terminated, all of the deferred offering costs will be written off within operating expenses in the Company’s statements of operations. There were no deferred offering costs capitalized as of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company’s financial instruments include cash, prepaid expenses, accounts payable, convertible notes and a loan from the Chief Executive Officer and stockholder of the Company. The carrying amounts of these items approximate fair value as of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and 2018 due to their short-term nature.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentration of credit risk consist of cash. All of the Company’s cash was deposited in one account at a financial institution, and the account balance may at times exceed federally insured limits. Management believes that the Company is not exposed to significant credit risk due to the financial strength of the depository institution in which the cash is held.
Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid expenses represent costs incurred that benefit future periods. These costs are amortized over a specific time-period based on the specific agreements.
Research and Development Expenses
Substantially all of the Company’s research and development expenses consist of expenses incurred in connection with the development of the Company’s product candidates. These expenses include fees paid to third parties to conduct certain research and development activities on the Company’s behalf, consulting costs, costs for laboratory supplies, product acquisition and license costs, certain payroll and personnel-related expenses, including salaries and bonuses, employee benefit costs and stock-based compensation expenses for the Company’s research and product development employees and allocated overheads, including information technology costs and utilities and expenses for issuance of shares pursuant to the anti-dilution clause in the purchase of IPR&D technology. The Company expenses both internal and external research and development expenses as they are incurred.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses represent personnel costs for employees involved in general corporate functions, including finance, accounting, legal and human resources, among others. Additional costs included in general and administrative expenses consist of professional fees for legal (including patent costs), audit and other consulting services, stock-based compensation and other general corporate overhead expenses as well as costs from a service agreement with a related party (See Note 6).
F-9
Patent Costs
The Company expenses all costs as incurred in connection with patent licenses and applications (including direct application fees, and the legal and consulting expenses related to making such applications) and such costs are reflected in general and administrative expenses in the statements of operations.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation for all share-based payments made to employees and non-employees by estimating the fair value on the date of grant and recognizing compensation expense over the requisite service period on a straight-line basis. The Company recognizes forfeitures related to stock-based compensation as they occur. The Company estimates the fair value of stock options using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The Black-Scholes model requires the input of subjective assumptions, including expected common stock volatility, expected dividend yield, expected term, risk-free interest rate, and the estimated fair value of the underlying common stock on the date of grant.
Common Stock Valuations
The Company is required to periodically estimate the fair value of common stock when issuing stock options and computing their estimated stock-based compensation expense. The fair value of common stock was determined on a periodic basis, with the assistance of an independent third-party valuation expert. The assumptions underlying these valuations represented Management’s best estimates, which involved inherent uncertainties and the application of significant levels of Management judgment.
In order to determine the fair value, the Company considered, among other things, contemporaneous transactions involving the sale of the Company’s common stock to unrelated third parties; the lack of marketability of the Company’s common stock; the market performance of comparable publicly traded companies.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for corporate income taxes in accordance with GAAP as stipulated in ASC, Topic 740, Income Taxes, (“ASC 740”). This standard entails the use of the asset and liability method of computing the provision for income tax expense. Current tax expense results from corporate tax payable at the Federal and California jurisdictions for the Company, which relate to the current accounting period. Deferred tax expense results primarily from temporary differences between financial statement and tax return reporting, which result in additional tax payable in future periods. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement basis and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates and law. Net future tax benefits are subject to a valuation allowance when management expects that it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Current and non-current tax assets and liabilities are based upon an estimate of taxes refundable or payable for each of the jurisdictions in which the Company is subject to tax. In the ordinary course of business there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying income tax positions. The Company assess income tax positions and record the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. For those income tax positions where it is not more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit is recognized in the financial statements. The Company’s policy is to recognize interest or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense.
F-10
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss includes all changes in equity (net assets) during a period from non-owner sources. There were no elements of other comprehensive income (loss) in the periods presented, as a result comprehensive loss is the same as net loss for each period presented.
Net Loss per Share
Basic net loss per common share is calculated by dividing the net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period, without consideration of potentially dilutive securities. Diluted net loss per share is computed by dividing the net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares and potentially dilutive securities outstanding for the period. For purposes of the diluted net loss per share calculation, common stock options are considered to be potentially dilutive securities. Basic and diluted net loss per share is presented in conformity with the two-class method required for participating securities. The Company has no participating securities and as such, the net loss was attributed entirely to common stockholders. As the Company has reported a net loss for all periods presented, diluted net loss per common share is the same as basic net loss per common share for those periods.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) or other standard setting bodies and adopted by the Company as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). This ASU requires a lessee to recognize in the statement of financial position a liability to make lease payments (the lease liability) and a right-of-use asset representing its right to use the underlying asset for the leases with a term of greater than 12 months. This ASU is effective for the Company’s fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, with early adoption permitted. The Company has adopted this standard effective as of January 1, 2019. The Company chose to adopt the package of practical expedients available from the FASB. As a policy election, the Company chose to expense and amortize, on a straight line, the leases with terms less than 12 months. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
| 3. | Significant Agreements |
In 2018, the Company entered into an exclusive license agreement with Sphaera, a stockholder, for the rights to further develop the drug candidate, UNI-494, for commercialization. No payments were made upon execution of the agreement but rather payments for $50,000 will be due commencing with the initiation by the Company of a second clinical trial and $50,000 on completion of such trial. At the time the FDA accepts a NDA application submitted by the Company for the product, the Company will pay Sphaera $1.65 million. Upon commercialization and sale of the drug product, royalty payments will also be payable quarterly to Sphaera equal to 2% of net sales on the preceding quarter.
In September 2018, the Company entered into an Assignment and Asset Purchase Agreement with Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Spectrum Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company purchased certain assets from Spectrum, including Spectrum’s right, title, interest in and intellectual property related to Renazorb RZB 012, also known as RENALAN™ (“Renalan”) and RZB 014, also known as SPI 014 (“SPI” and together with Renalan, the “Compounds”), to further develop and commercialize Renazorb and related compounds. In partial consideration for the Spectrum Agreement, the Company issued 1,348,750 shares of common stock to Spectrum valued at approximately $4,000 which represented four percent of the Company on a fully-diluted basis at the date of the execution of the Spectrum Agreement. The Spectrum Agreement has an anti-dilution provision, which provides that Spectrum maintain its ownership interest in the Company at 4% of the Company’s shares on a fully-diluted basis. Fully-diluted shares of common stock for purposes of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement assumes conversion of any security convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for common stock or any combination thereof, including any common stock reserved for issuance under a stock option plan, restricted stock plan, or other equity incentive plan approved by the Board of Directors of the Company immediately following the issuance of additional shares of our common stock (but prior to the issuance of any additional shares of common stock to Spectrum). Spectrum’s ownership shall not be subject to dilution until the earlier of thirty-six months from the first date the Company’s stock trades on a public market, or the date upon which the Company attains a public market capitalization of at least $50 million. As part of the anti-dilution clause, the Company issued 30,521 and 51,190 common stock for the first six months of 2020 and 2019, respectively and 149,762 during the year ended December 31, 2019. The Company recognized $30,000 and $49,000 for the first six months of 2020 and 2019, respectively, and $145,000 for the year 2019 as research and development expenses as cost to issue those shares. The Company is also required to pay Spectrum 40% of all of the Company’s sublicense income for any sublicense granted to certain sublicensees during the first 12 months after the Closing Date (as that term is defined in the Renazorb Purchase Agreement) and 20% of all other sublicense income. The Company’s payment obligations to Spectrum will expire on the twentieth (20th) anniversary of the Closing Date of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement.
F-11
| 4. | Balance Sheet Components |
Accounts payable as of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and 2018 consists of the following (in thousands):
| As of | As of | As of | ||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | ||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Trade accounts payable | $ | 54 | $ | 288 | $ | 369 | ||||||
| Credit card liability | 6 | 34 | 58 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 60 | $ | 322 | $ | 427 | ||||||
| 5. | Debt |
Convertible Notes
In 2018, the Company raised $550,000 from the issuance of twelve convertible promissory notes (Notes). These Notes bear interest at 10% per annum which was payable at maturity. The Notes principal and interest were due and payable on written demand by the majority of the Note holders on the two-year anniversary of the first Note issued. The first note was issued on October 5, 2017 and, accordingly, all Notes would have matured on October 5, 2019.
In the event the Company consummated an equity financing with an aggregate sales price of not less than $500,000, then the aggregate outstanding principal and unpaid interest would automatically convert into shares of the Company’s common stock. The per share price of the conversion would be equal to 75% of the price per share paid by the cash purchasers of the common stock sold in the financing.
The Company has accounted for the Notes as stock-settled debt and accreted the carrying amount of the Notes to the settlement amount through maturity. Unpaid and accrued interest on the Notes was approximately $59,000 for the year ended December 31, 2018 and was included with the convertible notes on the balance sheet.
On July 31, 2019, all Notes principal and accrued interest were converted into 1,159,065 shares of common stock upon the consummation of a 2019 equity financing in excess of $500,000. The Company recorded, as part of the conversion of the debt, a loss on conversion of $63,000 included in other expenses.
Paycheck Protection Program Loan
On April 23, 2020, the Company entered into an $18,000 loan with Silicon Valley Bank pursuant to the Small Business Administration’s (“SBA”) Paycheck Protection Program (“PPP”). The loan proceeds are intended to be used for payroll over the eight-week period following the date of the loan. The loan terms provide that no principal or interest payments are due and interest will accrue at 1% per annum commencing on April 23, 2020 through October 23, 2020 (deferral period). Commencing one month after the deferral period and continuing monthly through the maturity of the loan on April 23, 2022, equal monthly payments of principal and interest are due. The Company classified this loan as long-term liability.
| 6. | Related Party Transactions |
Loan from Chief Executive Officer and Stockholder
As of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the current liability loan from a stockholder of approximately $762,000, $460,000 and $147,000, respectively, represents the accumulation of deferred compensation due to the chief executive officer and stockholder. This amount bears no interest and is repayable on demand.
F-12
Service agreement with Globavir
On July 1, 2017, as amended on April 6, 2020, the Company entered into a Service Agreement with Globavir Biosciences, Inc. (“Globavir”), a related party (the “Service Agreement”). Globavir provides administrative and consulting services and shared office space and other costs in connection with the Company’s drug development program. The Service Agreement provides Globavir the right to receive $50,000 per month for such services through December 31, 2019 and $10,000 per month commencing on January 1, 2020. As of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, $103,000, $108,000 and $111,000 is payable to Globavir for such service fees. Amounts incurred by the Company under the Service Agreement were $60,000, $300,000, $600,000 and $600,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2020, June 30, 2019 and for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and are included in operating expenses in the statements of operations. The Service Agreement shall continue until December 31, 2020 (the “Initial Term”) unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms thereof. Unless terminated, the Service Agreement shall automatically renew for successive one month periods after the termination of the Initial Term.
Common stock purchase agreement and services agreement
On July 1, 2017, the Company entered into a Common Stock Purchase Agreement (“Stock Agreement”) with Globavir. The Company’s majority stockholder is also the majority stockholder in Globavir. The Stock Agreement provided for the distribution of 267,380 shares of the Company’s common stock, valued at $0.003 per share, to Globavir’s stockholders as payment for Globavir’s services and shared costs rendered on behalf of the Company in 2017, which were issued in 2018.
| 7. | Commitments and Contingencies |
Contingencies
The Company is subject to claims and legal proceedings that arise in the ordinary course of business. Such matters are inherently uncertain, and there can be no guarantee that the outcome of any such matter will be decided favorably to the Company or that the resolution of any such matter will not have a material adverse effect upon the Company’s financial statements. The Company currently has no pending claims or legal proceedings.
Indemnifications
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into contracts and agreements that contain a variety of representations and warranties and provide for general indemnifications, including for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party, in connection with any trade secret, copyright, patent or other intellectual property infringement claim by any third party with respect to its technology. The term of these indemnification agreements is generally perpetual any time after the execution of the agreement. The Company’s exposure under these agreements is unknown because it involves claims that may be made against the Company in the future, but that have not yet been made. To date, the Company has not paid any claims or been required to defend any action related to its indemnification obligations.
The Company believes that the likelihood of conditions arising that would trigger these indemnities is remote and, historically, the Company had not made any significant payment under such indemnification provisions. Accordingly, the Company has not recorded any liabilities relating to these agreements. However, the Company may record charges in the future as a result of these indemnification obligations.
Additionally, the Company has agreed to indemnify its directors and officers for certain events or occurrences while the director or officer is, or was serving, at the Company’s request in such capacity. The indemnification period covers all pertinent events and occurrences during the director’s or officer’s service. The Company intends to enter into new indemnification agreements with its officers and directors to further expand coverage of these individuals upon the Company’s completion of an initial public offering.
F-13
| 8. | Stockholders’ Deficit |
Authorized Common Stock
The Company is authorized to issue up to 200,000,000 shares of common stock at par value of $0.001 per share.
Issuance of Common Stock
During the six months ended June 30, 2020, the Company issued 143,020 shares to investors in exchange of cash at $0.98 per share and 30,521 shares to Spectrum following its anti-dilution provision (Note 3).
During 2019 the Company issued 1,238,615 shares to investors for a total of $1,166,000 with prices ranges from $0.83 to $0.98 per stock, 1,159,065 shares upon conversion of its convertible notes (Note 5), 149,762 shares to Spectrum following its anti-dilution provision (Note 3) and 51,522 shares to a vendor for settlement of an accounts payable for a total of $50,000.
During 2018, the Company issued 267,380 shares of common stock to the stockholders of Globavir, a related party, as payment in full for services and shared costs rendered on behalf of the Company in 2017 (Note 6). The Company issued 8,521,205 shares of common stock and raised approximately $260,000 net of issuance costs through the sale of shares in private placement offerings. In connection with the Spectrum Agreement, the Company issued 1,348,750 shares of common stock (Note 3).
Voting Rights of Common Stock
Each holder of shares of common stock shall be entitled to one vote for each share thereof held.
Preferred Stock
As of June 30, 2020, December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock authorized, par value of $0.001 per share and no shares of preferred stock were issued or outstanding.
| 9. | Stock-based Compensation |
In 2018, the Company adopted the 2018 Equity Incentive Plan (“2018 Plan”) which allows for the granting of incentive stock options (“ISO”), non-qualified stock options (“NSO”), stock appreciation rights, restricted stock and restricted stock units to the employees, members of the board of directors and consultants of the Company. In 2018, the Company granted ISOs and NSOs to consultants and directors from this plan. As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, 2,000,000 shares are authorized for issuance and 75,000 shares are available for future grant under the 2018 Plan.
In October 2019, the Company adopted the 2019 Stock Option Plan (“2019 Plan”) which allows for the granting of incentive stock options (“ISO”), non-qualified stock options (“NSO”) to the employees, members of the board of directors and consultants of the Company. In 2019 and during the first six months of 2020, the Company granted ISOs and NSOs to consultants and directors from the 2019 Plan. As of December 31, 2019, 1,000,000 shares are authorized for issuance and 325,000 shares are available for future grant under the 2019 Plan. On April 6, 2020 the Company increased the shares authorized for issuance to 1,500,000 shares total. As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, 205,000 and 325,000 shares available for future grant under the 2019 Plan, respectively.
F-14
The following table summarizes activity for stock options under both plans for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| Weighted- | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of | Average | |||||||||||||||
| Shares | Weighted- | Remaining | Aggregate | |||||||||||||
| Underlying | Average | Contractual | Intrinsic | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding | Exercise | Term | Value | |||||||||||||
| Options | Price | (in Years) | (in thousands) | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding, January 1, 2018 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||
| Options granted | 1,925,000 | 0.003 | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, December 31, 2018 | 1,925,000 | 0.003 | 9.66 | 1,284 | ||||||||||||
| Options granted | 675,000 | 0.76 | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, December 31, 2019 | 2,600,000 | 0.20 | 8.56 | 2,029 | ||||||||||||
| Options granted (unaudited) | 620,000 | 0.76 | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding, June 30, 2020 (unaudited) | 3,220,000 | 0.31 | 8.73 | 2,166 | ||||||||||||
| Shares vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2019 | 697,918 | - | 8.66 | 2,029 | ||||||||||||
| Shares vested and exercisable as of June 30, 2020 (unaudited) | 958,751 | $ | 0.02 | 8.19 | $ | 921 | ||||||||||
The grant date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $0.5 million and $0.0 million, respectively. The grant date fair value of options granted during the six months ended June 30, 2020 was $0.5 million.
As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the unrecognized compensation costs related to outstanding stock options was $0.9 million and $0.5 million, respectively, which is expected to be recognized as expense over approximately 3.7 years and 3.8 years, respectively.
The Company has recorded stock-based compensation expense, allocated by functional cost as follows for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 and for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 (in thousands):
| Year Ended | Year Ended | Six Months Ended | Six Months Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development | $ | - | $ | 14 | $ | - | $ | 61 | ||||||||
| General and administrative | - | 10 | - | 30 | ||||||||||||
| Total stock-based compensation | $ | - | $ | 24 | $ | - | $ | 91 | ||||||||
F-15
Fair Value of Stock Options
The assumptions are based on the following for each of the periods presented:
Expected Term - The expected term is calculated using the simplified method which is used when there is insufficient historical data about exercise patterns and post-vesting employment termination behavior. The simplified method is based on the vesting period and the contractual term for each grant, or for each vesting-tranche for awards with graded vesting. The mid-point between the vesting date and the maximum contractual expiration date is used as the expected term under this method.
Common Stock Fair Value - The fair value of the common stock underlying the Company’s stock options was estimated at each grant date and was principally based on the transactions with third parties in which common stock was sold for cash.
Volatility - The expected volatility being used is derived from the historical stock volatilities of a representative industry peer group of comparable publicly listed companies over a period approximately equal to the expected term of the options.
Risk-free Interest Rate - The risk-free interest rate is based on median U.S. Treasury zero coupon issues with remaining terms similar to the expected term on the options.
Expected Dividend - The Company has never declared nor paid any cash dividends and does not plan to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future, and therefore, used an expected dividend yield of zero.
The following averaged assumptions were used to calculate the fair value of awards granted to employees, directors and non-employees for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019, and for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020:
| Year Ended | Year Ended | Six Months Ended |
Six Months Ended |
|||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Expected volatility | 55.00 | % | 91.00 | % | - | % | 114.00 | % | ||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.84 | % | 1.54 - 1.79 | % | - | % | 0.44 – 0.51 | % | ||||||||
| Dividend yield | - | % | - | % | - | % | - | % | ||||||||
| Expected term | 6.25 years | 6.25 years | - years | 6.25 years | ||||||||||||
| 10. | Income Taxes |
A reconciliation of the provision for income taxes to the amount computed by applying the statutory income tax rate of 21% to the net loss is summarized for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 is as follows:
| Year Ended | Year Ended | |||||||
| December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Income taxes (benefit) at statutory rates | 21.00 | % | 21.00 | % | ||||
| State income tax (benefit), net of federal benefit | 5.92 | 5.90 | ||||||
| Change in valuation allowance | (23.71 | ) | (23.10 | ) | ||||
| Interest on convertible notes | (3.15 | ) | (1.90 | ) | ||||
| Others | (0.06 | ) | (1.90 | ) | ||||
| Effective income tax rate | - | % | - | % | ||||
For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company did not record a deferred income tax expense or benefit. Income tax expense has been nominal for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
F-16
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected tax consequences attributable to the differences between financial reporting and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities and operating loss carryforward, and they are measured using enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when differences are expected to reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded for loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets where it is more likely than not that such loss carryforward and deferred tax asset will not be realized. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are shown below (in thousands):
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | $ | - | $ | 7 | ||||
| Net operating losses carryforwards | 282 | 690 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses | 79 | 164 | ||||||
| Gross deferred tax assets | 361 | 861 | ||||||
| Less: Valuation allowance | (361 | ) | (861 | ) | ||||
| Deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowance | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
The valuation allowance increased by $0.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2019. We have concluded, based upon ASC 740, that it is more likely than not we will not realize any benefit from the deferred tax assets related to certain Federal and state’s net operating loss and credit carryforward. Accordingly, the Company has established a full valuation allowance against its Federal and state deferred tax assets.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had available Federal and California net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $2.5 million to reduce future taxable income, if any. Federal net operating losses generated prior to 2019 and all state net operating losses generated expire in varying amounts beginning in 2037. These net operating losses, generated after 2017, do not expire and will be able to offset 80% of taxable income generated in the future.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had research and development credit carryforwards of approximately $900 and $12,000 available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for federal and state income tax purposes, respectively. These credits have been provided a full reserve under ASC 740-10. The federal credit carryforwards begin to expire in 2037, and the state credit carryforwards can be carried forward indefinitely.
Utilization of net operating losses and tax credits may be subject to an annual limitation due to ownership change limitations provided in the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), and similar state provisions. The effect of an ownership change would be the imposition of annual limitation on the use of net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards attributable to periods before the change in ownership. An assessment of such ownership changes under Section 382 of the Code was not completed through December 31, 2019 and, as such the Company is not able to determine the impact on the NOLs and tax credit carryforwards, if any, as of the date of the financial statements. To the extent that an assessment is completed in the future, the Company’s ability to utilize tax attributes could be restricted on a year-by-year basis and certain attributes could expire before they are utilized.
On March 27, 2020, the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (“CARES Act”) was enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The CARES Act, among other things, permits NOL carryovers and carrybacks to offset 100% of taxable income for taxable years beginning before 2021. In addition, the CARES Act allows NOLs incurred in 2018, 2019, and 2020 to be carried back to each of the five preceding taxable years to generate a refund of previously paid income taxes. Due to the Company’s history of NOLs, the CARES Act is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
F-17
The Company applies the guidance under ASC 740, subtopic 10-50-15, Unrecognized Tax Benefit Related Disclosures (formerly FASB Interpretation 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes). For benefits to be realized, a tax position must be more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by tax authorities. The amount recognized is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon settlement. This interpretation also provides guidance on measurement, de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the total unrecognized tax benefit was approximately $12,000 and $2,000, respectively. The Company does not expect any material changes to the estimated amount of liability associated with its uncertain tax positions within the next 12 months. There was no change in the balance of the gross unrecognized tax benefit during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had no accrued interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
The Company files U.S. and state income tax returns with varying statutes of limitations. Tax years 2016 and forward remain open to examination due to the carryover of NOL carryforwards. There are no ongoing examinations by taxing authorities at this time.
| 11. | Net loss per share |
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| Year Ended | Year Ended | Six Months Ended | Six Months Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| Numerator: | (unaudited) | (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,120 | ) | $ | (2,165 | ) | $ | (899 | ) | $ | (682 | ) | ||||
| Denominator: | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding used in computing net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 29,010,940 | 34,915,828 | 34,155,838 | 36,433,549 | ||||||||||||
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | ||||
F-18
The following outstanding shares of potentially dilutive securities were excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share for the periods presented because including them would have been antidilutive:
| Year Ended | Year Ended | Six Months Ended | Six Months Ended | |||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||
| Options to purchase common stock | 1,925,000 | 2,600,000 | 1,925,000 | 3,220,000 | ||||||||||||
| Total | 1,925,000 | 2,600,000 | 1,925,000 | 3,220,000 | ||||||||||||
| 12. | Subsequent Events |
On July 6, 2020 the Company granted additional 160,000 options to consultants at an exercise price of $0.76 per option. The options will vest over 4 years provided the services continue to be performed by the recipients.
In July and August, 2020, the Company issued convertible notes in the aggregate principal amount of $800,000. The notes bear interest at a rate of 12% per annum and mature in July and August, 2021. The notes shall automatically convert into shares of the Company’s common stock upon the closing of a financing pursuant to which the Company receives gross proceeds of at least $500,000 (“Qualified Financing”) or upon a change of control. The notes shall convert into such numbers of shares of the Company’s common stock equal to the conversion amount divided by the Conversion Price. “Conversion Price” means (i) in the event of a Qualified Financing, 70% of the price per share (or conversion price, as applicable) of common stock (or securities convertible into common stock, as applicable) sold in such financing or (ii) in the event of a change of control, the price per share reflected in such transaction.
F-19
Shares

Common Stock
Prospectus
, 2020
Until , 2020 (25 days after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that effect transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery requirement is in addition to the dealers’ obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as an underwriter and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
PART II—INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following table sets forth all expenses, other than the underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by the registrant in connection with the sale of the securities being registered. All the amounts shown are estimates except the SEC registration fee and the FINRA filing fee.
| Amount to be paid | ||||
| SEC registration fee | $ | * | ||
| FINRA filing fee | $ | * | ||
| The Nasdaq Capital Market initial listing fee | $ | 55,000 | ||
| Transfer agent and registrar fees | $ | * | ||
| Accounting fees and expenses | $ | * | ||
| Legal fees and expenses | $ | * | ||
| Printing and engraving expenses | $ | * | ||
| Miscellaneous | $ | * | ||
| Total | $ | * | ||
| * | To be filed by amendment. |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 102 of the DGCL permits a corporation to eliminate the personal liability of directors of a corporation to the corporation or its stockholders for monetary damages for a breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except where the director breached his duty of loyalty, failed to act in good faith, engaged in intentional misconduct or knowingly violated a law, authorized the payment of a dividend or approved a stock repurchase in violation of Delaware corporate law or obtained an improper personal benefit. Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation provides that no director of the Company shall be personally liable to it or its stockholders for monetary damages for any breach of fiduciary duty as a director, notwithstanding any provision of law imposing such liability, except to the extent that the DGCL prohibits the elimination or limitation of liability of directors for breaches of fiduciary duty.
Section 145 of the DGCL provides that a corporation has the power to indemnify a director, officer, employee, or agent of the corporation, or a person serving at the request of the corporation for another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise in related capacities against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by the person in connection with an action, suit or proceeding to which he was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, ending or completed action, suit or proceeding by reason of such position, if such person acted in good faith and in a manner he reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, and, in any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his conduct was unlawful, except that, in the case of actions brought by or in the right of the corporation, no indemnification shall be made with respect to any claim, issue or matter as to which such person shall have been adjudged to be liable to the corporation unless and only to the extent that the Court of Chancery or other adjudicating court determines that, despite the adjudication of liability but in view of all of the circumstances of the case, such person is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnity for such expenses which the Court of Chancery or such other court shall deem proper.
Upon consummation of this offering, our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws will provide indemnification for our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL. We will indemnify each person who was or is a party or threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding (other than an action by or in the right of us) by reason of the fact that he or she is or was, or has agreed to become, a director or officer, or is or was serving, or has agreed to serve, at our request as a director, officer, partner, employee or trustee of, or in a similar capacity with, another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise (all such persons being referred to as an “Indemnitee”), or by reason of any action alleged to have been taken or omitted in such capacity, against all expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred in connection with such action, suit or proceeding and any appeal therefrom, if such Indemnitee acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in, or not opposed to, our best interests, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, he or she had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful. Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws will provide that we will indemnify any Indemnitee who was or is a party to an action or suit by or in the right of us to procure a judgment in our favor by reason of the fact that the Indemnitee is or was, or has agreed to become, a director or officer, or is or was serving, or has agreed to serve, at our request as a director, officer, partner, employee or trustee of, or in a similar capacity with, another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise, or by reason of any action alleged to have been taken or omitted in such capacity, against all expenses (including attorneys’ fees) and, to the extent permitted by law, amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred in connection with such action, suit or proceeding, and any appeal therefrom, if the Indemnitee acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in, or not opposed to, our best interests, except that no indemnification shall be made with respect to any claim, issue or matter as to which such person shall have been adjudged to be liable to us, unless a court determines that, despite such adjudication but in view of all of the circumstances, he or she is entitled to indemnification of such expenses. Notwithstanding the foregoing, to the extent that any Indemnitee has been successful, on the merits or otherwise, he or she will be indemnified by us against all expenses (including attorneys’ fees) actually and reasonably incurred in connection therewith. Expenses must be advanced to an Indemnitee under certain circumstances.
| II-1 |
Prior to the consummation of this offering, we intend to enter into separate indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers. Each indemnification agreement shall provide, among other things, for indemnification to the fullest extent permitted by law and our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation against any and all expenses, judgments, fines, penalties and amounts paid in settlement of any claim. The indemnification agreements shall provide for the advancement or payment of all expenses to the indemnitee and for the reimbursement to us if it is found that such indemnitee is not entitled to such indemnification.
In addition, we carry officer and director insurance for claims based on acts or omissions of such officers and directors in their capacity as such.
In any underwriting agreement we enter into in connection with the sale of common stock being registered hereby, the underwriters will agree to indemnify, under certain conditions, us, our directors, our officers and persons who control us within the meaning of the Securities Act against certain liabilities.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Set forth below is information regarding securities issued by us since during the prior three years that were not registered under the Securities Act.
2020
From February to May 2020, we issued an aggregate of 143,020 shares of common stock in a private placement to accredited investors.
In March and June 2020, we issued an aggregate of 30,521 shares of common stock pursuant to an anti-dilution provision under an Assignment and Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Renazorb Purchase Agreement”) with Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Spectrum”).
From April to May 2020 we issued an aggregate of 620,000 options to purchase our common stock to consultants under our 2019 Stock Option Plan.
From July to August 2020, we issued aggregate principal amount of $800,000 in convertible promissory notes to accredited investors.
In July 2020, we issued an aggregate of 160,000 options to consultants to purchase common stock under our 2019 Stock Option Plan.
2019
During 2019 we issued a total of 1,238,615 shares of common stock in private placements to accredited investors.
In July 2019, we issued 1,159,065 shares of common stock in conversion of certain outstanding promissory notes.
From March to December 2019, we issued an aggregate of 149,762 shares of common stock pursuant to an anti-dilution provision under the Renazorb Purchase Agreement with Spectrum.
In July 2019, we issued 51,522 shares of common stock in settlement of certain accounts payable with a vendor.
In October and December 2019, we issued a total of 675,000 options to purchase common stock under our 2019 Stock Option Plan.
2018
During 2018, we issued a total of 8,521,205 shares of common stock in private placements to accredited investors.
In September 2018, we issued 1,348,750 shares of common stock in connection with the consummation of the Renazorb Purchase Agreement with Spectrum.
In June 2018, we issued 267,380 shares of common stock to Globavir BioSciences, Inc. (“Globavir”), a related party, pursuant to a services agreement.
From January to July 2018, we issued an aggregate principal amount of $550,000 in convertible promissory notes to accredited investors.
In July 2018, we issued a total of 1,925,000 options to purchase common stock under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan.
2017
In July 2017, we issued 22,978,809 shares of common stock to Globavir, a related party, pursuant to a services agreement.
From October to December 2017, we issued an aggregate principal amount of $175,000 in convertible promissory notes to accredited investors.
The foregoing offers and issuances were exempt from registration under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act or Rule 701 thereunder.
| II-2 |
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit No. | Description | |
| 1.1* | Form of Underwriting Agreement | |
| 3.1* | Certificate of Incorporation | |
| 3.2* | Certificate of Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation | |
| 3.6* | Bylaws of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. | |
| 3.7* | Form of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, to be effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering | |
| 3.8* | Form of Amended and Restated Bylaws, to be effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering | |
| 4.1* | Specimen Stock Certificate evidencing the shares of common stock | |
| 5.1* | Opinion of Sheppard, Mullin, Richter & Hampton LLP | |
| 10.1+* | 2018 Equity Incentive Plan | |
| 10.2+* | 2019 Stock Option Plan | |
| 10.3* | Assignment and Asset Purchase Agreement by and between the Company and Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc., dated September 20, 2018 | |
| 10.4* | Exclusive License Agreement by and between the Company and Sphaera Pharma Pte. Ltd., dated October 1, 2017 | |
| 10.6* | Service Agreement by and between the Company and Globavir Biosciences, Inc. dated July 1, 2017 | |
| 23.1* | Consent of Mayer Hoffman McCann P.C., independent registered public accounting firm | |
| 23.2* | Consent of Sheppard, Mullin, Richter & Hampton, LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1) | |
| 24.1 | Power of Attorney (included on the signature page to this registration statement) |
| * | To be filed by amendment. |
| + | Indicates a management contract or any compensatory plan, contract or arrangement. |
Financial Statement Schedules
Schedules have been omitted because the information required to be set forth therein is not applicable or is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
Item 17. Undertakings
(a) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the underwriters at the closing specified in the underwriting agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
b) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. has been advised that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction, the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
(c) The undersigned hereby further undertakes that:
(1) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc. pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(2) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
| II-3 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this Registration Statement on Form S-1 to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized in the City of Los Altos, State of California, on the day of , 2020.
| UNICYCIVE THERAPEUTICS, INC. | ||
| By: | ||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D. | ||
| Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman | ||
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Shalabh Gupta, his true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent with full power of substitution and re-substitution, for him and in his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities to sign any or all amendments (including, without limitation, post-effective amendments) to this Registration Statement, any related Registration Statement filed pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and any or all pre- or post-effective amendments thereto, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and all other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully for all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming that said attorney-in-fact and agent, or any substitute or substitutes for him, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof. Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated have signed this Registration Statement below.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, this Registration Statement on Form S-1 has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated below.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| Chief Executive Officer, President and Chairman | ||||
| Shalabh Gupta, M.D. | (Principal Executive Officer and Principal Accounting and Financial Officer) | |||
| Director | ||||
| John Ryan, M.D., Ph.D. | ||||
| Director | ||||
| Sandeep Laumas, M.D. |
II-4